Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (27): 5933-5940.doi: 10.12307/2025.839
Visual analysis of application of three-dimensional finite element method in femoral head necrosis
Liu Yuhang, Li Hongyu, Wang Yong, Wang Fengxing
- Guangxi Orthopedic Hospital, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-06-26Accepted:2024-08-28Online:2025-09-28Published:2025-03-07 -
Contact:Li Hongyu, MD, Chief physician, Guangxi Orthopedic Hospital, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Liu Yuhang, Master candidate, Guangxi Orthopedic Hospital, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Nanning Qingxiu District Science and Technology Plan Project, No. 2020042 (to LHY); Guangxi Natural Science Fund Project (General Project), No. 2023GXNSFAA026208 (to LHY); Guangxi Natural Science Fund Project (General Project), No. 2014GXNSFAA118186 (to LHY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Yuhang, Li Hongyu, Wang Yong, Wang Fengxing. Visual analysis of application of three-dimensional finite element method in femoral head necrosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5933-5940.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
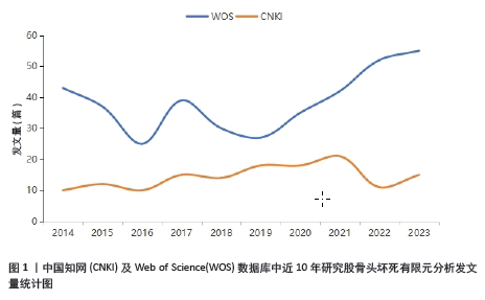
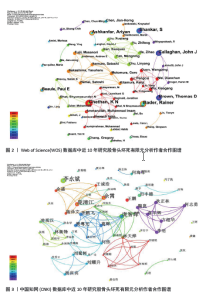
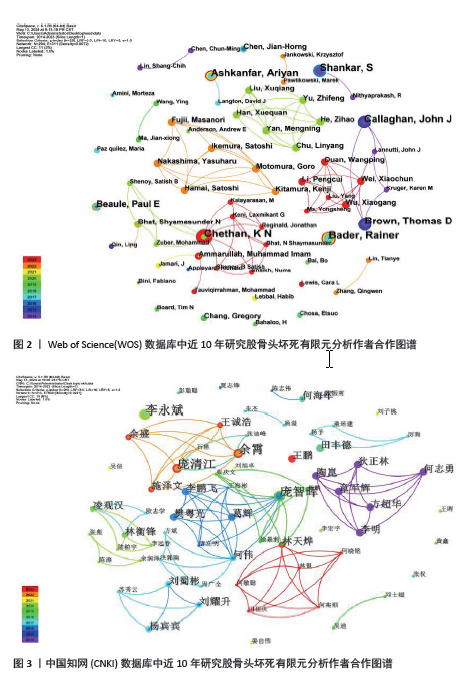
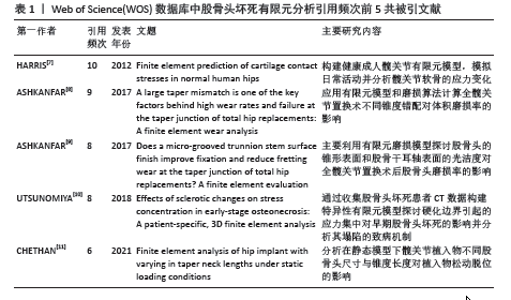
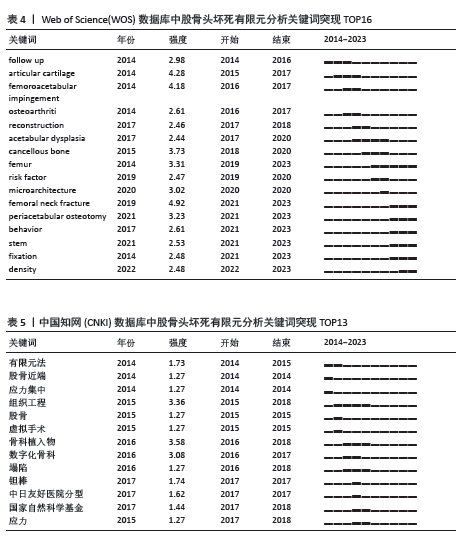
2.1 发文量分析 对自2014年1月至2023年12月检索到的文献进行分析,如图1所示。自2014-2016年以来,英文文献的发文量呈现一个下滑趋势,随着髋关节假体的微动磨损模型的出现,英文文献在2017年的发文量出现一个小高峰,随后在2018年至今一直处于一个平稳上升的趋势,并在2023年达到年发文量55篇的峰值。而中文文献相较于英文文献一直处于较低水平,在2014-2021年8年间一直处于一个缓慢增长的趋势,但在2022年有下滑的趋势,于2023年再次有所增长。 2.2 作者合作分析 作者合作图谱中反映了10年间不同作者的发文量及之间的关联性,可以更直观地展示研究最前沿的作者。在WOS数据库中,2014-2023年间共有294位作者及311条连线,网络密度为0.007 2,节点越大代表发文量越多,而连线则代表作者间的合作,其中Chethan,KN和Bader, Rainer发文量最多,均为6篇,见图2。在CNKI数据库中,共有213位作者以及500条连线,其中余霄、庞智晖、庞清江及李永斌4人发文量最多,均为3篇,见图3。"
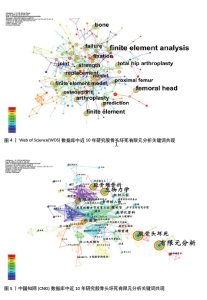
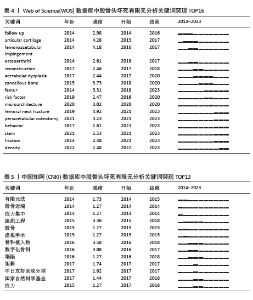
