Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (25): 5374-5381.doi: 10.12307/2025.528
Previous Articles Next Articles
Regulation of THZ1, an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase 7, on stemness of glioma stem cells and its mechanism
Hu Enxi1, He Wenying2, Tao Xiang1, Du Peijing1, Wang Libin1, 3
- 1First Clinical Medical College of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; 2Basic Medicine College, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; 3Union Shenzhen Hospital, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2024-05-15Accepted:2024-07-10Online:2025-09-08Published:2024-12-25 -
Contact:Wang Libin, MD, Professor, First Clinical Medical College of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; Union Shenzhen Hospital, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Hu Enxi, Master candidate, First Clinical Medical College of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission Basic Research General Project (Shenzhen Natural Science Foundation), No. JCYJ20230807115807015 (to WLB); National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82260610 (to WLB); Key Project of Ningxia Medical University-Level Education and Teaching Reform Research, No. NYJY2022011 (to WLB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hu Enxi, He Wenying, Tao Xiang, Du Peijing, Wang Libin. Regulation of THZ1, an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase 7, on stemness of glioma stem cells and its mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5374-5381.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
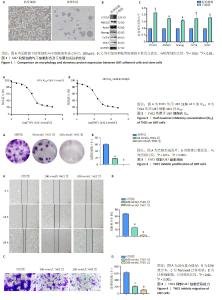
2.1 脑胶质瘤U87干细胞特性验证 脑胶质瘤U87细胞复苏培养贴壁后,显微镜下观察细胞呈典型的星形状、胞体较长,按1 000个/孔接种于超低黏附6孔板并用干细胞培养基进行培养,随着培养时间的延长,干细胞球体逐渐变大,可见遮光性好、中间密度高的干细胞球体,见图1A;将干细胞球体吹散后传代,收集第2代成球细胞进行Western blot验证干性蛋白的表达,结果显示:与贴壁细胞相比,第2代U87干细胞干性蛋白Nestin、CD133、ABCG2、Nanog、OCT4、SOX2表达明显升高,见图1B,C,说明第2代成球细胞具有高表达干性蛋白的特征。 2.2 THZ1作用于U87细胞的IC50 根据预实验结果,设定THZ1浓度梯度为0,10,20,40,80,160,320,640,1 280,2 560 nmol/L,作用时间设为24,48 h,CCK-8结果显示THZ1作用24 h的IC50为159.7 nmol/L,见图2A,作用48 h的IC50为122.8 nmol/L,见图2B,考虑到药物的细胞毒作用,U87干细胞给药浓度为100 nmol/L。 2.3 THZ1抑制U87细胞增殖 CCK-8结果显示,随着THZ1作用浓度增加以及处理时间延长,其减弱U87细胞活力效应越显著。克隆形成实验结果显示,与对照组相比,THZ1浓度为50 nmol/L时,细胞集落数量明显减少,THZ1浓度为100 nmol/L时,细胞未形成集落,见图3A,B;说明THZ1可以抑制U87细胞增殖。 2.4 THZ1减弱U87细胞的迁移能力 细胞划痕愈合实验显示,与对照组相比,THZ1浓度为100,200 nmol/L时,12,24 h划痕愈合率依次下降,说明THZ1减弱U87细胞的水平迁移能力,见图4A,B;Transwell实验显示,随着THZ1作用浓度越高(0,100,200 nmol/L),U87细胞从上室迁移到下室的细胞数越少,说明THZ1减弱U87细胞垂直迁移能力,见图4C,D。"
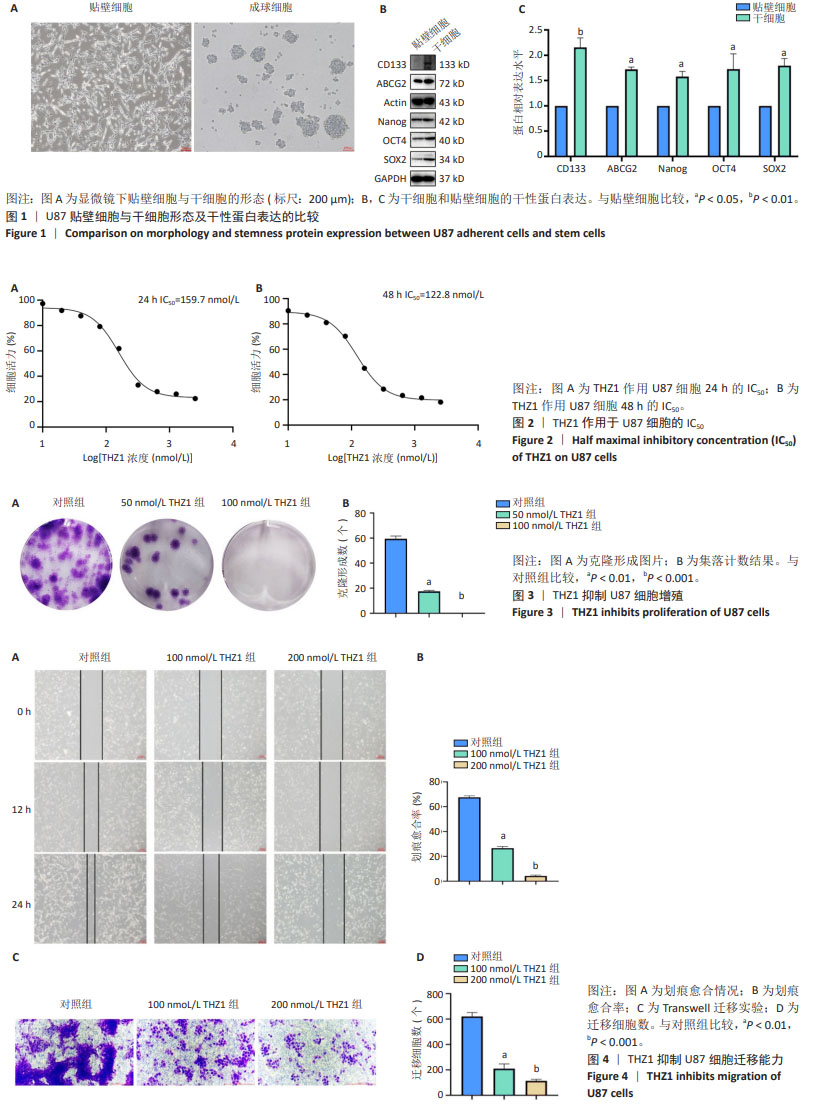
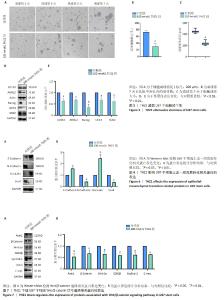
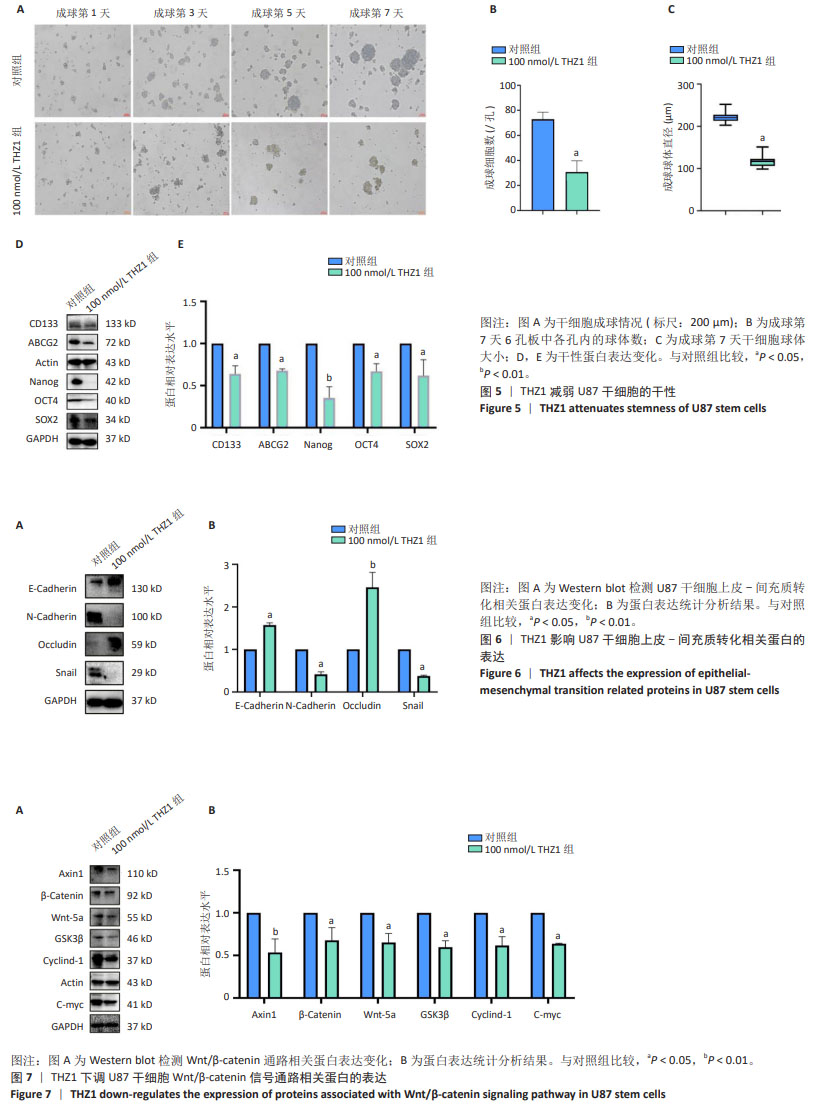
