Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (22): 5832-5843.doi: 10.12307/2026.228
Previous Articles Next Articles
The role of exercise-regulated mitophagy in cardiovascular diseases
Ji Long1, Gong Guopan1, Kong Xiangkui1, Jin Pan2, Chen Ziyang1, 3, Pu Rui1, 3
- 1College of Education and Sports Sciences, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China; 2Yangtze University School of Medicine, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China; 3Laboratory of Exercise and Human Science, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2025-09-10Accepted:2025-10-17Online:2026-08-08Published:2025-12-27 -
Contact:Pu Rui, MS, Lecturer, College of Education and Sports Sciences, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China; Laboratory of Exercise and Human Science, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Ji Long, MS candidate, College of Education and Sports Sciences, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81860386 (to JP); 2022 Jingzhou Healthcare Science and Technology Program, No. 2022HC36 (to JP); 2024 Youth Project of Social Science Foundation of Yangtze University, No. 2024csq006 (to CZY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ji Long, Gong Guopan, Kong Xiangkui, Jin Pan, Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui. The role of exercise-regulated mitophagy in cardiovascular diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(22): 5832-5843.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
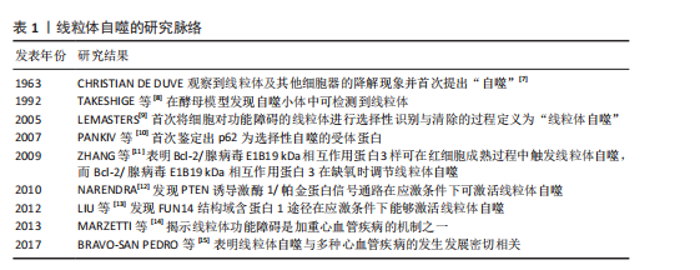
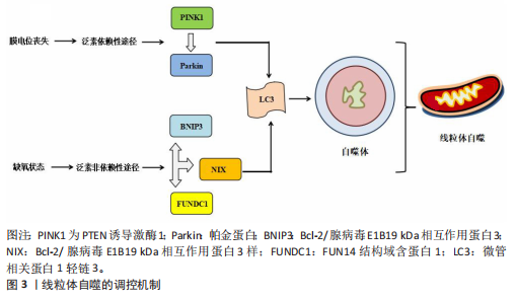
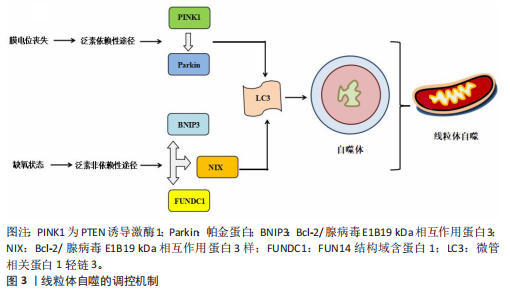
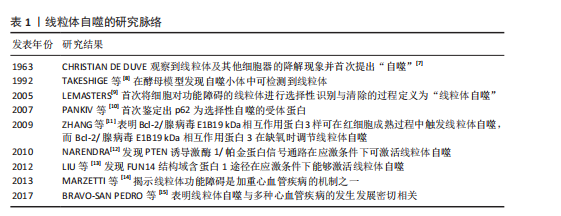
2.1 线粒体自噬概述 2.1.1 线粒体自噬的发现发展 线粒体自噬的提出经历了系统而渐进的研究过程。在20世纪60年代,生物学家CHRISTIAN DE DUVE在研究大鼠肝脏溶酶体过程中首次观察到线粒体及其他细胞器的降解现象并提出了“自噬”这一概念[7]。1992年,TAKESHIGE等[8]通过酵母模型发现,在葡萄糖饥饿状态下,自噬小体中可检测到线粒体,提示线粒体可能为自噬的特异性靶标之一。直到2005年,LEMASTERS[9]首次将细胞对功能障碍的线粒体进行选择性识别与清除的过程定义为“线粒体自噬”。 随着研究的不断深入,PANKIV等[10]首次鉴定出序列特异性核蛋白62(又称p62)为选择性自噬的受体蛋白,揭示了它在识别损伤细胞器并与自噬体结合中的作用。ZHANG等[11]研究发现,Bcl-2/腺病毒E1B19 kDa相互作用蛋白3样可在红细胞成熟过程中激活线粒体自噬,而Bcl-2/腺病毒E1B19 kDa相互作用蛋白3(Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B19 kDa-interacting protein 3,BNIP3)能够在缺氧时调节线粒体自噬。在后续研究中,NARENDRA等[12]和LIU等[13]相继发现PTEN诱导激酶1/帕金蛋白信号通路及FUN14结构域含蛋白1途径在应激条件下能够激活线粒体自噬。2013年,MARZETTI等[14]研究表明,线粒体功能障碍不仅是加重心血管疾病的机制之一,也是加速多种与年龄相关的慢性疾病进程的重要病理因素。随着研究的不断深入,BRAVO-SAN PEDRO等[15]研究表明,线粒体自噬与多种心血管疾病的发生发展密切相关,提示线粒体自噬作为潜在干预靶点具有重要研究价值。线粒体自噬的研究脉络见表1。 2.1.2 线粒体自噬的调控机制 泛素依赖性途径:PTEN诱导激酶1/帕金蛋白信号通路是经典的泛素依赖性线粒体自噬调控机制[16]。在线粒体去极化或功能障碍时,PTEN诱导激酶1作为线粒体损伤的感应因子进入线粒体内膜的过程受阻,进而可介导E3泛素连接酶帕金蛋白转位至受损线粒体表面识别泛素并结合线粒体膜蛋白[17-18];随后,泛素化的线粒体通过与微管相关蛋白1轻链3相互作用进一步募集自噬起始复合物中的Unc-51样自噬激酶1等关键因子,诱导吞噬泡的形成[19],最终,受损的线粒体被包裹形成自噬小体,与溶酶体融合后降解为小分子物质被细胞再利用。 泛素非依赖性途径:不同于PTEN诱导激酶1/帕金蛋白介导的泛素依赖性途径,线粒体外膜上存在BNIP3、Bcl-2/腺病毒E1B19 kDa相互作用蛋白3样及FUN14结构域含蛋白1等自噬受体蛋白,能够直接与N端的微管相关蛋白1轻链3结合并激活线粒体自噬[20]。BNIP3可通过调控自噬小体与溶酶体融合促进线粒体的分裂,而Bcl-2/腺病毒E1B19 kDa相互作用蛋白3样能够介导受损线粒体的清除并减少活性氧的生成,进而抑制氧化应激反应[21]。FUN14结构域含蛋白1作为泛素非依赖性线粒体自噬的关键受体之一,它的调控机制与磷酸化状态密切相关。Src激酶在常氧条件下通过磷酸化FUN14结构域含蛋白1并抑制与微管相关蛋白1轻链3的相互作用,从而影响线粒体自噬;而缺氧时,Src激酶活性降低,FUN14结构域含蛋白1去磷酸化,增强了与微管相关蛋白1轻链3的结合并激活线粒体自噬[22]。深入研究发现,线粒体内膜上的抗增殖蛋白2及心磷脂在清除受损线粒体过程中发挥了自噬受体的功能[23],其中,心磷脂在内膜外化后与微管相关蛋白1轻链3结合,而抗增殖蛋白2依赖微管相关蛋白1轻链3结合结构域与微管相关蛋白1轻链3相互作用,介导受损线粒体的选择性识别与包裹,进而触发线粒体自噬。此外,线粒体动力相关蛋白1、线粒体融合蛋白2、线粒体分裂蛋白1等线粒体动力学相关蛋白也参与了线粒体自噬过程[24]。线粒体自噬的调控机制见图3。"
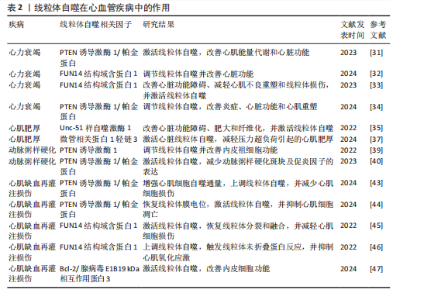
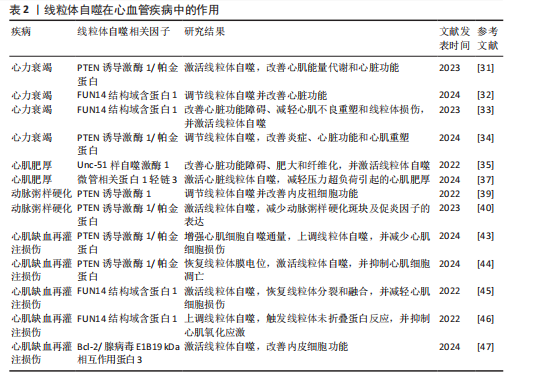
2.2 线粒体自噬在心血管疾病中的作用 线粒体自噬已被证明是心血管疾病防治的新靶标。新近研究表明,线粒体自噬相关信号通路的异常调控是心力衰竭、心肌肥厚、动脉粥样硬化及心肌缺血再灌注损伤等多种心血管疾病的病理机制之一。 2.2.1 线粒体自噬在心血管疾病中的诊断 线粒体自噬不仅在维持细胞稳态中发挥关键作用,也在疾病的早期诊断中具有重要价值。研究表明,心力衰竭患者心肌中PTEN诱导激酶1、BNIP3、Bcl-2/腺病毒E1B19 kDa相互作用蛋白3样及FUN14结构域含蛋白1等关键线粒体自噬因子表达显著下调,进而抑制了心肌线粒体自噬,而在健康个体中相关因子表达正常[25]。RANJBARVAZIRI等[26]研究发现,与健康对照组相比,肥厚性心肌病患者体内活性氧水平升高且线粒体自噬功能异常。此外有研究显示,心肌缺血再灌注损伤患者心肌中BNIP3信号通路及微管相关蛋白1轻链3表达水平显著下调,进一步证实了线粒体自噬在维持心肌功能与减轻细胞损伤中的重要作用[27]。上述研究表明,线粒体自噬相关因子及其信号通路的变化可作为心血管疾病诊断的潜在分子指标。YTH结构域包含蛋白1通过介导RNA甲基化修饰的识别与调控,在心血管疾病的发生发展中发挥着关键作用,并具有潜在的诊断价值。研究发现,在肥厚性心肌病患者治疗过程中,YTH结构域包含蛋白1过表达可通过上调心肌细胞中PTEN诱导激酶1/帕金蛋白介导的线粒体自噬,清除受损的线粒体并改善心肌细胞功能[28]。此外,心肌缺血再灌注损伤的进展与年龄增长有关,老年患者体内微管相关蛋白1轻链3表达显著下调且线粒体自噬功能严重受损,从而进一步加重了心肌损伤[29]。新近研究表明,微小RNA-21-3p能够抑制线粒体自噬,而微小RNA-21-3p抑制剂能够降低M1巨噬细胞的极化,并通过激活线粒体自噬改善心肌结构和纤维化[30]。 