2.4 研究热点分析 2.4.1 关键词共现分析 关键词作为对文章主要研究内容的凝练体现,对某个研究领域的关键词共现分析能更好地展现出研究热点趋势及变化。当2个及以上关键词同时出现时则可称为共现,共现分析则是对关键词的频次及中心性进行计算,当关键词被其他文章引用时,它的中心性就会提升,因此关键词的频次或中心性越高,则代表其在某个时间段越重要[12]。在软件中使用Pathfinder结合Pruning sliced networks算法,根据WOS数据库对2014-2023年10年间相关文献分析得出共有300个关键词和551条连线,见图4,其中关键词频次排名为:finite element analysis(163次)、femoral head(83次)、arthroplasty(44次)、fixation(40次)、replacement(39次),中心性排名为:finite element method(0.21)、hip joint(0.21)、stability(0.19)、fixation(0.15)、contact pressure(0.15)。根据CNKI数据库对2014-2023年10年间相关文献分析得出共有269个关键词和748条连线,见图5,其中关键词频次排名为:有限元分析(91次)、生物力学(45次)、股骨头坏死(42次)、股骨颈骨折(33次)、内固定(16次),中心性排名为:内固定(0.45)、3d打印(0.44)、健脾活骨方(0.43)、三维重建(0.42)、股骨头坏死(0.38)。"
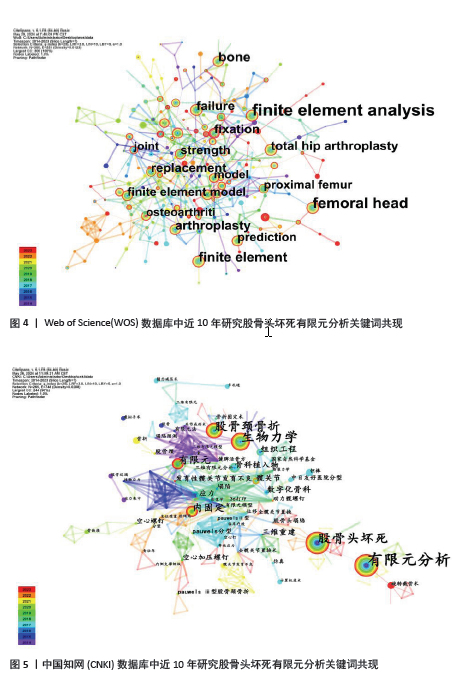
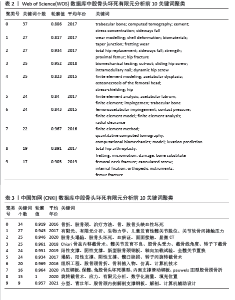
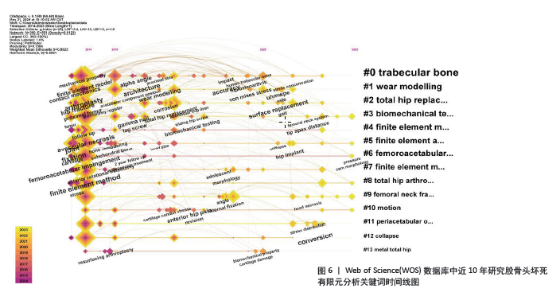
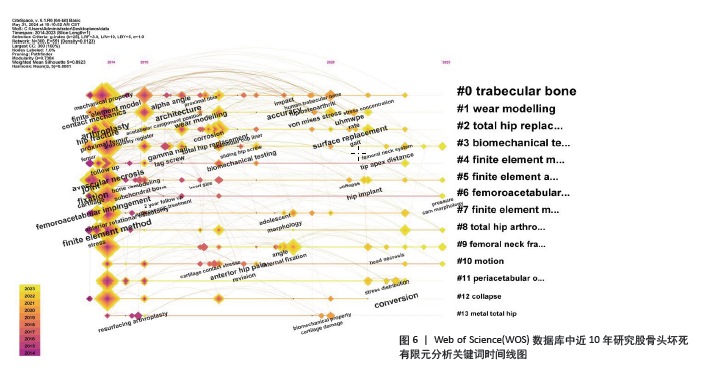
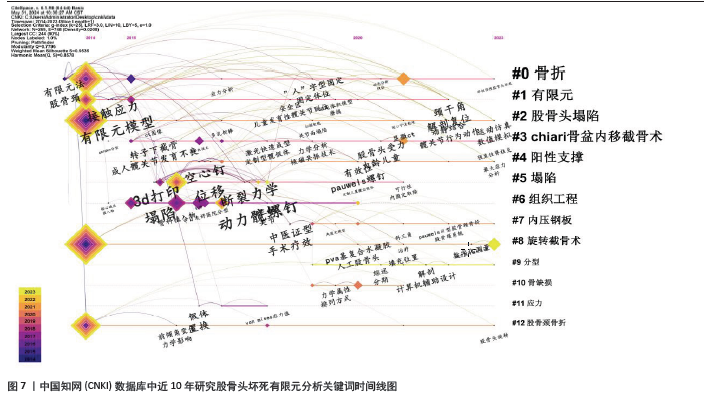
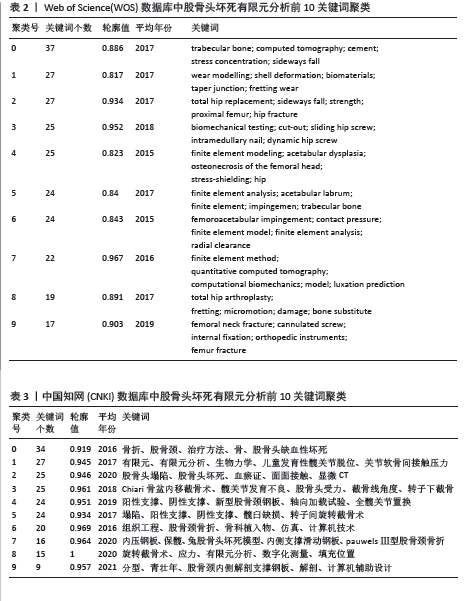
2.4.2 关键词聚类分析 关键词聚类是指通过分析将研究领域内相似的关键词联系起来整合成一个整体,并将其中使用频次最高的关键词作为其聚类名称。在软件中使用Pathfinder结合Pruning sliced networks算法,根据收集的WOS及CNKI数据分析得到的关键词聚类图谱进一步提取出的聚类详细信息,按照关键词个数排名选取出排名前10的聚类见表2,3,其中包括关键词个数、轮廓值、平均年份及关键词组成。其中,轮廓值> 0.7意味着同质性较好、可信度较高[13]。表中首个关键词均为该聚类名称,WOS数据库中前10个聚类名称分别为#0 trabecular bone、#1 wear modelling、#2 total hip replacement、#3 biomechanical testing、#4 finite element modeling、#5 finite element analysis、#6 femoroacetabular impingement、#7 finite element method、#8 total hip arthroplasty、#9 femoral neck fracture; CNKI数据库中前10个聚类名称分别为#0 骨折、#1 有限元、#2 股骨头塌陷、#3 Chiari骨盆内移截骨术、#4 阳性支撑、#5 塌陷、#6 组织工程、#7 内压钢板、#8 旋转截骨术、#9 分型。 "
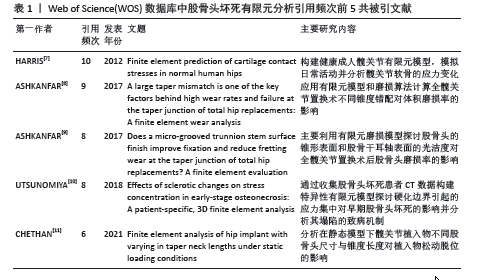
| [1] FUKUSHIMA W, FUJIOKA M, KUBO T, et al. Nationwide epidemiologic survey of idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(10):2715-2724. [2] ZHAO DW, YU M, HU K, et al. Prevalence of Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head and its Associated Risk Factors in the Chinese Population: Results from a Nationally Representative Survey. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015;128(21):2843-2850. [3] ZHENG QY, TAO Y, GENG L, et al. Non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head induced by steroid and alcohol exposure is associated with intestinal flora alterations and metabolomic profiles. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024;19(1):236. [4] YANG Y, CHENG X, CHEN W, et al. Partial femoral head replacement: a new innovative hip-preserving approach for treating osteonecrosis of the femoral head and its finite element analysis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12:1352882. [5] ESCUDIER JC, OLLIVIER M, DONNEZ M, et