Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (23): 5031-5040.doi: 10.12307/2025.507
Previous Articles Next Articles
Immunomodulatory effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on type 2 diabetes mellitus
Chen Chunlan1, Ye Meiyi1, Pan Yuwei2, Yuan Jia3, Zhou Pengjun1, 4
- 1Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Preventive Healthcare, Affiliated TCM Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510130, Guangdong Province, China; 3Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Foshan 528200, Guangdong Province, China; 4Biomedical Base, College of Life Science and Technology, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2024-03-27Accepted:2024-06-03Online:2025-08-18Published:2024-09-30 -
Contact:Zhou Pengjun, Lecturer, Master’s supervisor, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China; Biomedical Base, College of Life Science and Technology, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, Guangdong Province, China; Co-corresponding author: Yuan Jia, Chief physician, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Foshan 528200, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Chen Chunlan, Master candidate, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Guangzhou Basic and Applied Basic General Project, No. 2023A04J1143 (to ZPJ); Guangdong Province Key Discipline of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Clinical) Construction Project, No. [2021]129 (to YJ); Foshan City “14th Five-Year Plan” Medical High-level Key Specialized Construction Project, No. FSGSP145086 (to YJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Chunlan, Ye Meiyi, Pan Yuwei, Yuan Jia, Zhou Pengjun. Immunomodulatory effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 5031-5040.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

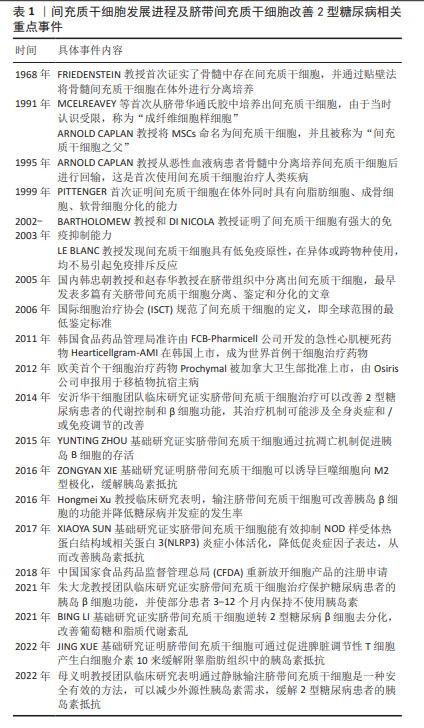
2.1 2型糖尿病的发病机制 2型糖尿病是一种以全身低度炎症为特征的慢性代谢性疾病,其发病机制与炎症反应、氧化应激、胰岛淀粉样变性、内质网应激、肌肉与肝脏及胰腺部位异位脂肪沉积、脂毒性以及糖毒性等引起的胰岛素抵抗及胰岛β细胞功能障碍密切相关,研究显示免疫细胞浸润、炎症反应等是导致胰岛素抵抗及胰岛β细胞功能障碍的主要诱因[18]。 胰岛β细胞是胰腺中产生和释放胰岛素的细胞,机体持续高血糖和胰岛素合成异常将引起胰岛β细胞耗竭,同时免疫环境损伤将导致胰岛β细胞丢失,这使得胰岛素分泌不足并使靶器官对胰岛素敏感性降低,机体出现葡萄糖耐量受损,最终导致显性高血糖和2型糖尿病的发生[19]。胰岛素抵抗是一种复杂的病理生理学状态,其特点是靶器官对胰岛素敏感性及利用率降低,机体不能有效地促进骨骼肌、心肌及脂肪组织摄取葡萄糖和抑制肝脏的糖原分解及糖异生[20],从而加速胰岛β细胞功能衰竭,导致糖尿病的发生。 在胰岛β细胞受损和胰岛素抵抗过程中,免疫细胞数量、比例、浸润、炎症因子释放因素发挥至关重要的作用。脂肪组织包含大多数类型的免疫细胞,在肥胖条件下,脂肪组织中促炎免疫细胞的激活和浸润形成复杂的炎症和胰岛素抵抗交互网络,包括巨噬细胞、中性粒细胞、嗜酸性粒细胞、肥大细胞、NK细胞、MAIT细胞、CD4+T细胞、CD8+T细胞、Treg细胞和B细胞以及促炎性细胞因子高水平状态[21],其中,巨噬细胞在胰岛素抵抗中的募集、积聚和激活可促使慢性低度炎症的形成[22]。 巨噬细胞是一种广泛分布于全身血液和组织的免疫细胞,具有异质性和可塑性[23],其表型和功能受特定组织微环境刺激和信号的调节[24],巨噬细胞可分为经典激活的促炎M1型巨噬细胞和交替激活的抗炎M2型巨噬细胞,M1/M2巨噬细胞的平衡决定着器官在炎症中的损伤程度[25]。研究发现,正常胰岛的巨噬细胞表现出M2表型,而在2型糖尿病胰岛中巨噬细胞浸润程度增加并且巨噬细胞极化为M1表型[26-27],M1型巨噬细胞可引起促炎细胞因子大量分泌,如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6等,从而促进炎症发展并导致胰岛素抵抗及胰岛β细胞功能障碍[28]。而选择性激活的M2型巨噬细胞可通过限制适应性免疫激活和抗炎作用拮抗M1型巨噬细胞的促炎作用,在胰岛β细胞保护、修复和再生过程中发挥重要作用[29]。 2.2 2型糖尿病的一般治疗策略 目前针对2型糖尿病的治疗策略主要包括饮食调整、运动治疗、药物治疗及胰岛移植等[30]。