综上所述,线粒体自噬相关因子PTEN诱导激酶1、帕金蛋白、BNIP3、Bcl-2/腺病毒E1B19kDa相互作用蛋白3样、FUN14结构域含蛋白1及微管相关蛋白1轻链3可作为心血管疾病诊断的潜在生物标记物,为心血管疾病的早期诊断与预后评估提供了理论参考。 2.2.2 线粒体自噬在心血管疾病中的治疗线粒体自噬与心力衰竭:心力衰竭是心血管疾病的一种病理综合征。研究发现,暖心康(红参、毛冬青)可通过激活PTEN诱导激酶1/帕金蛋白通路介导的线粒体自噬,改善心力衰竭小鼠的心肌能量代谢与心脏功能;在体外实验中,暖心康能够进一步减轻缺氧诱导的线粒体功能损伤,从而增强对心肌细胞的保护作用[31]。FUN14结构域含蛋白1途径介导的线粒体自噬,在心力衰竭的病理进程中也扮演着重要角色。DONG等[32]发现,心阳片(红参、黄芪、益母草、毛冬青)通过增强线粒体未折叠蛋白反应激活FUN14结构域含蛋白1介导的线粒体自噬,从而改善小鼠心脏功能,同时受体相互作用蛋白激酶3的过表达能够增强这一保护效应。此外,WANG等[33]通过分子对接和表面等离子共振技术证实,人参皂苷Rg3能够通过与Unc-51 样自噬激酶1相互作用激活FUN14结构域含蛋白1介导的线粒体自噬,进而改善心力衰竭大鼠的心脏功能障碍、减轻心肌不良重塑和线粒体损伤。由此可见,药物干预可通过调控PTEN诱导激酶1/帕金蛋白与FUN14结构域含蛋白1信号通路激活线粒体自噬,从而改善心肌功能。近年来,微小RNA和外泌体在调控线粒体自噬中的作用逐渐受到研究者们的关注。CHEN等[34]研究表明,心力衰竭大鼠心包脂肪组织细胞外囊泡中的微小RNA-27a-3p能够通过上调PTEN诱导激酶1/帕金蛋白信号通路激活线粒体自噬,从而改善炎症因子的表达、心脏功能及心肌重塑,减轻心力衰竭症状。上述研究提示,微小RNA可能是调控线粒体自噬的重要因子,靶向微小RNA有望成为治疗心力衰竭等心血管疾病的潜在选择。 线粒体自噬与心肌肥厚:心肌肥厚可分为生理性与病理性两类,生理性心肌肥厚常见于运动训练或妊娠等生理状态;而病理性心肌肥厚多见于高血压、心肌病等病理因素所致,易进展为心力衰竭等严重的心血管疾病。研究表明,心肌肥厚小鼠心脏中自噬相关基因7的激活可诱导短暂的自噬发生,而激活Unc-51样自噬激酶1介导的线粒体自噬能够改善心脏功能障碍、肥大和纤维化[35],提示线粒体自噬的激活在改善心脏重构中发挥有益效应。SHOKRI等[36]研究表明,药物干预能够激活线粒体自噬,并下调Bax蛋白表达、上调Bcl-2蛋白,进而抑制线粒体依赖性细胞凋亡,缓解甲亢诱发的心肌肥厚,研究表明,线粒体自噬的激活可抑制心肌细胞凋亡,进而改善心肌肥厚相关的病理损伤。HE等[37]研究发现,心肌肥厚大鼠线粒体功能受损严重,而司美格鲁肽干预能够显著上调微管相关蛋白1轻链3表达并增加自噬体数量,从而激活心脏线粒体自噬,减轻压力超负荷引起的心肌肥厚。另有研究发现,维生素D能够上调心肌中PTEN诱导激酶1、线粒体融合蛋白2、线粒体动力相关蛋白1等线粒体自噬相关因子的表达,进而改善甲亢引起的心肌损伤、氧化应激和心肌肥厚[38]。综上所述,靶向激活线粒体自噬在不同病因诱发的病理性心肌肥厚中均能发挥保护作用,这为心血管疾病的治疗提供了潜在的干预靶点。 线粒体自噬与动脉粥样硬化:动脉粥样硬化的病理机制主要为血管内皮功能障碍和持续性炎症反应。有研究表明,动脉粥样硬化小鼠在匹伐他汀干预后可激活PTEN诱导激酶1诱导的线粒体自噬,从而改善内皮祖细胞功能[39]。CAO等[40]在心脉康干预的动脉粥样硬化小鼠模型中发现,PTEN诱导激酶1基因敲除小鼠的线粒体自噬显著下调,而正常小鼠中PTEN诱导激酶1/帕金蛋白通路上调并激活线粒体自噬,从而减少体内动脉粥样硬化斑块及促炎因子的表达。上述研究提示,PTEN诱导激酶1介导的线粒体自噬可能是缓解动脉粥样硬化的因素。心肌胰岛素抵抗加重会引起高血糖和血脂异常,从而促进动脉粥样硬化的进展。研究表明,在营养过剩状态下,Bcl-2/腺病毒E1B19 kDa相互作用蛋白3样通过激活线粒体自噬能够抑制心肌胰岛素抵抗[41]。此外,JIN等[42]发现卡斯帕酶1抑制剂能够降低线粒体活性氧水平,并抑制NLR家族含有Pyrin结构域3炎症小体对线粒体的损伤,从而促进帕金蛋白磷酸化并激活线粒体自噬,进而改善小鼠的血管炎症和动脉粥样硬化。上述研究进一步验证了线粒体自噬激活在动脉粥样硬化治疗中的作用,然而,线粒体自噬的调控效应可能受干预方式及个体生理状态的影响,未来研究应系统对比不同干预策略对线粒体自噬相关信号通路的调控作用,以期为临床干预提供更科学的理论支撑。 线粒体自噬与心肌缺血再灌注损伤:心肌缺血再灌注损伤,又称缺血性心肌病,是由于冠状动脉粥样硬化导致心肌长期慢性缺血,进而引发心肌微血管内皮损伤和灌注障碍的一种病理状态。CHEN等[43]通过建立心肌缺血再灌注损伤小鼠模型发现,小鼠心肌细胞中线粒体自噬水平提高,进一步研究发现,天麻素可通过调控PTEN诱导激酶1/帕金蛋白通路增强心肌细胞的自噬通量,从而减轻心肌细胞损伤。另有研究表明,达格列净能够降低断裂线粒体DNA水平、恢复线粒体膜电位、抑制心肌细胞凋亡,机制可能与激活PTEN诱导激酶1/帕金蛋白介导的线粒体自噬有关[44]。上述2项研究提示,PTEN诱导激酶1/帕金蛋白轴调控的线粒体自噬在心肌缺血再灌注损伤中具有保护效益。另外,CAI等[45]的体内外实验表明,心肌缺血再灌注损伤可引起心肌微血管壁和内皮细胞损伤,而激活腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶/Unc-51样自噬激酶1/FUN14结构域含蛋白1介导的线粒体自噬能够恢复线粒体分裂和融合,从而减轻心肌细胞损伤;深入研究发现,敲除小鼠体内FUN14结构域含蛋白1后可导致线粒体功能障碍,进一步加重心肌微血管和内皮细胞损伤。另有研究发现,在心肌缺血再灌注损伤下,寡霉素能够上调FUN14结构域含蛋白1介导的线粒体自噬并触发线粒体未折叠蛋白反应,进而显著抑制心肌氧化应激[46],提示FUN14结构域含蛋白1信号通路与线粒体可协同调控心肌细胞内自噬水平,进而减轻心肌缺血再灌注损伤。CHEN等[47]研究发现,BNIP3介导的线粒体自噬激活不仅能够改善内皮细胞功能,还能减轻心肌梗死后的再灌注损伤,提示靶向BNIP3信号通路调控线粒体自噬可能成为心血管疾病治疗的新方向。综上所述,现阶段有关线粒体自噬调控机制的研究仍以动物实验为主,基于动物与人体在生理学方面的差异,这些研究成果在临床转化中存在一定的局限,未来研究可开展有针对性的人体实验,以推动实验成果向临床应用转化,为心血管疾病的治疗提供科学依据。 线粒体自噬与其他心血管疾病:病毒性心肌病、心肌梗死、心肌损伤及心脏衰老也是心血管疾病的重要病理因素。Bax抑制子1是一种应激反应蛋白,具有心脏保护功能。研究发现,Bax抑制子1过表达能够改善脓毒症诱导的心脏功能障碍,深入研究发现,这一效应与激活帕金蛋白介导的线粒体自噬并促进受损线粒体的清除,进而减轻心肌细胞损伤有关[48]。AI等[49]研究表明,心肌梗死幸存者心肌细胞中帕金蛋白信号通路的上调可激活线粒体自噬,从而保护心肌组织免受进一步损伤。另有研究发现,Bax抑制子1能够诱导线粒体未折叠蛋白反应并上调FUN14结构域含蛋白1信号通路,从而激活线粒体自噬,改善心肌损伤[50]。新近研究表明,枸杞多糖干预能够恢复衰老小鼠心肌细胞中受损的PTEN诱导激酶1/帕金蛋白信号通路并激活线粒体自噬,进而改善心脏能量代谢、延缓心脏衰老[51]。此外,GONG等[52]研究发现,五环三萜类化合物通过调控FUN14结构域含蛋白1上游泛素E3连接酶膜相关环状蛋白5,可选择性的激活FUN14结构域含蛋白1介导的线粒体自噬,延缓心脏衰老;进一步研究发现,FUN14结构域含蛋白1基因敲除会引发小鼠线粒体损伤、氧化应激及细胞凋亡。 综上所述,线粒体自噬在心血管疾病的治疗中具有重要作用,但不同信号通路在心血管疾病中的调控存在一定差异。PTEN诱导激酶1/帕金蛋白信号通路介导的线粒体自噬主要参与心力衰竭、心肌肥厚、动脉粥样硬化及心肌缺血再灌注损伤,病理效应包括改善心脏功能、减轻心肌损伤、抑制氧化应激及下调炎症因子表达,进而延缓心血管疾病的发生发展。BNIP3/Bcl-2/腺病毒E1B19 kDa相互作用蛋白3样介导的线粒体自噬,能够通过抑制心肌胰岛素抵抗及改善内皮细胞功能在动脉粥样硬化与心肌缺血再灌注损伤中缓解病理进程。此外,FUN14结构域含蛋白1途径通过维护心脏功能、抑制心肌不良重塑及降低心肌损伤,在心力衰竭、心肌缺血再灌注损伤及心脏衰老中扮演着重要角色,近年来逐渐成为心血管保护研究的焦点。线粒体自噬在心血管疾病中的作用见表2。 2.3 运动对线粒体自噬的影响 研究表明,运动可通过多途径调控线粒体自噬,包括调节线粒体自噬相关因子的表达、影响自噬体形成以及调控线粒体相关动力学及生物合成过程。基于此,该文就不同运动方式对线粒体自噬调控作用的研究进行综述。 2.3.1 有氧运动对线粒体自噬的影响 有氧运动是防治慢性疾病的重要非药物干预手段,能够改善线粒体功能、质量控制及上调线粒体自噬活性,从而在维持线粒体稳态中发挥关键作用。研究表明,为期12周的中等强度跑步机运动可通过提升烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸水平上调沉默信息调节因子1的去乙酰化活性,进而激活叉头框转录因子O1信号通路[53],这一信号通路的激活能够上调PTEN诱导激酶1/帕金蛋白介导的线粒体自噬,从而改善小鼠的线粒体功能障碍。ZOU等[54]研究发现,非酒精性脂肪肝病斑马鱼肝脏中自噬体数量减少且线粒体自噬功能受损严重,中等强度游泳干预能够显著下调p62水平并上调PTEN诱导激酶1/帕金蛋白信号通路,从而激活线粒体自噬。另有研究发现,为期8周的中等强度跑轮运动通过上调PTEN诱导激酶1、BNIP3及微管相关蛋白1轻链3的表达以及下调p62水平,激活非酒精性脂肪肝小鼠肝脏的线粒体自噬[55]。上述研究一致表明,中等强度有氧运动能够有效激活线粒体自噬并改善线粒体功能。随着研究的进一步深入,有氧运动联合中药调控线粒体自噬也得到了新的进展。陶晓雪等[56]研究发现,进行为期4周的有氧运动联合生慧汤干预"