al. Superimposition of maximal stress and necrosis areas at the top of the femoral head in hip aseptic osteonecrosis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2018;104(3):353-358. [6] XU M, MOTOMURA G, UTSUNOMIYA T, et al. Effects of bone mineral density at the lateral sclerotic boundary on the femoral head collapse onset in osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A preliminary study. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2024;111:106156. [7] HARRIS MD, ANDERSON AE, HENAK CR, et al. Finite element prediction of cartilage contact stresses in normal human hips. J Orthop Res. 2012;30(7):1133-1139. [8] ASHKANFAR A, LANGTON DJ, JOYCE TJ. A large taper mismatch is one of the key factors behind high wear rates and failure at the taper junction of total hip replacements: A finite element wear analysis. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017;69:257-266. [9] ASHKANFAR A, LANGTON DJ, JOYCE TJ. Does a micro-grooved trunnion stem surface finish improve fixation and reduce fretting wear at the taper junction of total hip replacements? A finite element evaluation. J Biomech. 2017; 63:47-54. [10] UTSUNOMIYA T, MOTOMURA G, IKEMURA S, et al. Effects of sclerotic changes on stress concentration in early-stage osteonecrosis: A patient-specific, 3D finite element analysis. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(12):3169-3177. [11] CHETHAN KN, SHYAMASUNDER BHAT N, ZUBER M, et al. Finite element analysis of hip implant with varying in taper neck lengths under static loading conditions. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021;208:106273. [12] CHEN C, HU Z, LIU S, et al. Emerging trends in regenerative medicine: a scientometric analysis in CiteSpace. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12(5):593-608. [13] CHEN C. Searching for intellectual turning points: progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004; 101(Suppl 1):5303-5310. [14] BREKELMANS WA, POORT HW, SLOOFF TJ. A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts. Acta Orthop Scand. 1972;43(5):301-317. [15] DONALDSON FE, COBURN JC, SIEGEL KL. Total hip arthroplasty head-neck contact mechanics: a stochastic investigation of key parameters. J Biomech. 