饮食管理是糖尿病治疗的基础,包括有效的饮食控制、限制摄取糖分和糖类物质、食物的合理搭配、控制总热量摄取量等[31]。运动疗法被广泛应用于降低血糖水平及提升身体代谢能力等方面,运动对于降低血糖水平具有积极作用[32]。适度的有氧运动可以促进肌肉对葡萄糖的吸收和利用,从而有助于调节血液中的葡萄糖含量。此外,长期坚持运动还可提高胰岛素敏感性,使机体更有效地利用胰岛素控制血糖水平[33]。药物治疗有胰岛素增敏药、促胰岛素分泌药、肠促胰岛素增强药、钠-葡萄糖共转运蛋白2抑制药、双胍类降糖药、α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制药和外源性胰岛素供给等[34]。胰岛素增敏药即噻唑烷二酮类降糖药物,能增强胰岛素敏感性,促进胰岛素充分利用,改善糖代谢[35];磺脲类和格列奈类药物都属于促胰岛素分泌药,其降糖机制主要是通过刺激胰岛β细胞分泌胰岛素,增加体内的胰岛素水平而降低血糖,对有一定胰岛功能的患者疗效较好[36];肠促胰岛素增强药如二肽基肽酶4抑制剂和胰高血糖素样肽1受体激动剂能够增强肠促胰岛素水平[37];钠-葡萄糖共转运蛋白2抑制药可抑制肾脏对葡萄糖的重吸收,使过量的葡萄糖从尿液中排出,降低血糖[38];双胍类降糖药抑制肝糖原异生,减少葡萄糖的来源,增强组织对葡萄糖的摄取和利用,增强胰岛素敏感性,抑制胰高血糖素的释放[39];α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制药可逆性地抑制小肠黏膜上的α-葡萄糖苷酶,延缓碳水化合物分解为葡萄糖的速度[40];对于2型晚期胰岛功能显著衰退类型患者,可通过胰岛移植改善2型糖尿病进展。 2.3 UC-MSCs在2型糖尿病中的作用 近年来,随着基础与应用基础研究的深入,发现注射UC-MSCs可有效改善2型糖尿病高血糖症状、降低炎症活性、改善胰岛β细胞功能、缓解胰岛素抵抗进而延缓2型糖尿病的进展[41-42];同时,研究表明同种异体UC-MSCs移植是一种安全的2型糖尿病治疗策略[43-44]。表1为间充质干细胞发展进程及UC-MSCs改善2型糖尿病相关重点事件。在一项单中心、双盲、随机、安慰剂对照的试验中,ZANG等[43]将91例患者随机分配为UC-MSCs治疗组(n=45)及安慰剂组(n=46),UC-MSCs组每4周静脉输注1次,每次输注总数为1×106/kg,输注3次,在第48周时,UC-MSCs组有20%的患者达到了糖化血红蛋白水平 < 7.0%和每日所需胰岛素减少 ≥ 50%的治疗效果,而安慰剂组只有4.55%的患者达到该效果(P < 0.05)。此外,与安慰剂组相比,UC-MSCs组每日所需胰岛素减少百分比显著增加(27.78% vs. 15.62%,P < 0.05),UC-MSCs移植后患者糖化血红蛋白水平明显下降,并且在治疗期间未发生任何相关重大不良事件,这项研究结果表明UC-MSCs移植治疗2型糖尿病在有效性和安全性方面具备优势。LIAN等[45]招募34例2型糖尿病患者随机分为UC-MSCs治疗组24例及安慰剂组10例,UC-MSCs组每周静脉注射1次,每次输注总数为1×106/kg,输注3次,结果显示UC-MSCs移植治疗2型糖尿病具有良好的耐受性和较高的安全性,为UC-MSCs作为一种2型糖尿病新型治疗技术的未来临床应用奠定了一定的基础。"
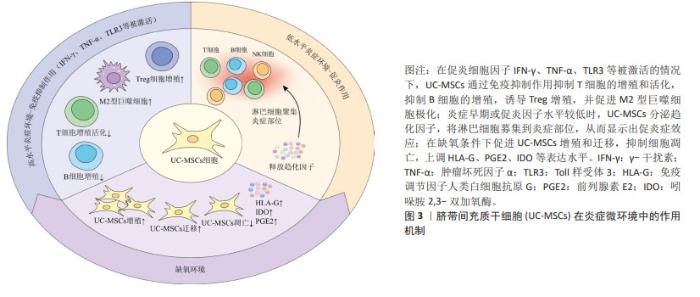
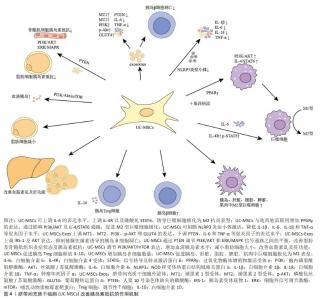
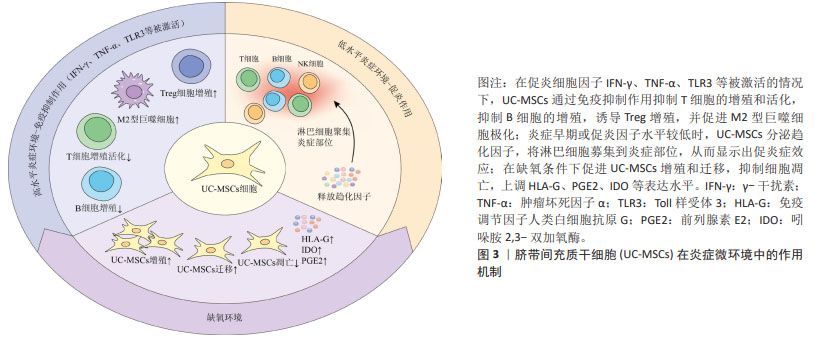
基础研究表明,UC-MSCs可以调节先天性和适应性免疫系统中各种免疫细胞的活化和功能,并广泛应用于治疗各种免疫介导的炎症性疾病[46]。UC-MSCs的免疫调节能力取决于其所暴露的炎症环境,在促炎细胞因子如γ干扰素和肿瘤坏死因子α高表达或Toll样受体3被配体激活的情况下[47],UC-MSCs会发生免疫抑制作用,可抑制T细胞的增殖和活化,抑制受刺激B细胞的增殖,诱导Treg的增殖,促进巨噬细胞向抗炎M2表型的极化。另一方面,在炎症细胞因子水平较低或炎症早期阶段,UC-MSCs通过分泌趋化因子,将淋巴细胞募集到炎症部位,从而显示出促炎症效应[48]。除了炎症刺激外,UC-MSCs的免疫调节还会受到缺氧因素的影响,事实上,缺氧是病理炎症组织微环境的典型特征,病理性缺氧可以通过免疫细胞失调驱动组织功能障碍和疾病发展,对炎症过程产生深远影响[49]。UC-MSCs在缺氧条件下会促进细胞增殖和迁移,增强免疫调节因子人类白细胞抗原G、前列腺素E2和吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶表达,同时抑制细胞凋亡[50]。综上,免疫调节在UC-MSCs治疗2型糖尿病中发挥着重要作用,为疾病治疗机制提供新的见解。图3为UC-MSCs在炎症中的作用机制。"
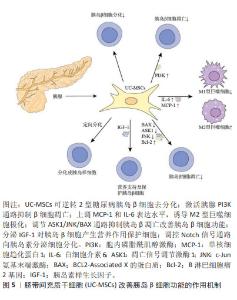
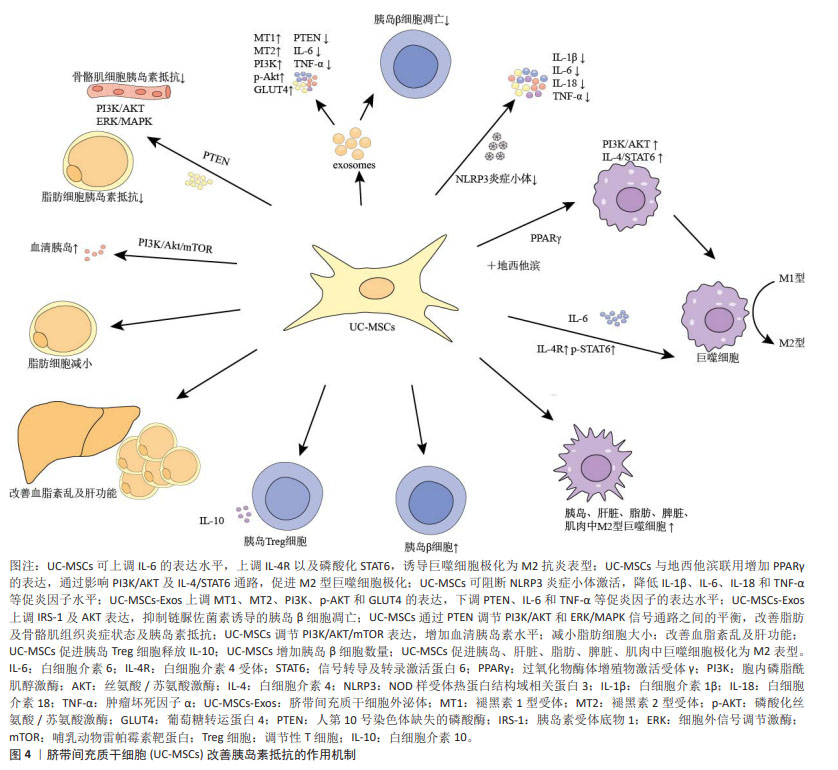
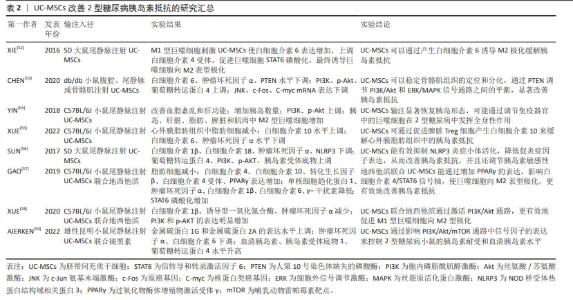
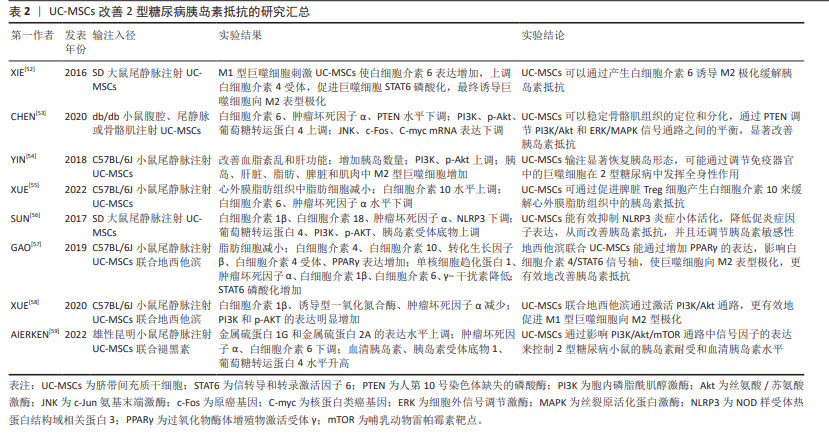
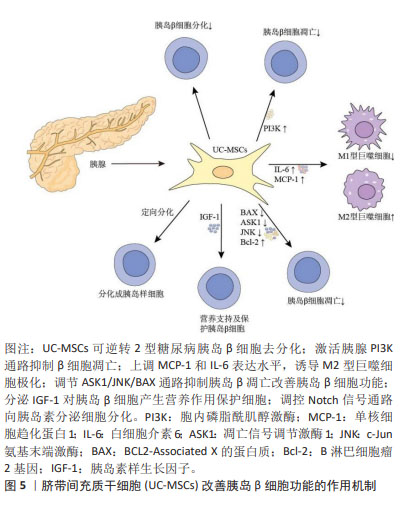
目前研究发现UC-MSCs可通过免疫调节作用释放可溶性因子,降低2型糖尿病患者体内的炎症反应,改善靶器官胰岛素抵抗。可溶性因子(如细胞因子)是巨噬细胞与其靶细胞串联过程中最具特征性的信号分子,细胞因子和趋化因子可与特定细胞表面受体结合并激活细胞内相关信号通路的蛋白。细胞因子具有自分泌或旁分泌效应,巨噬细胞会根据其活化状态产生不同的细胞因子[60]。白细胞介素6是一种与肥胖和胰岛素抵抗有关的促炎细胞因子[61],但由于免疫系统的复杂性,白细胞介素6被认为是UC-MSCs在巨噬细胞极化过程中的一个重要因子,可促进巨噬细胞向M2型极化,抑制肝脏的过度炎症,在预防肥胖相关的胰岛素抵抗中起到了有益的作用[62-63]。XIE等[52]发现UC-MSCs输注可通过增加2型糖尿病大鼠白细胞介素6的表达水平,上调白细胞介素4受体的表达,促进巨噬细胞中STAT6的磷酸化,将脂肪组织巨噬细胞极化为M2抗炎表型;此外CHEN等[53]选择db/db小鼠作为研究对象,发现UC-MSCs能够降低外周血中肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6水平,并且通过PTEN调节PI3K/Akt和Erk/MAPK信号通路之间的平衡,显著降低骨骼肌组织及脂肪组织的炎症反应,改善胰岛素抵抗。