2.5 THZ1减弱U87干细胞的干性 成球实验结果显示,100 nmol/L THZ1处理后,U87干细胞成球率及球体直径都低于对照组,图5A-C;进一步通过Western blot验证干性蛋白表达变化,结果显示THZ1组干性蛋白CD133、ABCG2、Nanog、OCT4、SOX2表达明显低于对照组,见图5D,E。 2.6 THZ1下调U87干细胞上皮-间充质转化相关蛋白的表达 与对照组相比,THZ1处理U87干细胞48 h后上皮-间充质转化相关蛋白表达发生了改变,上皮相关蛋白E-cadherin、Occludin表达升高,而间质相关蛋白N-cadherin、Snail表达下降,见图6A,B,说明THZ1减弱了U87干细胞的上皮-间充质转化能力。 2.7 THZ1下调U87干细胞Wnt/β-catenin信号通路相关蛋白的表达 THZ1组Axin1、β-Catenin、Wnt-5a、GSK3β、Cyclind-1、C-myc的表达都低于对照组,见图7A,B。"
| [1] KLEMM F, MAAS RR, BOWMAN RL, et al. Interrogation of the Microenvironmental Landscape in Brain Tumors Reveals Disease-Specific Alterations of Immune Cells. Cell. 2020;181(7):1643-1660.e17. [2] TAN AC, ASHLEY DM, LÓPEZ GY, et al. Management of glioblastoma: State of the art and future directions. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70(4): 299-312. [3] KARLSSON J, LULY KM, TZENG SY, et al. Nanoparticle designs for delivery of nucleic acid therapeutics as brain cancer therapies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;179:113999. [4] PRASETYANTI PR, MEDEMA JP. Intra-tumor heterogeneity from a cancer stem cell perspective. Mol Cancer. 2017;16(1):41. [5] LI D, WANG L, JIANG B, et al. Improving cancer immunotherapy by preventing cancer stem cell and immune cell linking in the tumor microenvironment. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;170:116043. [6] SHEN Q, HILL T, CAI X, et al. Physical confinement during cancer cell migration triggers therapeutic resistance and cancer stem cell-like behavior. Cancer Lett. 2021;506:142-151. [7] TSAI YT, WU AC, YANG WB, et al. ANGPTL4 Induces TMZ Resistance of Glioblastoma by Promoting Cancer Stemness Enrichment via the EGFR/AKT/4E-BP1 Cascade. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(22):5625. [8] LAMBERT AW, WEINBERG RA. Linking EMT programmes to normal and neoplastic epithelial stem cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 2021;21(5):325-338. [9] HE P, DAI Q, WU X. New insight in urological cancer therapy: From epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) to application of nano-biomaterials. Environ Res. 2023;229:115672. [10] RAMESH V, BRABLETZ T, CEPPI P. Targeting EMT in Cancer with Repurposed Metabolic Inhibitors. Trends Cancer. 2020;6(11):942-950. [11] NUSSE R, CLEVERS H. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling, Disease, and Emerging Therapeutic Modalities. Cell. 2017;169(6):985-999. [12] NAJAFI M, FARHOOD B, MORTEZAEE K. Cancer stem cells (CSCs) in cancer progression and therapy. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(6):8381-8395. [13] LI Q, LAI Q, HE C, et al. RUNX1 promotes tumour metastasis by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway and EMT in colorectal cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38(1):334. [14] SUN J, ZHANG Q, SUN X, et al. THZ1 targeting CDK7 suppresses c-KIT transcriptional activity in gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Cell Commun Signal. 