2014;47(7):1634-1641. [16] AFFATATO S, RUGGIERO A, JABER SA, et al. Wear Behaviours and Oxidation Effects on Different UHMWPE Acetabular Cups Using a Hip Joint Simulator. Materials (Basel). 2018; 11(3):433. [17] AFFATATO S, MEROLA M, RUGGIERO A. Development of a Novel in Silico Model to Investigate the Influence of Radial Clearance on the Acetabular Cup Contact Pressure in Hip Implants. Materials (Basel). 2018;11(8):1282. [18] TAUVIQIRRAHMAN M, AMMARULLAH MI, JAMARI J, et al. Analysis of contact pressure in a 3D model of dual-mobility hip joint prosthesis under a gait cycle. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):3564. [19] 张天一,董巍,米盼盼,等.三维有限元分析大转子骨瓣转移治疗股骨头缺血坏死应力分布变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2018, 22(7):1090-1095. [20] 宋和强,张大伟,王鹏,等.股骨颈内固定系统固定股骨颈基底部旋转截骨的有限元分析[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2023, 20(3):12-18. [21] 高永昌,付彦涛,赵昕,等.步行运动下缺血性坏死股骨头力学性能及塌陷风险预测[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(33): 5265-5269. [22] 刘镕阁,徐雁.三维有限元建模分析在髋关节撞击综合征诊疗中的应用研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2021,40(4):317-321. [23] ASKARI E, ANDERSEN MS. A closed-form formulation for the conformal articulation of metal-on-polyethylene hip prostheses: Contact mechanics and sliding distance. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2018;232(12):1196-1208. [24] YUAN D, WU Z, YANG L, et al. Biomechanical analysis of the drilling parameters for early osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022;219:106737. [25] KANAIZUMI A, SUZUKI D, NAGOYA S, et al. Patient-specific three-dimensional evaluation of interface micromotion in two different short stem designs in cementless total hip arthroplasty: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):437. [26] HIDAYAT T, ISMAIL R, TAUVIQIRRAHMAN M, et al. Running-in behavior of dual-mobility cup during the gait cycle: A finite element analysis. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2024;238(1): 99-111. [27] 李子荣,刘朝晖,孙伟,等.基于三柱结构的股骨头坏死分型:中日友好医院分型[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,32(6):515-520. [28] 王宏润,李宏宇,韦明照.基于三柱结构分型股骨头坏死的有限元研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(9):832-836. [29] 胡元斌,周岳来,李永顺,等.有限元分析髓芯减压并同种异体植骨治疗股骨头缺血性坏死的生物力学改变[J].中国医学物理学杂志,2020,37(2):243-248. [30] 庞智晖,何伟.