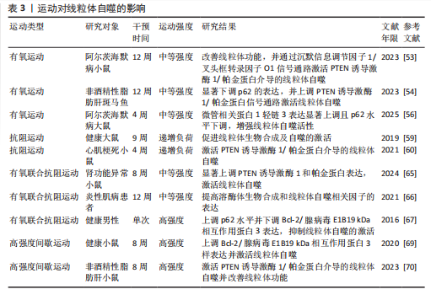
后,小鼠体内微管相关蛋白1轻链3表达显著上调且p62水平下调,线粒体自噬活性增强,提示运动联合中药对线粒体自噬也具有调控作用。此外,OPICHKA等[57]对11名男性的研究发现,在低温环境下进行一次60 min的自行车运动能够诱导线粒体生物合成和自噬的发生。另有研究发现,2型糖尿病患者在夜间进行运动更有利于线粒体自噬的激活,不仅降低了时钟基因蛋白的表达,还抑制了细胞的过度凋亡[58]。 综上所述,有氧运动以及与中药联合均可激活线粒体自噬,这为进一步阐明运动调控线粒体自噬的作用机制提供了实验依据。 2.3.2 抗阻运动对线粒体自噬的影响 抗阻运动作为常见的运动干预方式,也被用于探讨对线粒体自噬的调控作用。研究发现,为期9周的递增负荷抗阻运动能够减少大鼠体内氯喹诱导的淀粉样β蛋白,促进线粒体生物合成及自噬的激活;进一步研究发现,运动通过激活去乙酰化酶3通路增强线粒体氧化能力[59]。另有研究发现,为期4周的递增负荷抗阻运动可激活心肌梗死小鼠体内PTEN诱导激酶1/帕金蛋白介导的线粒体自噬[60]。上述研究提示,递增负荷抗阻运动对线粒体自噬的激活具有显著效应。MARSHALL等[61]研究表明,进行为期一周的单侧抗阻运动干预后,老年男性体内线粒体生物合成及Unc-51样自噬激酶1、微管相关蛋白1轻链3和BNIP3/Bcl-2/腺病毒E1B19 kDa相互作用蛋白3样信号通路未发生显著变化。另有研究发现,为期10周的抗阻运动未显著激活健康老年人骨骼肌中的线粒体自噬和生物合成,但线粒体动力相关蛋白1水平有上调[62]。DíAZ-CASTRO等[63]研究表明,单次单腿抗阻运动可激活健康男性骨骼肌中Bcl-2/腺病毒E1B19 kDa相互作用蛋白3样介导的线粒体自噬,增强自噬体样结构的数量。由此可见,运动对线粒体自噬的影响可能与受试者的年龄及干预时长有关。OGBORN等[64]研究发现,进行单次抗阻运动干预后,健康成人与老年人体内线粒体自噬相关调控因子PTEN诱导激酶1、帕金蛋白及Bcl-2/腺病毒E1B19 kDa相互作用蛋白3样未显著表达,提示抗阻运动未能激活线粒体自噬。 综上所述,抗阻运动对线粒体自噬的影响可能受运动干预时长、研究对象生物学差异及年龄的影响,未来研究应扩大样本量,并系统探讨物种差异、干预时长及年龄因素对线粒体自噬的调控作用,以进一步揭示运动在疾病防治中的分子机制。 2.3.3 有氧联合抗阻运动对线粒体自噬的影响 有氧运动联合抗阻运动兼具提升心肺适能与增强肌力的双重效益,其中,有氧运动有助于改善肺通气功能与心血管耐力,而抗阻运动显著提升肌肉力量和功能。研究表明,为期8周的中等强度有氧联合抗阻运动可显著上调肾功能异常小鼠体内PTEN诱导激酶1和帕金蛋白表达,并激活线粒体自噬[65]。BORGES等[66]研究发现,进行为期12周的中等强度有氧联合抗阻运动干预后,炎性肌病患者体内受损的蛋白质和细胞器得到显著改善;进一步研究发现,有氧联合抗阻运动提高了溶酶体生物合成和线粒体自噬相关因子在骨骼肌中的表达。上述研究提示,长期中等强度有氧联合抗阻运动可通过上调线粒体自噬相关因子的表达激活线粒体自噬。此外,在一项关于运动后饮酒的研究发现,8名健康男性进行有氧联合抗阻运动后同时摄入酒精和碳水化合物,会上调体内p62水平并下调BNIP3表达,从而抑制线粒体自噬的激活;值得注意的是,运动后同时摄入酒精和蛋白质会诱发线粒体生物合成,进而保护细胞稳态[67]。 综上所述,有氧联合抗阻运动对线粒体自噬具有一定的调控作用,但相关研究较少,并且多集中于特定疾病人群,对运动强度、持续时间及年龄差异等因素的探讨仍显不足,因此,尚难全面揭示有氧联合抗阻运动在不同人群中调控线粒体自噬的机制。未来研究可在大样本量基础上,通过长期试验干预系统对比不同人群、运动强度及持续时间对线粒体自噬的调控效应,以进一步阐明运动的作用机制及分子调控途径。 2.3.4 高强度间歇运动对线粒体自噬的影响 高强度间歇运动是高强度运动与低强度恢复交替进行的一种运动方式。研究表明,进行为期12周的高强度间歇运动干预后,肥胖老年人骨骼肌中线粒体生物合成显著提高、线粒体自噬激活;深入研究发现,这一效应可能与帕金蛋白、线粒体融合蛋白1及线粒体融合蛋白2的上调从而提升线粒体数量和质量有关[68]。廖波等[69]研究发现,为期8周的高强度间歇运动可显著上调Bcl-2/腺病毒E1B19 kDa相互作用蛋白3样表达并激活线粒体自噬,进而改善线粒体功能。上述实验提示,高强度间歇运动能够通过调节PTEN诱导激酶1/帕金蛋白、Bcl-2/腺病毒E1B19 kDa相互作用蛋白3样信号通路激活线粒体自噬。另有研究发现,为期8周的高强度间歇运动可激活非酒精性脂肪肝小鼠体内PTEN诱导激酶1/帕金蛋白介导的线粒体自噬,进而改善线粒体功能[70]。何炜等[71]通过急性心肌梗死大鼠模型发现,短期高强度间歇运动训练即可提高急性心肌梗死后心肌健康线粒体含量,从而改善心肌能量代谢和舒缩功能。此外,YAMAUCHI等[72]研究表明,为期4周的高强度间歇运动能够显著上调PTEN诱导激酶1、帕金蛋白、BNIP3和Bcl-2/腺病毒E1B19 kDa相互作用蛋白3样的表达,从而激活小鼠骨骼肌线粒体自噬;值得注意的是,单次高强度间歇运动可通过增强小鼠体内腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶、Unc-51样自噬激酶1的表达及线粒体动力相关蛋白1的磷酸化水平激活线粒体自噬。由此可见,线粒体自噬的激活不依赖于高强度间歇运动的持续时间,单次运动也能诱导线粒体自噬的发生。 综上所述,上述运动方式均可通过调控线粒体自噬相关因子的表达激活线粒体自噬。此外,有氧运动还能促进自噬体的形成,从而提高对线粒体自噬的调控能力;抗阻运动能调节线粒体生物合成;有氧联合抗阻运动可通过促进溶酶体生物合成进一步影响线粒体自噬;高强度间歇运动通过调节线粒体动力学相关蛋白的表达,进而增强线粒体自噬功能。运动对线粒体自噬的影响见表3。 2.4 运动调控线粒体自噬在心血管保护中的作用机制 运动已成为防治心血管疾病的非药物干预策略,并且合理的运动能够激活线粒体自噬。运动干预可通过调控线粒体自噬减缓心肌纤维化、抑制心肌细胞凋亡、调节心肌氧化应激及改善内皮细胞功能,进而发挥心血管保护作用。 2.4.1 运动调控线粒体自噬减缓心肌纤维化 心肌纤维化是多种心血管疾病的主要病理特征,并且在疾病的病理进展中起着关键作用。研究表明,为期4周的中等强度有氧运动能够激活心肌梗死大鼠的线粒体自噬,减缓心肌纤维化并改善心功能,从而对心脏发挥保护作用[73]。GUO等[74]研究发现,心力衰竭小鼠的线粒体自噬功能受损严重,为期8周的中等强度有氧运动或高强度间歇运动干预可显著提高心力衰竭小鼠心肌自噬通量、恢复线粒体自噬、有效减缓心肌纤维化;进一步研究发现,中等强度有氧运动在改善心肌功能方面更显著。由此可见,中等强度有氧运动与高强度间歇运动均可通过调控线粒体自噬减缓心肌纤维化进程,并且中等强度有氧运动的效果更佳。另有研究发现,抗阻运动与有氧联合抗阻运动均能上调帕金蛋白途径介导的线粒体自噬,进而有效延缓慢性心力衰竭小鼠心肌纤维化的进展[75],提示抗阻运动与有氧联合抗阻运动在调控线粒体自噬减缓心肌纤维化中也发挥有益作用。一项运动联合线粒体辅酶Q干预的研究表明,二者联合干预后可上调线粒体自噬相关因子PTEN诱导激酶1和线粒体融合蛋白2的表达水平,进而通过调控心脏线粒体质量控制减轻心肌纤维化程度[76]。 2.4.2 运动调控线粒体自噬抑制心肌细胞凋亡 心肌细胞凋亡是加速心血管疾病进程的重要病理机制之一。近年来,运动干预作为一种重要的非药物治疗手段,通过调控线粒体自噬相关信号通路可有效抑制心肌细胞凋亡,在心血管疾病的防治中展现出广阔的临床应用前景。M2型胆碱能受体是分布于心脏副交感神经的重要受体,与心血管疾病的发生发展密切相关[77]。研究表明,有氧运动能够激活M2型胆碱能受体调控PTEN诱导激酶1/帕金蛋白途径介导的心肌线粒体自噬及内质网应激,从而抑制心肌细胞凋亡,进而减轻心肌缺血再灌注损伤"
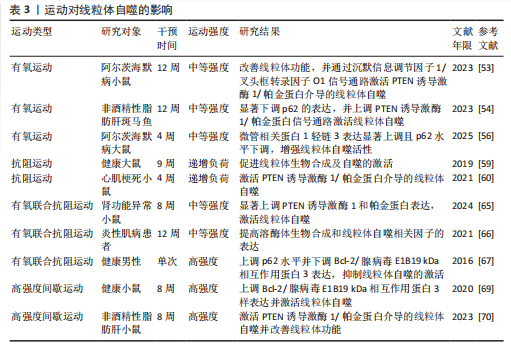
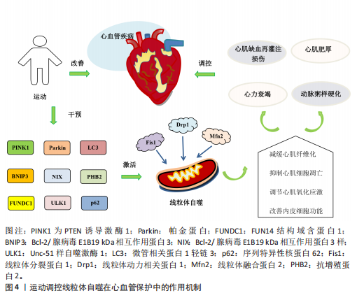
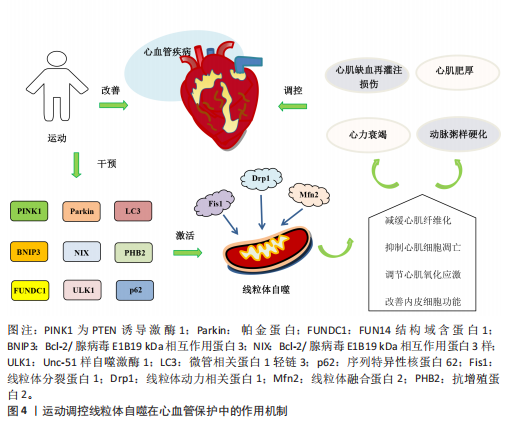
