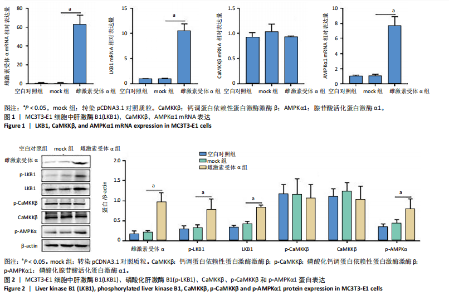
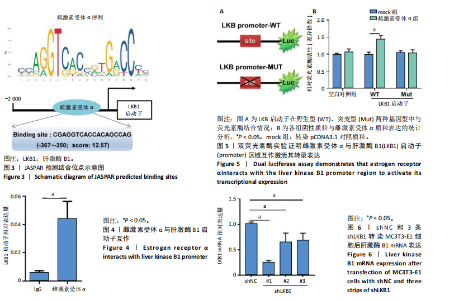
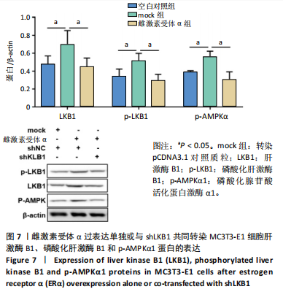
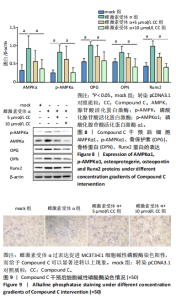
[1] XU SJ, SHAO M, WANG Q, et al. Ecdysterone promotes osteoblast differentiation through ERα mediated AMPK α signal inhibition and β-catenin signal activation. Nanosci Nanotechnol Lett. 2017;9(9):1419-1426.
[2] 徐绍俊, 黄建烽, 邵敏, 等. 补肾方剂对绝经后骨质疏松症大鼠的影响及其作用机制研究[J]. 中药新药与临床药理,2017,28(5):588-593.
[3] 姜涛. 基于 ERα/AMPK/Sirt1信号通路探讨PMOP的发病机制及淫羊藿苷的干预[D]. 广州:广州中医药大学,2020.
[4] 姜涛, 邵敏, 陈庆真, 等. ERα-AMPK-Sirt1 信号通路在骨质疏松症中的作用[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(8):1166-1171.
[5] 柳振华, 李庆国. 骨代谢实验室诊断进展[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2011,8(4):463-466.
[6] QUE Y, YANG Y, ZAFAR H, et al. Tetracycline-grafted mPEG-PLGA micelles for bone-targeting and osteoporotic improvement. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:993095.
[7] 薛瑶珺, 周广文, 朱伟, 等. 从自噬角度探讨肾虚痰浊型绝经后骨质疏松症的发病[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志,2023,32(17):2398-2403.
[8] 易生辉, 招文华, 任辉, 等. 中西医治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的研究进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2022,28(5):274-282.
[9] 叶维建, 李国山, 黄建芳. 甲状旁腺激素对绝经后骨质疏松大鼠骨密度和骨生物力学的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2022,42(8):1991-1994.
[10] 《中国骨质疏松杂志》骨代谢专家组. 骨代谢生化指标临床应用专家共识(2023修订版)[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(4):469-476.
[11] HAN XG, WANG DW, BI ZG, et al. Regulatory effect of estrogen receptor-α-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway on osteoblast proliferation. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2016;30(2):381-387.
[12] 钟建春, 谢兴文, 李鼎鹏, 等. 中药植物雌激素防治绝经后骨质疏松研究概况[J]. 时珍国医国药,2021,32(7):1723-1726.
[13] 张利霞. 骨代谢生化指标测定在中老年骨质疏松症早期诊断中的应用研究[J]. 中国实用医药,2015,10(24):45-46.
[14] KE F, YUKI M, SEIJI K, et al. Unkeito Suppresses RANKL-Mediated Osteoclastogenesis via the Blimp1–Bcl6 and NF-κB Signaling Pathways and Enhancing Osteoclast Apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(14):7814.
[15] 沈国蔚, 成心锟, 颜世昌, 等. CFTR在雌激素诱导破骨细胞凋亡中的作用机制研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2018,33(11):1150-1152.
[16] TROUVIN A, GOËB V. Receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand and osteoprotegerin: maintaining the balance to prevent bone loss. Clin Interv Aging. 2010;5:345-354.
[17] 李伟娟, 谢保平, 石丽颖, 等. 从 ERα/RANK 通路探讨淫羊藿苷抑制破骨细胞分化作用[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2017,23(7):121-126.
[18] MARTIN-MILLAN M, ALMEIDA M, AMBROGINI E, et al. The estrogen receptor-α in osteoclasts mediates the protective effects of estrogens on cancellous but not cortical bone. Mol Endocrinol. 2010;24(2):323-334.
[19] 陈庆真. 补肾中药调控ERα-AMPK-Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路促进成骨细胞增殖、分化的研究[D]. 广州:广州中医药大学,2020.
[20] FUJII T, MURATA K, MUN S H, et al. MEF2C regulates osteoclastogenesis and pathologic bone resorption via c-FOS. Bone Res. 2021;9(1):4.
[21] LIU Z, LEE HL, SUH JS, et al. The ERalpha/KDM6B regulatory axis modulates osteogenic differentiation in human mesenchymal stem cells. Bone Res. 2022;10(1):3.
[22] LIU C, ZHANG W, GAO M, et al. A Degradable and Osteogenic Mg-Based MAO-MT-PLGA Drug/Ion Delivery System for Treating an Osteoporotic Fracture. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(7):1481.
[23] 齐艳喆, 王姿, 欧阳厚淦, 等. 中药调控p38 MAPK、ERK1/2、JNK等治疗骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2023, 29(12):222-229.
[24] 王镜勋, 张方晴, 李如灿, 等. 基于网络药理学、分子对接和实验验证的补骨脂效应成分及其抗骨质疏松作用机制探讨[J]. 中国现代中药,2024,26(4):653-664.
[25] 邵家豪, 李超, 张贤.骨质疏松中的自噬相关信号通路[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2021,27(12):1863-1867.
[26] 冯玉, 冯南, 郭义锦, 等. 西红花苷通过LKB1/AMPK/mTOR通路抑制食管癌细胞的增殖、凋亡和侵袭[J]. 解剖学研究,2023,45(5): 447-453.
[27] MCCARTHY AD, CORTIZO AM, SEDLINSKY C. Metformin revisited: Does this regulator of AMP-activated protein kinase secondarily affect bone metabolism and prevent diabetic osteopathy. World J Diabetes. 2016;7(6):122.
[28] BROWN KA, MCINNES KJ, TAKAGI K, et al. LKB1 expression is inhibited by estradiol-17β in MCF-7 cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2011;127(3-5):439-443.
[29] FERRON M, WEI J, YOSHIZAWA T, et al. Insulin signaling in osteoblasts integrates bone remodeling and energy metabolism. Cell. 2010;142(2): 296-308.
[30] FULZELE K, RIDDLE RC, DIGIROLAMO DJ, et al. Erratum: Insulin Receptor Signaling in Osteoblasts Regulates Postnatal Bone Acquisition and Body Composition. Cell. 2022;185(4):746.
|