基于临床和影像的股骨头坏死围塌陷期“微观辨证论治体系”的构建[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2013,7(3):363-368. [31] YU T, XIE L, CHU F. A sclerotic rim provides mechanical support for the femoral head in osteonecrosis. Orthopedics. 2015;38(5): e374-e379. [32] TOH SMS, ASHKANFAR A, ENGLISH R, et al. How does bicycling affect the longevity of Total Hip Arthroplasty? A finite element wear analysis. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2023;139:105673. [33] TRAN TN, WOLF M, WINTER P, et al. Hip joint mechanics in patients with osteonecrosis of the femoral head following treatment by advanced core decompression. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2022;94:105635. [34] 刘钊,徐西林,申意伟,等.塌陷预测方法联合分期分型对股骨头坏死治疗的指导作用与前景[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(6):929-934. [35] 陆舜,林天烨,何敏聪,等.基于前外侧保留角预测股骨头坏死塌陷的有限元分析[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2023,37(11): 1394-1402. [36] 毛瑞,郝鹏,黄鑫,等.预防股骨头坏死塌陷的内置物设计及有限元分析[J].北京生物医学工程,2022,41(6):558-563. |
| [1] | Xu Hao, Ding Lu, Li Xiao. Investigating the effect of the mechanical wear on abutment screw in Morse taper connection implant implant system by using finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Li Liangkui, Huang Yongcan, Wang Peng, Yu Binsheng. Effect of anterior controllable anteriodisplacement and fusion on vertebrae-ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament complex and implants: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1761-1767. |
| [3] | Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao. Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1768-1774. |
| [4] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [5] | Chen Xi, Tang Tao, Chen Tongbing, Li Qing, Zhang Wen. Mechanical stability of intertrochanteric fracture of femur with different internal fixation systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1783-1788. |
| [6] | Fu Enhong, Yang Hang, Liang Cheng, Zhang Xiaogang, Zhang Yali, Jin Zhongmin. OpenSim-based prediction of lower-limb biomechanical behavior in adolescents with plantarflexor weakness [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1789-1795. |
| [7] | Huang Haobo, Liang Xinyuan, Ye Guozhong, Xie Qingxiang, Su Boyuan. Suture tape and headless compression screws in treatment of Lisfranc injury with comminuted fractures of the first and second proximal metatarsal bones [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1803-1809. |