并改善心脏功能[78]。DUN等[79]研究发现,为期8周的游泳可减少肥胖小鼠内脏脂肪含量,降低因肥胖诱导的心肌损伤,这与运动激活线粒体自噬抑制心肌细胞凋亡有关。Bax蛋白可抑制BNIP3、Bcl-2/腺病毒E1B19 kDa相互作用蛋白3样及FUN14结构域含蛋白1介导的泛素非依赖性线粒体自噬过程。在有关衰老与线粒体功能损伤的实验中发现,中等强度有氧运动能改善因衰老引起的线粒体动态失衡和过度的线粒体自噬,从而下调小鼠体内Bax蛋白和裂解的半胱天冬酶3表达、上调Bcl-2蛋白水平,进而抑制心肌细胞凋亡[80]。唐亮等[81]研究表明,为期12周的中等强度有氧运动显著降低了老年小鼠心肌细胞的凋亡率,改善了因衰老引起的心脏功能障碍。上述研究表明,运动能够调控线粒体自噬抑制心肌细胞凋亡,在心血管疾病的防治中发挥积极作用。 2.4.3 运动调控线粒体自噬调节心肌氧化应激 氧化应激能够导致大量活性氧和自由基的生成,从而加剧细胞膜脂质过氧化、DNA损伤及蛋白质变性等病理过程,进而促进心血管系统的炎症反应及动脉粥样硬化的发生。研究表明,有氧运动能够显著增加自噬体数量及上调微管相关蛋白1轻链3的表达、降低p62水平,从而抑制心肌氧化应激,有效预防心脏损伤[82]。李海英[83]研究发现,为期12周的中等强度有氧运动可显著抑制心肌衰老小鼠的氧化应激,并抑制炎症因子的表达,这一变化与上调微管相关蛋白1轻链3与BNIP3表达激活线粒体自噬有关。另有研究发现,动脉粥样硬化大鼠在疾病进展中体内活性氧水平显著升高,进而引发线粒体损伤;经过为期9周的中等强度有氧运动干预后,动脉粥样硬化大鼠抗增殖蛋白2表达显著上调并激活线粒体自噬,从而促进受损线粒体的清除及减轻心肌氧化应激[84]。上述研究表明,有氧运动能够通过激活线粒体自噬调节心肌氧化应激,进而保护心血管免受进一步损伤。LI等[60]研究表明,递增负荷抗阻运动可显著缓解心肌氧化应激,改善心肌梗死后心脏功能,这一效应可能与激活PTEN诱导激酶1/帕金蛋白介导的线粒体自噬有关。另有研究探讨了有氧联合抗阻运动在衰老心脏进程中的调控作用,例如,HAN等[85]研究发现,有氧联合抗阻运动能够上调上游激活因子2基因的表达抑制心肌细胞衰老、激活线粒体自噬减缓心肌氧化应激,从而改善与年龄相关的病理性心脏肥大,并显著提升心脏功能。 2.4.4 运动调控线粒体自噬改善内皮细胞功能 内皮细胞功能障碍不仅是心血管疾病发病机制中的关键环节,也是加速血管结构重构及诱发多器官功能紊乱的重要病理因素[86],因此,靶向干预内皮细胞功能是防治心血管疾病的重要策略。GIOSCIA-RYAN等[87]研究表明,运动干预能够通过改善线粒体功能有效延缓血管老化。新近研究发现,老年小鼠的冠状动脉及心脏微血管内皮细胞中FUN14结构域含蛋白1表达显著下调,因而导致线粒体自噬受损并诱发内皮细胞功能障碍;运动可通过上调 FUN14结构域含蛋白1表达恢复线粒体自噬活性,从而抑制心肌缺血再灌注损伤诱导的炎症因子表达,缓解内皮细胞衰老;此外,在FUN14结构域含蛋白1基因敲击小鼠中,运动诱导的心血管保护效应被显著削弱,而FUN14结构域含蛋白1过表达能延缓内皮细胞的衰老[88]。上述研究表明,FUN14结构域含蛋白1介导的线粒体自噬能够改善内皮细胞功能并延缓血管老化,这可能成为未来研究心血管疾病治疗中的新方向。运动调控线粒体自噬在心血管保护中的作用机制见图4。"
| [1] PERRY AS, DOOLEY EE, MASTER H, et al. Physical Activity Over the Lifecourse and Cardiovascular Disease. Circ Res. 2023; 132(12):1725-1740. [2] CHEN H, CHEN C, SPANOS M, et al. Exercise training maintains cardiovascular health: signaling pathways involved and potential therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):306. [3] REN J, WU NN, WANG S, et al. Mitophagy in cardiovascular diseases: molecular mechanisms, pathogenesis, and treatment. Physiol Rev. 2022;28(10):836-849. [4] FERENTINOS P, TSAKIRIDES C, SWAINSON M, et al. The impact of different forms of exercise on circulating endothelial progenitor cells in cardiovascular and metabolic disease. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2022; 122(4):815-860. [5] DONG Q, ZHU Y, ZHANG X, et al. Phytochemicals Targeting Mitophagy to Treat Heart Diseases: Retrospective Insights and Prospective Directions. Phytother Res. 2025;39(3):1592-1614. [6] FORTE M, D’AMBROSIO L, SCHIATTARELLA GG, et al. Mitophagy modulation for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Eur J Clin Invest. 2024;54(8):e14199. [7] DETER RL, DE DUVE C. Influence of glucagon, an inducer of cellular autophagy, on some physical properties of rat liver lysosomes. J Cell Biol. 1967;33(2):437-449. [8] TAKESHIGE K, BABA M, TSUBOI S, et al. Autophagy in yeast demonstrated with proteinase-deficient mutants and conditions for its induction. J Cell Biol. 1992;119(2):301-311. [9] LEMASTERS JJ. Selective mitochondrial autophagy, or mitophagy, as a targeted defense against oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and aging. Rejuvenation Res. 2005;8(1):3-5. [10] PANKIV S, CLAUSEN TH, LAMARK T, et al. p62/SQSTM1 binds directly to Atg8/LC3 to facilitate degradation of ubiquitinated protein aggregates by autophagy. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(33):24131-24145. [11] ZHANG J, NEY PA. Role of BNIP3 and NIX in cell death, autophagy, and mitophagy. Cell Death Differ. 2009;16(7):939-946. [12] NARENDRA DP, JIN SM, TANAKA A, et al. PINK1 is selectively stabilized on impaired mitochondria to activate Parkin. PLoS Biol. 2010;8(1):e1000298. [13] LIU L, FENG D, CHEN G, et al. Mitochondrial outer-membrane protein FUNDC1 mediates hypoxia-induced mitophagy in mammalian cells. Nature Cell Biology. 2012;14(2):177-185. [14] MARZETTI E, CSISZAR A, DUTTA D, et al. Role of mitochondrial dysfunction and altered autophagy in cardiovascular aging and disease: from mechanisms to therapeutics. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013;305(4):H459-H476. [15] BRAVO-SAN PEDRO JM, KROEMER G, GALLUZZI L. Autophagy and Mitophagy in Cardiovascular Disease. Circ Res. 2017; 120(11):1812-1824. [16] HAN R, LIU Y, LI S, et al. PINK1-PRKN mediated mitophagy: differences between in vitro and in vivo models. Autophagy. 2023;19(5):1396-1405. [17] CONNELLY EM, FRANKEL KS, SHAW GS. Parkin and mitochondrial signalling. Cell Signal. 2023;106:110631. [18] LU Y, LI Z, ZHANG S, et al. Cellular mitophagy: Mechanism, roles in diseases and small molecule pharmacological regulation. Theranostics. 2023;13(2):736-766. [19] IORIO R, CELENZA G, PETRICCA S. Mitophagy: Molecular Mechanisms, New Concepts on Parkin Activation and the Emerging Role of AMPK/ULK1 Axis. Cells. 2021;11(1):30. [20] TURKIEH A, EL MASRI Y, PINET F, et al. Mitophagy Regulation Following Myocardial Infarction. Cells. 