2022;20(1):138. [15] CHOW PM, CHANG YW, KUO KL, et al. CDK7 inhibition by THZ1 suppresses cancer stemness in both chemonaïve and chemoresistant urothelial carcinoma via the hedgehog signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 2021;507:70-79. [16] ATTIA YM, SALAMA SA, SHOUMAN SA, et al. Targeting CDK7 reverses tamoxifen resistance through regulating stemness in ER+ breast cancer. Pharmacol Rep. 2022;74(2):366-378. [17] HORBINSKI C, BERGER T, PACKER RJ, et al. Clinical implications of the 2021 edition of the WHO classification of central nervous system tumours. Nat Rev Neurol. 2022;18(9):515-529. [18] BARTHEL L, HADAMITZKY M, DAMMANN P, et al. Glioma: molecular signature and crossroads with tumor microenvironment. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2022;41(1):53-75. [19] CAYROL F, PRADITSUKTAVORN P, FERNANDO TM, et al. THZ1 targeting CDK7 suppresses STAT transcriptional activity and sensitizes T-cell lymphomas to BCL2 inhibitors. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14290. [20] CHEN HD, HUANG CS, XU QC, et al. Therapeutic Targeting of CDK7 Suppresses Tumor Progression in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(7):1207-1217. [21] TANG L, JIN J, XU K, et al. SOX9 interacts with FOXC1 to activate MYC and regulate CDK7 inhibitor sensitivity in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncogenesis. 2020;9(5):47. [22] CHENG ZJ, MIAO DL, SU QY, et al. THZ1 suppresses human non-small-cell lung cancer cells in vitro through interference with cancer metabolism. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019;40(6):814-822. [23] ABUDUREHEMAN T, XIA J, LI MH, et al. CDK7 Inhibitor THZ1 Induces the Cell Apoptosis of B-Cell Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia by Perturbing Cellular Metabolism. Front Oncol. 2021;11:663360. [24] HUANG T, DING X, XU G, et al. CDK7 inhibitor THZ1 inhibits MCL1 synthesis and drives cholangiocarcinoma apoptosis in combination with BCL2/BCL-XL inhibitor ABT-263. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(8):602. [25] ZHANG T, LI J, YANG M, et al. CDK7/GRP78 signaling axis contributes to tumor growth and metastasis in osteosarcoma. Oncogene. 2022; 41(40):4524-4536. [26] XIA L, ZHENG Z, LIU JY, et al. Targeting Triple-Negative Breast Cancer with Combination Therapy of EGFR CAR T Cells and CDK7 Inhibition. Cancer Immunol Res. 2021;9(6):707-722. [27] HUANG T, SONG X, XU D, et al. Stem cell programs in cancer initiation, progression, and therapy resistance. Theranostics. 2020;10(19): 8721-8743. [28] SUVÀ ML, TIROSH I. The Glioma Stem Cell Model in the Era of Single-Cell Genomics. Cancer Cell. 2020;37(5):630-636. [29] BOYD NH, TRAN AN, BERNSTOCK JD, et al. Glioma stem cells and their roles within the hypoxic tumor microenvironment. Theranostics. 2021;11(2):665-683. [30] CHEN X, NIU W, FAN X, et al. Oct4A palmitoylation modulates tumorigenicity and stemness in human glioblastoma cells. Neuro Oncol. 