YIN等[54]研究还发现UC-MSCs可增加2型糖尿病小鼠胰岛、肝脏、脾脏和肌肉中M2型巨噬细胞数量。白细胞介素10被认为是一种强效抗炎细胞因子,能够诱导巨噬细胞极化为M2表型[64],多项研究证实,肥胖会导致全身白细胞介素10水平下降[65],而多次UC-MSCs输注可增加胰岛素抵抗肥胖小鼠模型脾脏中Treg细胞分泌白细胞介素10[55],也可促进巨噬细胞极化为M2表型,从而缓解胰岛素抵抗,增加靶器官对胰岛素的敏感性。此外,NLRP3炎症小体在2型糖尿病和胰岛素抵抗的发病机制中尤为重要,慢性炎症与葡萄糖代谢异常激活和NLRP3炎症小体活化密切相关[66]。慢性高血糖小鼠的胰岛细胞受到细胞外高浓度血糖的刺激,激活NLRP3炎症小体,诱导白细胞介素1β生成和分泌,从而引起胰岛素抵抗[67-68]。SUN等[56]研究进一步发现通过2型糖尿病大鼠尾静脉注射UC-MSCs可阻断NLRP3炎症小体激活,降低白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素18和肿瘤坏死因子α等炎性细胞因子水平,产生抗炎作用,有效缓解棕榈酸和脂多糖诱导的胰岛素抵抗,进而改善2型糖尿病大鼠的高血糖状态。UC-MSCs还可通过增加小鼠肝脏中LC3Ⅱ/Ⅰ水平,增强肝脏自噬作用,改善胰岛素抵抗[69]。 同时,一系列与UC-MSCs相关的联合治疗策略不断被报道,GAO等[57]通过联合使用UC-MSCs与地西他滨治疗2型糖尿病小鼠,发现地西他滨可延长UC-MSCs在体内的作用时间,促进过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ的表达,更有效地维持2型糖尿病小鼠巨噬细胞极化为M2表型的作用。同时,UC-MSCs与低剂量地西他滨联合治疗,通过增强PI3K/AKT通路促进M1型巨噬细胞极化为M2表型,从而降低组织炎症反应,并延长UC-MSCs的抗糖尿病作用,更有效地缓解2型糖尿病小鼠的胰岛素抵抗[58]。AIERKEN等[59]研究发现,褪黑素能有效缓解UC-MSCs的衰老,促进UC-MSCs增殖和分化[70-71],褪黑素与UC-MSCs联合治疗亦可通过激活PI3K/AKT信号通路,上调金属硫蛋白1G和金属硫蛋白2A的表达,下调胰岛细胞中肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6的表达,达到改善2型糖尿病小鼠胰岛素抵抗的效果。 UC-MSCs分泌的外泌体(UC-MSCs-Exos)是直径30-200 nm的小囊泡,作为关键的旁分泌效应物之一,UC-MSCs-Exos可通过携带来自亲本细胞的生物活性物质在细胞间通讯中发挥重要作用[72]。最近研究发现UC-MSCs-Exos对参与先天性和适应性免疫反应的不同效应细胞具有明显的抑制作用,可通过调节免疫作用改善2型糖尿病胰岛素抵抗[73-74]。CHEN等[75]将UC-MSCs-Exos作用于胰岛素抵抗脂肪细胞模型,发现UC-MSCs-Exos可通过上调脂联素和Sirtuin-1(SIRT1)的表达、下调瘦素(Leptin)、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α等促炎因子的表达水平,增强慢性炎症和高血糖损伤脂肪细胞的胰岛素敏感性。此外,SUN等[76]研究表明给2型糖尿病大鼠静脉注射UC-MSCs-Exos可抑制链脲佐菌素诱导的胰岛β细胞凋亡,上调胰岛素受体底物1、蛋白激酶B表达并增强下游信号通路的激活,降低2型糖尿病大鼠血清中促炎细胞因子肿瘤坏死因子α的表达,提示UC-MSCs-Exos可通过调节炎症因子的分泌来减轻2型糖尿病大鼠炎症反应与胰岛素抵抗。 总之,在2型糖尿病中炎症状态与胰岛素抵抗关系密切[77-78]。UC-MSCs具有改善系统性炎症和恢复免疫微环境稳态的强大能力,它们能够逆转2型糖尿病引起的促炎因子的表达并促进表皮生长因子和白细胞介素10的释放,抑制NLRP3炎症小体激活,促进巨噬细胞向M2型极化,改善组织炎症反应。促炎递质减少和抗炎细胞因子升高的现象可能代表着免疫功能正常化到平衡状态,从而减少全身炎症反应,减轻靶器官的胰岛素抵抗,改善2型糖尿病的进展。 2.3.2 UC-MSCs改善胰岛β细胞功能 进行性胰岛β细胞功能障碍是2型糖尿病的另一个主要特征,且同样与胰岛内M1型巨噬细胞的浸润密切相关[79]。图5为UC-MSCs改善胰岛β细胞功能的作用机制,表3为UC-MSCs改善2型糖尿病胰岛β细胞功能的研究汇总[80-84]。"
| [1] NCD COUNTDOWN 2030 COLLABORATORS. NCD Countdown 2030: worldwide trends in non-communicable disease mortality and progress towards Sustainable Development Goal target 3.4. Lancet. 2018;392(10152):1072-1088. [2] SUN H, SAEEDI P, KARURANGA S, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, Regional and Country-Level Diabetes Prevalence Estimates for 2021 and Projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;183:109119. [3] CHATTERJEE S, KHUNTI K, DAVIES MJ. Type 2 Diabetes. Lancet. 2017; 389(10085):2239-2251. [4] MAJETY P, LOZADA ORQUERA FA, EDEM D, et al. Pharmacological Approaches to the Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1118848. [5] SIVAKUMAR PM, PRABHAWATHI V, ZARRABI A, et al. Current Trends in the Therapeutic Strategies for Diabetes Management. Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(23):4616-4637. [6] MARRANO N, BIONDI G, CIGNARELLI A, et al. Functional Loss of Pancreatic Islets in Type 2 Diabetes: How Can We Halt It? Metabolism. 