2022;11(2):30. [21] CLAGUE MJ, URBÉ S. Diverse routes to mitophagy governed by ubiquitylation and mitochondrial import. Trends Cell Biol. 2025;35(6):527-538. [22] ZHANG W. The mitophagy receptor FUN14 domain-containing 1 (FUNDC1): A promising biomarker and potential therapeutic target of human diseases. Genes Dis. 2021;8(5):640-654. [23] DEGLI ESPOSTI M. Did mitophagy follow the origin of mitochondria? Autophagy. 2024;20(5):985-993. [24] TÁBARA LC, SEGAWA M, PRUDENT J. Molecular mechanisms of mitochondrial dynamics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2025; 26(2):123-146. [25] SVAGUSA T, SIKIRIC S, MILAVIC M, et al. Heart failure in patients is associated with downregulation of mitochondrial quality control genes. Eur J Clin Invest. 2023;53(11):e14054. [26] RANJBARVAZIRI S, KOOIKER KB, ELLENBERGER M, et al. Altered Cardiac Energetics and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 2021;144(21):1714-1731. [27] CHEN Z, LIU T, YUAN H, et al. Bioinformatics integration reveals key genes associated with mitophagy in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024;24(1):183. [28] LI Y, ZHANG W, DAI Y, et al. Identification and verification of IGFBP3 and YTHDC1 as biomarkers associated with immune infiltration and mitophagy in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Front Genet. 2022;13: 986995. [29] OLIVEIRA AN, YANAGAWA B, QUAN A, et al. Human cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury: Blunted stress response with age. J Card Surg. 2021;36(10):3643-3651. [30] HUANG Y, HUANG Y, CAI Z, et al. MiR-21-3p inhibitor exerts myocardial protective effects by altering macrophage polarization state and reducing excessive mitophagy. Commun Biol. 2024;7(1):1371. [31] GUAN Z, CHEN J, WANG L, et al. Nuanxinkang prevents the development of myocardial infarction-induced chronic heart failure by promoting PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Phytomedicine. 2023;108:154494. [32] DONG X, ZHUANG HW, WEN RJ, et al. Xinyang tablet alleviated cardiac dysfunction in a cardiac pressure overload model by regulating the receptor-interacting serum/three-protein kinase 3/FUN14 domain containing 1-mediated mitochondrial unfolded protein response and mitophagy. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024;330:118152. [33] WANG X, LING G, WEI Y, et al. Activation of ULK1 to trigger FUNDC1-mediated mitophagy in heart failure: Effect of Ginsenoside Rg3 intervention. Phytomedicine. 2023;120:155042. [34] CHEN Z, ZHANG M, XU Q, et al. Huangqi-Danshen decoction improves heart failure by regulating pericardial adipose tissue derived extracellular vesicular miR-27a-3p to activate AMPKα2 mediated mitophagy. Phytomedicine. 2024;135:156187. [35] NAH J, SHIRAKABE A, MUKAI R, et al. Ulk1-dependent alternative mitophagy plays a protective role during pressure overload in the heart. Cardiovasc Res. 2022;118(12):2638-2651. [36] SHOKRI F, ZAREI M, KOMAKI A, et al. Effect of diminazene on cardiac hypertrophy through mitophagy in rat models with hyperthyroidism induced by levothyroxine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024;397(2):1151-1162. [37] HE W, WEI J, LIU X, et al. Semaglutide ameliorates pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy by improving cardiac mitophagy to suppress the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1): 11824. [38] SHOKRI F, RAMEZANI-ALIAKBARI K, ZAREI M, et al. Cardioprotective effect of Vitamin D on cardiac hypertrophy through improvement of mitophagy and apoptosis in an experimental rat model of levothyroxine -induced hyperthyroidism. Mol Biol Rep. 2024;51(1):969. [39] YANG J, SUN M, CHENG R, et al. Pitavastatin activates mitophagy to protect EPC proliferation through a calcium-dependent CAMK1-PINK1 pathway in atherosclerotic mice. Commun Biol. 2022;5(1):124. [40] CAO Y, CHEN X, PAN F, et al. Xinmaikang-mediated mitophagy attenuates atherosclerosis via the PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway. Phytomedicine. 