2023;25(1):82-96. [31] AKHMETKALIYEV A, ALIBRAHIM N, SHAFIEE D, et al. EMT/MET plasticity in cancer and Go-or-Grow decisions in quiescence: the two sides of the same coin? Mol Cancer. 2023;22(1):90. [32] LAMBERT AW, FIORE C, CHUTAKE Y, et al. ΔNp63/p73 drive metastatic colonization by controlling a regenerative epithelial stem cell program in quasi-mesenchymal cancer stem cells. Dev Cell. 2022;57(24): 2714-2730.e8. [33] BAI X, NI J, BERETOV J, et al. Cancer stem cell in breast cancer therapeutic resistance. Cancer Treat Rev. 2018;69:152-163. [34] MCCABE EM, RASMUSSEN TP. lncRNA involvement in cancer stem cell function and epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021;75:38-48. [35] BABU D, MUDIRAJ A, YADAV N, et al. Rabeprazole has efficacy per se and reduces resistance to temozolomide in glioma via EMT inhibition. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2021;44(4):889-905. [36] ZHANG J, CAI H, SUN L, et al. LGR5, a novel functional glioma stem cell marker, promotes EMT by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and predicts poor survival of glioma patients. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37(1):225. [37] LIU J, XIAO Q, XIAO J, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signalling: function, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):3. [38] YU F, YU C, LI F, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling in cancers and targeted therapies. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):307. [39] WEI B, CAO J, TIAN JH, et al. Mortalin maintains breast cancer stem cells stemness via activation of Wnt/GSK3β/β-catenin signaling pathway. Am J Cancer Res. 2021;11(6):2696-2716. [40] GRINAT J, HEUBERGER J, VIDAL RO, et al. The epigenetic regulator Mll1 is required for Wnt-driven intestinal tumorigenesis and cancer stemness. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):6422. [41] YIN J, DING F, CHENG Z, et al. METTL3-mediated m6A modification of LINC00839 maintains glioma stem cells and radiation resistance by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(7):417. |
| [1] | Li Jun, Gong Jingjing, Sun Guobin, Guo Rui, Ding Yang, Qiang Lijuan, Zhang Xiaoli, Fang Zhanhai . miR-27a-3p promotes the proliferation of human hypertrophic scar fibroblasts by regulating mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1609-1617. |
| [2] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [3] | Hu Taotao, Liu Bing, Chen Cheng, Yin Zongyin, Kan Daohong, Ni Jie, Ye Lingxiao, Zheng Xiangbing, Yan Min, Zou Yong. Human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing neuregulin-1 promote skin wound healing in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1343-1349. |