| [8] | Zhang Hao, Wang Qing, Zhang Jian, Li Guangzhou, Wang Gaoju. Comparison of posterior C2-3 fixation combined with bucking bar technique and posterior C2-3 fixation alone in treatment of unstable Hangman fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1848-1854. |
| [9] | Su Lintao, Jiang Jianfeng, Ma Jun, Huang Liangliang, Lei Changyu, Han Yaozheng, Kang Hui. Precise application of O-arm navigation system in thoracolumbar fractures with developmental pedicle stenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1855-1862. |
| [10] | Gao Zhenyang, Zeng Xiuan, Yang Qibing, Kou Xianshuai, Wang Kejing, Li Meng. Computer-simulated repositioning combined with pelvic reduction frame for treatment of anteroposterior compression-III pelvic fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1870-1875. |
| [11] | Jin Jiming, Hao Yangquan, Zhao Rushun, Zhang Yuting, Jiang Yonghong, Xu Peng, Lu Chao. Application of bilateral hip magnetic resonance imaging to predict risk of osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1890-1896. |
| [12] | Sun Xiaojun, Wang Huaming, Zhang Dehong, Song Xuewen, Huang Jin, Zhang Chen, Pei Shengtai. Effect of finite element method in treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1897-1904. |
| [13] | Zhang Haojun, Li Hongyi, Zhang Hui, Chen Haoran, Zhang Lizhong, Geng Jie, Hou Chuandong, Yu Qi, He Peifeng, Jia Jinpeng, Lu Xuechun. Identification and drug sensitivity analysis of key molecular markers in mesenchymal cell-derived osteosarcoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1448-1456. |
| [14] | Lu Jieming, Li Yajing, Du Peijie, Xu Dongqing. Effects of artificial turf versus natural grass on biomechanical performance of the lower limbs in young females during jump-landing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1101-1107. |
| [15] | Li Shuai, Liu Hua, Shang Yonghui, Liu Yicong, Zhao Qihang, Liu Wen. Stress distribution on the maxilla when wearing the Twin-block appliance for Class II malocclusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 881-887. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||