2023; 119:154955. [41] DASILVAROSA SC, MARTENS MD, FIELD JT, et al. BNIP3L/Nix-induced mitochondrial fission, mitophagy, and impaired myocyte glucose uptake are abrogated by PRKA/PKA phosphorylation. Autophagy, 2021; 17(9):2257-2272. [42] JIN Y, LIU Y, XU L, et al. Novel role for caspase 1 inhibitor VX765 in suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and atherosclerosis via promoting mitophagy and efferocytosis. Cell Death Dis. 2022; 13(5):512. [43] CHEN L, LV Y, WU H, et al. Gastrodin exerts perioperative myocardial protection by improving mitophagy through the PINK1/Parkin pathway to reduce myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Phytomedicine. 2024;133:155900. [44] CHEN W, ZHANG Y, WANG Z, et al. Dapagliflozin Alleviates Myocardial Ischaemia Reperfusion Injury by Activating Mitophagy. Front Pharmacol. 2024;22(3): 203-217. [45] CAI C, GUO Z, CHANG X, et al. Empagliflozin attenuates cardiac microvascular ischemia/reperfusion through activating the AMPKα1/ULK1/FUNDC1/mitophagy pathway. Redox Biol. 2022;52:102288. [46] JI H, WANG J, MUID D, et al. FUNDC1 activates the mitochondrial unfolded protein response to preserve mitochondrial quality control in cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell Signal. 2022;92:110249. [47] CHEN L, YANG X, WANG K, et al. Humanin inhibits lymphatic endothelial cells dysfunction to alleviate myocardial infarction-reperfusion injury via BNIP3-mediated mitophagy. Free Radic Res. 2024; 58(3):180-193. [48] HUANG W, LOU A, WANG J, et al. TMBIM1 ameliorates sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction by promoting Parkin-mediated mitophagy. FASEB J. 2025;39(4):e70397. [49] AI L, DE FREITAS GERMANO J, HUANG C, et al. Enhanced Parkin-mediated mitophagy mitigates adverse left ventricular remodelling after myocardial infarction: role of PR-364. Eur Heart J. 2025;46(4):380-393. [50] WANG J, WANG X, DU W, et al. BI-1 ameliorates myocardial injury by activating the mitochondrial unfolded protein response and FUNDC1-related mitophagy in cardiorenal syndrome type 3. Cell Signal. 2022;91:110218. [51] PENG T, XIANG J, TIAN Y, et al. Lycium barbarum glycopeptide ameliorates aging phenotypes and enhances cardiac metabolism by activating the PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy pathway in D-galactose-induced mice. Exp Gerontol. 2025;200:112686. [52] GONG Y, LUO Y, LIU S, et al. Pentacyclic triterpene oleanolic acid protects against cardiac aging through regulation of mitophagy and mitochondrial integrity. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2022; 1868(7):166402. [53] ZHAO N, ZHANG X, LI B, et al. Treadmill Exercise Improves PINK1/Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy Activity Against Alzheimer’s Disease Pathologies by Upregulated SIRT1-FOXO1/3 Axis in APP/PS1 Mice. Mol Neurobiol. 2023;60(1):277-291. [54] ZOU YY, TANG XB, CHEN ZL, et al. Exercise intervention improves mitochondrial quality in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease zebrafish. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1162485. [55] ROSA-CALDWELL ME, POOLE KE, SEIJA A, et al. Exercise during weight loss improves hepatic mitophagy. Sports Med Health Sci. 2022;4(3):183-189. [56] 陶晓雪,萧闵,唐琨洋,等.运动联合生慧汤干预M1AChR调控线粒体自噬提高阿尔茨海默病模型大鼠学习记忆能力[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2026,32(1):120-130. [57] OPICHKA M, SHUTE R, MARSHALL K, et al. Effects of exercise in a cold environment on gene expression for mitochondrial biogenesis and mitophagy. Cryobiology. 2019;90:47-53. [58] ZHANG Z,LI X,ZHANG J, et al. Chrono-Aerobic Exercise Optimizes Metabolic State in DB/DB Mice through CLOCK-Mitophagy-Apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(16):9308. [59] KOO JH, KANG EB, CHO JY. Resistance Exercise Improves Mitochondrial Quality Control in a Rat Model of Sporadic Inclusion Body Myositis. Gerontology. 2019;65(3): 240-252. [60] LI H, QIN S, LIANG Q, et al. Exercise Training Enhances Myocardial Mitophagy and Improves Cardiac Function via Irisin/FNDC5-PINK1/Parkin Pathway in MI Mice. Biomedicines. 