| [4] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [5] | Liu Qi, Li Linzhen, Li Yusheng, Jiao Hongzhuo, Yang Cheng, Zhang Juntao. Icariin-containing serum promotes chondrocyte proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of stem cells in the co-culture system of three kinds of cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
| [6] | Huang Ting, Zheng Xiaohan, Zhong Yuanji, Wei Yanzhao, Wei Xufang, Cao Xudong, Feng Xiaoli, Zhao Zhenqiang. Effects of macrophage migration inhibitory factor on survival, proliferation, and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1380-1387. |
| [7] | Chi Wenxin, Zhang Cunxin, Gao Kai, Lyu Chaoliang, Zhang Kefeng. Mechanism by which nobiletin inhibits inflammatory response of BV2 microglia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1321-1327. |
| [8] | Lang Mecuo, Zhang Yilin, Wang Li. MiR-338-3p affects proliferation and apoptosis of alveolar bone osteoblasts by targeting receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 899-907. |
| [9] | Niu Yongkang, Feng Zhiwei, Wang Yaobin, Liu Zhongcheng, Xiang Dejian, Liang Xiaoyuan, Yi Zhi, Zhan Hongwei, Geng Bin, Xia Yayi. Resveratrol activates extracellular-regulated protein kinase 5 signaling protein to promote proliferation of mouse MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 908-916. |
| [10] | Shi Tongtong, Deng Rongxia, Zhang Jianguang. Differences in physicochemical properties and collagen secretion stimulation of natural and synthetic hydroxyapatite particles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7278-7285. |
| [11] | Yin Hang, Song Kui. Effect of crocin hydrogel on chondrocytes and MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7293-7300. |
| [12] | Shao Xuekun, Shi Dianhua, Ding Zhiping, Qiu Zhuoya, Wang Ping, Wang Yi, Wang Cheng, Ding Xiaoyan, Sun Tiefeng. Calcined deer antler slices promote proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6601-6608. |
| [13] | Lin Shuqian, Zhao Xilong, Gao Jing, Pan Xinghua, Li Zian, Ruan Guangping. Comparison of biological characteristics of mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells after interference and overexpression of telomere Cajal body protein-1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6616-6624. |
| [14] | Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Liu Weipeng, Yang Hui, Luan Zuo, Qu Suqing. Effect of fibronectin on differentiation of human neural stem cells into oligodendrocyte precursor cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6661-6666. |
| [15] | Kang Linzhi, Liu Zhenshuai, Wei Jiaxu, Chang Na, Zhu Dacheng. Inhibitory effects of sinomenine hydrochloride in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia CEM cells and transcriptomic analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6674-6680. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||