2020;110:154304. [7] 阮光萍,姚翔,刘高米洋,等.脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗树鼩创伤性全身炎症反应综合征[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(25): 3994-4000. [8] EBRAHIMI F, PIROUZMAND F, COSME PECHO RD, et al. Application of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Regenerative Medicine: A New Approach in Modern Medical Science. Biotechnol Prog. 2023;39(6):e3374. [9] LU LL, LIU YJ, YANG SG, et al. Isolation and Characterization of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Hematopoiesis-Supportive Function and Other Potentials. Haematologica. 2006;91(8): 1017-1026. [10] JIN HJ, BAE YK, KIM M, et al. Comparative Analysis of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Bone Marrow, Adipose Tissue, and Umbilical Cord Blood as Sources of Cell Therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2013; 14(9):17986-18001. [11] WEISS ML, MEDICETTY S, BLEDSOE AR, et al. Human Umbilical Cord Matrix Stem Cells: Preliminary Characterization and Effect of Transplantation in a Rodent Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Stem Cells. 2006;24(3):781-792. [12] PITTENGER MF, MACKAY AM, BECK SC, et al. Multilineage Potential of Adult Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Science. 1999;284(5411): 143-147. [13] FRASER JK, WULUR I, ALFONSO Z, et al. Fat Tissue: An Underappreciated Source of Stem Cells for Biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 2006; 24(4):150-154. [14] VENKATESAN M, ZHANG N, MARTEAU B, et al. Spatial Subcellular Organelle Networks in Single Cells. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):5374. [15] HORI A, TAKAHASHI A, MIHARU Y, et al. Superior Migration Ability of Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (MSCs) toward Activated Lymphocytes in Comparison with Those of Bone Marrow and Adipose-Derived MSCs. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024;12:1329218. [16] WANG J, YIN YQ, CHENG Y, et al. The Impact of Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on the Pancreatic Function of Type 2 Diabetic Mice and Their Regulatory Role on NLRP3 Inflammasomes. Chin J Intern Med. 2023;62(9):1077-1084. [17] GAO D, JIAO J, WANG Z, et al. The Roles of Cell-Cell and Organ-Organ Crosstalk in the Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Associated Inflammatory Microenvironment. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2022;66:15-25. [18] DARYABOR G, ATASHZAR MR, KABELITZ D, et al. The Effects of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on Organ Metabolism and the Immune System. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1582. [19] RUBIO-NAVARRO A, GOMEZ-BANOY N, STOLL L, et al. A Beta Cell Subset with Enhanced Insulin Secretion and Glucose Metabolism Is Reduced in Type 2 Diabetes. Nat Cell Biol. 2023;25(4):565-578. [20] ZHAO X, AN X, YANG C, et al. The Crucial Role and Mechanism of Insulin Resistance in Metabolic Disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1149239. [21] ASGHAR A, SHEIKH N. Role of Immune Cells in Obesity Induced Low Grade Inflammation and Insulin Resistance. Cell Immunol. 