2021;9(6):701. [61] MARSHALL RN, SMEUNINX B, SEABRIGHT AP, et al. No effect of five days of bed rest or short-term resistance exercise prehabilitation on markers of skeletal muscle mitochondrial content and dynamics in older adults. Physiol Rep. 2022;10(13):e15345. [62] MESQUITA PHC, LAMB DA, PARRY HA, et al. Acute and chronic effects of resistance training on skeletal muscle markers of mitochondrial remodeling in older adults. Physiol Rep. 2020;8(15):e14526. [63] DÍAZ-CASTRO F, TUÑÓN-SUÁREZ M, RIVERA P, et al. A single bout of resistance exercise triggers mitophagy, potentially involving the ejection of mitochondria in human skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2024;240(9):e14203. [64] OGBORN DI, MCKAY BR, CRANE JD, et al.Effects of age and unaccustomed resistance exercise on mitochondrial transcript and protein abundance in skeletal muscle of men. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2015;308(8): R734-R741. [65] 杨青,张斌,刘羽佳,等.不同运动方式调控线粒体生物合成和自噬改善肥胖大鼠肾功能异常研究[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2024,43(10):803-814. [66] BORGES IBP, DE OLIVEIRA DS, MARIE SKN, et al. Exercise Training Attenuates Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway and Increases the Genes Related to Autophagy on the Skeletal Muscle of Patients With Inflammatory Myopathies. J Clin Rheumatol. 2021;27(6S):S224-S231. [67] SMILES WJ, PARR EB, COFFEY VG, et al. Protein coingestion with alcohol following strenuous exercise attenuates alcohol-induced intramyocellular apoptosis and inhibition of autophagy. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2016;311(5):E836-E849. [68] MARCANGELI V,YOUSSEF L,DULAC M, et al.Impact of high-intensity interval training with or without l-citrulline on physical performance, skeletal muscle, and adipose tissue in obese older adults.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022;13(33): 1526-1540. [69] 廖波,黄冲,胡帅,等.高强度间歇运动对中年小鼠心肌自噬/线粒体自噬相关蛋白表达和线粒体呼吸功能的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2020,39(9):704-710. [70] 何苗,李佳航,刘鑫,等.中等强度和高强度间歇运动对非酒精性脂肪肝小鼠心肌线粒体自噬的影响[J].中国比较医学杂志,2023,33(11):1-9. [71] 何炜,李玉明,周欣,等.短时高强度间歇运动训练心肌梗死模型大鼠心室重构及线粒体变化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(40):5986-5993. [72] YAMAUCHI N, TAMAI K, KIMURA L, et al. High-intensity interval training in the form of isometric contraction improves fatigue resistance in dystrophin-deficient muscle.J Physiol. 2023;601(14):2917-2933. [73] 保苏丽.运动通过ATG7调控线粒体自噬改善大鼠心肌梗死后心功能[D].昆明:昆明医科大学,2024. [74] GUO C, CHEN MJ, ZHAO JR, et al. Exercise training improves cardiac function and regulates myocardial mitophagy differently in ischaemic and pressure-overload heart failure mice. Exp Physiol. 2022;107(6):562-574. [75] GUO C, WU RY, DOU JH, et al. Mitophagy-dependent cardioprotection of resistance training on heart failure. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2023;135(6):1390-1401. [76] ROSTAMZADEH F, NAJAFIPOUR H, AMINIZADEH S, et al. Therapeutic effects of the combination of moderate-intensity endurance training and MitoQ supplementation in rats with isoproterenol-induced myocardial injury: The role of mitochondrial fusion, fission, and mitophagy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;170:116020. [77] LIAO F, ZHENG Y, CAI J, et al. Catestatin attenuates endoplasmic reticulum induced cell apoptosis by activation type 2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor in cardiac ischemia/reperfusion. Sci Rep. 2015;5:16590. [78] CHEN W, MA M, SONG Y, et al. Exercise Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Regulating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Mitophagy Through M. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2024;40(4-6):209-221. [79] DUN Y, HU Z, YOU B, et al. Exercise prevents fatal stress-induced myocardial injury in obese mice. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1223423. [80] NO MH, HEO JW, YOO SZ, et al. Effects of aging and exercise training on mitochondrial function and apoptosis in the rat heart. Pflugers Arch. 2020;472(2):179-193. [81] 唐亮,王合霞,王庆博,等.有氧运动调控线粒体质量控制系统逆转衰老大鼠心脏的病理性重塑[J].中国组织工程研究, 2024,28(16):2534-2541. [82] LEE Y, KWON I, JANG Y, et al. Endurance Exercise Attenuates Doxorubicin-induced Cardiotoxicity. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2020; 52(1):25-36. [83] 李海英.运动通过干预线粒体自噬调控心肌炎症反应的机制研究[D].北京:中国人民解放军军事医学科学院,2016. [84] 宋明箫.PHB2在耐力训练减缓动脉粥样硬化过程中PINK1-Parkin线粒体自噬通路中的作用[D].天津:天津体育学院,2022. [85] HAN X, ASHRAF M, SHI H, et al. Combined Endurance and Resistance Exercise Mitigates Age-Associated Cardiac Dysfunction. Adv Biol (Weinh). 2024;9(6):e2400137. [86] HALL IF, KISHTA F, XU Y, et al. Endothelial to mesenchymal transition: at the axis of cardiovascular health and disease. Cardiovasc Res. 2024; 120(3):223-236. [87] GIOSCIA-RYAN RA, CLAYTON ZS, ZIGLER MC, et al. Lifelong voluntary aerobic exercise prevents age- and Western diet- induced vascular dysfunction, mitochondrial oxidative stress and inflammation in mice. J Physiol. 2021; 599(3):911-925. [88] MA L, LI K, WEI W, et al. Exercise protects aged mice against coronary endothelial senescence via FUNDC1-dependent mitophagy. Redox Biol. 2023; 62:102693. |
| [1] | Zhang Qingtong, Chen Leqin, Liu Chang, Chen Yuting, Guo Ruiwu. Neuromechanism of the endocannabinoid system in regulating exercise motivation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-11. |
| [2] | Chen Qiuhan, Yang Long, Yuan Daizhu, Wu Zhanyu, Zou Zihao, Ye Chuan. Peri-knee osteotomy for treatment of knee osteoarthritis: optimization of treatment strategies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2303-2312. |
| [3] | Zhao Feifan, Cao Yujing. Risk factors and coping strategies of internal fixation failure in treatment of intertrochanteric fracture with proximal femoral nail antirotation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2323-2333. |
| [4] | Jiang Xianglong, Li Zhongshan, Che Tongtong. Application effects and mechanisms of low-frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields in muscle repair and growth [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2350-2360. |
| [5] | Liu Jinlong, Abuduwupuer·Haibier, Bai Zhen, Su Danyang, Miao Xin, Li Fei, Yang Xiaopeng. Efficacy of different nonsurgical treatments for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a systematic review and network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2370-2379. |
| [6] | Pan Dong, Yang Jialing, Tian Wei, Wang Dongji, Zhu Zheng, Ma Wenchao, Liu Na, Fu Changxi. Resistance exercise activates skeletal muscle satellite cells in aged rats: role of adiponectin receptor 1 pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1736-1746. |
| [7] | Chen Yulin, He Yingying, Hu Kai, Chen Zhifan, Nie Sha Meng Yanhui, Li Runzhen, Zhang Xiaoduo , Li Yuxi, Tang Yaoping. Effect and mechanism of exosome-like vesicles derived from Trichosanthes kirilowii Maxim. in preventing and treating atherosclerosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1768-1781. |
| [8] | Cao Yong, Teng Hongliang, Tai Pengfei, Li Junda, Zhu Tengqi, Li Zhaojin. Interactions between cytokines and satellite cells in muscle regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1808-1817. |
| [9] | Wang Zhenze, Liu Fende, Zhang Rui, Li Wujun. Mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of arteriosclerosis obliterans of lower extremities: systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1869-1876. |
| [10] | Hou Chaowen, Li Zhaojin, Kong Jianda, Zhang Shuli. Main physiological changes in skeletal muscle aging and the multimechanism regulatory role of exercise [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1464-1475. |
| [11] | Sun Yaotian, Xu Kai, Wang Peiyun. Potential mechanisms by which exercise regulates iron metabolism in immune inflammatory diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1486-1498. |
| [12] | Liu Yu, Lei Senlin, Zhou Jintao, Liu Hui, Li Xianhui. Mechanisms by which aerobic and resistance exercises improve obesity-related cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1171-1183. |
| [13] | Wen Fan, Xiang Yang, Zhu Huan, Tuo Yanfang, Li Feng. Exercise improves microvascular function in patients with type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1225-1235. |
| [14] | Chen Qiang, Wu Wenjuan, Jiang Shuhua, Huang Da. Physical exercise improves physical function in burn patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1269-1281. |
| [15] | Jiang Yang, Peng Hao, Song Yanping, Yao Na, Song Yueyu, Yin Xingxiao, Li Yanqi, Chen Qigang. Isometric exercise reduces resting blood pressure: a meta-analysis of moderating factors and dose effects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 975-986. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||