2017;315: 18-26. [22] ROHM TV, MEIER DT, OLEFSKY JM, et al. Inflammation in Obesity, Diabetes, and Related Disorders. Immunity. 2022;55(1):31-55. [23] MOSSER DM, HAMIDZADEH K, GONCALVES R. Macrophages and the Maintenance of Homeostasis. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021;18(3):579-587. [24] BANU S, SUR D. Role of Macrophage in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Macrophage Polarization a New Paradigm for Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2023;23(1):2-11. [25] SHAPOURI-MOGHADDAM A, MOHAMMADIAN S, VAZINI H, et al. Macrophage Plasticity, Polarization, and Function in Health and Disease. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(9):6425-6440. [26] CUENCO J, DALMAS E. Islet Inflammation and Beta Cell Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2022;274:227-251. [27] YING W, FU W, LEE YS, et al. The Role of Macrophages in Obesity-Associated Islet Inflammation and Beta-Cell Abnormalities. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020;16(2):81-90. [28] PENG Y, ZHOU M, YANG H, et al. Regulatory Mechanism of M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization in the Development of Autoimmune Diseases. Mediators Inflamm. 2023;2023:8821610. [29] ARABPOUR M, SAGHAZADEH A, REZAEI N. Anti-Inflammatory and M2 Macrophage Polarization-Promoting Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;97:107823. [30] SU J, LUO Y, HU S, et al. Advances in Research on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Targets and Therapeutic Agents. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(17): 13381. [31] JING T, ZHANG S, BAI M, et al. Effect of Dietary Approaches on Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review with Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials. Nutrients. 2023;15(14):3156. [32] SOO J, RAMAN A, LAWLER NG, et al. The Role of Exercise and Hypoxia on Glucose Transport and Regulation. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2023;123(6): 1147-1165. [33] MAGKOS F, HJORTH MF, ASTRUP A. Diet and Exercise in the Prevention and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020; 16(10):545-555. [34] DAHLEN AD, DASHI G, MASLOV I, et al. Trends in Antidiabetic Drug Discovery: FDA Approved Drugs, New Drugs in Clinical Trials and Global Sales. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:807548. [35] MASTROTOTARO L, RODEN M. Insulin Resistance and Insulin Sensitizing Agents. Metabolism. 2021;125:154892. [36] LV W, WANG X, XU Q, et al. Mechanisms and Characteristics of Sulfonylureas and Glinides. Curr Top Med Chem. 2020;20(1):37-56. [37] GILBERT MP, PRATLEY RE. GLP-1 Analogs and DPP-4 Inhibitors in Type 2 Diabetes Therapy: Review of Head-to-Head Clinical Trials. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11:178. [38] POWELL J, GARLAND SG. Ertugliflozin: A New Option in the SGLT-2 Inhibitor Market for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Ann Pharmacother. 2019;53(5):478-485. [39] GRYTSAI O, MYRGORODSKA I, ROCCHI S, et al. Biguanides Drugs: Past Success Stories and Promising Future for Drug Discovery. Eur J Med Chem. 2021;224:113726. [40] AGRAWAL N, SHARMA M, SINGH S, et al. Recent Advances of Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors: A Comprehensive Review. Curr Top Med Chem. 2022;22(25):2069-2086. [41] 谢田琴,刘建萍.脐带间充质干细胞在糖尿病治疗中的研究进展[J].生命科学,2020,32(8):837-844. [42] SABABATHY M, RAMANATHAN G, ABD RAHAMAN NY, et al. A ‘One Stone, Two Birds’ Approach with Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Type Ii Diabetes Mellitus. Regen Med. 2023;18(12):913-934. [43] ZANG L, LI Y, HAO H, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Chinese Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Single-Center, Double-Blinded, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Phase Ii Trial. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):180. [44] MATHUR A, TAURIN S, ALSHAMMARY S. The Safety and Efficacy of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes- a Literature Review. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023;16:769-777. [45] LIAN XF, LU DH, LIU HL, et al. Safety Evaluation of Human Umbilical Cord-Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treatment: A Phase 2 Clinical Trial. World J Clin Cases. 2023;11(21):5083-5096. [46] 许玲玉,张丰姣,张辉,等.间充质干细胞在成人隐匿性自身免疫性糖尿病患者中免疫抑制作用的研究[J].中国糖尿病杂志,2021, 29(10):763-773. [47] HUANG Y, WU Q, TAM PKH. Immunomodulatory Mechanisms of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Potential Clinical Applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(17):10023. [48] SHI Y, WANG Y, LI Q, et al. Immunoregulatory Mechanisms of Mesenchymal Stem and Stromal Cells in Inflammatory Diseases. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2018;14(8):493-507. [49] SHOBATAKE R, OTA H, TAKAHASHI N, et al. The Impact of Intermittent Hypoxia on Metabolism and Cognition. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(21): 12957. [50] GUPTA S, RAWAT S, KRISHNAKUMAR V, et al. Hypoxia Preconditioning Elicit Differential Response in Tissue-Specific MSCs Via Immunomodulation and Exosomal Secretion. Cell Tissue Res. 2022;388(3):535-548. [51] BI S, NIE Q, WANG WQ, et al. Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Therapy for Insulin Resistance: A Novel Strategy in Clinical Implication. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;13(8):658-664. [52] XIE Z, HAO H, TONG C, et al. Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Elicit Macrophages into an Anti-Inflammatory Phenotype to Alleviate Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetic Rats. Stem Cells. 2016;34(3):627-639. [53] CHEN G, FAN XY, ZHENG XP, et al. Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorate Insulin Resistance Via PTEN-Mediated Crosstalk between the PI3K/Akt and Erk/MAPKs Signaling Pathways in the Skeletal Muscles of Db/Db Mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):401. [54] YIN Y, HAO H, CHENG Y, et al. The Homing of Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and the Subsequent Modulation of Macrophage Polarization in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;60:235-245. [55] XUE J, GAO J, GU Y, et al. Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Insulin Resistance in Diet-Induced Obese Mice Via an Interaction with Splenocytes. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):109. [56] SUN X, HAO H, HAN Q, et al. Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorate Insulin Resistance by Suppressing NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes Rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):241. [57] GAO J, CHENG Y, HAO H, et al. Decitabine Assists Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Improving Glucose Homeostasis by Modulating Macrophage Polarization in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):259. [58] XUE J, CHENG Y, HAO H, et al. Low-Dose Decitabine Assists Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Protecting Cells Via the Modulation of the Macrophage Phenotype in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:4689798. [59] AIERKEN A, LI B, LIU P, et al. Melatonin Treatment Improves Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy in a Mouse Model of Type Ii Diabetes Mellitus Via the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):164. [60] COSENTINO C, REGAZZI R. Crosstalk between Macrophages and Pancreatic Beta-Cells in Islet Development, Homeostasis and Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1765. [61] KAUR S, BANSAL Y, KUMAR R, et al. A Panoramic Review of IL-6: Structure, Pathophysiological Roles and Inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem. 2020;28(5):115327. [62] GURIA S, HOORY A, DAS S, et al. Adipose Tissue Macrophages and Their Role in Obesity-Associated Insulin Resistance: An Overview of the Complex Dynamics at Play. Biosci Rep. 2023;43(3):BSR20220200. [63] JIA Q, MORGAN-BATHKE ME, JENSEN MD. Adipose Tissue Macrophage Burden, Systemic Inflammation, and Insulin Resistance. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2020;319(2):E254-E264. [64] SARAIVA M, VIEIRA P, O’GARRA A. Biology and Therapeutic Potential of Interleukin-10. J Exp Med. 2020;217(1):e20190418. [65] MAN K, KALLIES A, VASANTHAKUMAR A. Resident and Migratory Adipose Immune Cells Control Systemic Metabolism and Thermogenesis. Cell Mol Immunol. 2022;19(3):421-431. [66] QI Y, DU X, YAO X, et al. Vildagliptin Inhibits High Free Fatty Acid (FFA)-Induced NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Endothelial Cells. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47(1):1067-1074. [67] BARRA NG, HENRIKSBO BD, ANHE FF, et al. The NLRP3 Inflammasome Regulates Adipose Tissue Metabolism. Biochem J. 2020;477(6): 1089-1107. [68] LU S, LI Y, QIAN Z, et al. Role of the Inflammasome in Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1052756. [69] 邹俊彦,薛婧,尹雅琪,等.脐带间充质干细胞(UC-MSC)通过增强自噬缓解2型糖尿病小鼠肝脏胰岛素抵抗[J].南开大学学报(自然科学版),2021,54(1):30-34. [70] LI B, CHENG X, AIERKEN A, et al. Melatonin Promotes the Therapeutic Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by Regulating TGF-Beta Pathway. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:722365. [71] FANG J, YAN Y, TENG X, et al. Melatonin Prevents Senescence of Canine Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells through Activating NRF2 and Inhibiting ER Stress. Aging (Albany NY). 2018;10(10):2954-2972. [72] SHEN Z, HUANG W, LIU J, et al. Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes on Autoimmune Diseases. Front Immunol. 2021; 12:749192. [73] WANG S, LEI B, ZHANG E, et al. Targeted Therapy for Inflammatory Diseases with Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Derived Exosomes: From Basic to Clinics. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022;17:1757-1781. [74] YAP SK, TAN KL, ABD RAHAMAN NY, et al. Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Ameliorated Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Rats. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(3):649. [75] CHEN MT, ZHAO YT, ZHOU LY, et al. Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Enhance Insulin Sensitivity in Insulin Resistant Human Adipocytes. Curr Med Sci. 2021;41(1):87-93. [76] SUN Y, SHI H, YIN S, et al. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosomes Alleviate Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by Reversing Peripheral Insulin Resistance and Relieving β-Cell Destruction. ACS Nano. 2018; 12(8):7613-7628. [77] LI H, MENG Y, HE S, et al. Macrophages, Chronic Inflammation, and Insulin Resistance. Cells. 2022;11(19):3001. [78] PUSCHEL GP, KLAUDER J, HENKEL J. Macrophages, Low-Grade Inflammation, Insulin Resistance and Hyperinsulinemia: A Mutual Ambiguous Relationship in the Development of Metabolic Diseases. J Clin Med. 2022;11(15):4358. [79] RODRIGUEZ-COMAS J, MORENO-VEDIA J, OBACH M, et al. Alpha1-Antitrypsin Ameliorates Islet Amyloid-Induced Glucose Intolerance and Beta-Cell Dysfunction. Mol Metab. 2020;37:100984. [80] ZHOU Y, HU Q, CHEN F, et al. Human Umbilical Cord Matrix-Derived Stem Cells Exert Trophic Effects on β-Cell Survival in Diabetic Rats and Isolated Islets. Dis Model Mech. 2015;8(12):1625-1633. [81] YIN Y, HAO H, CHENG Y, et al. Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Direct Macrophage Polarization to Alleviate Pancreatic Islets Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(7):760. [82] PAN XH, HUANG X, RUAN GP, et al. Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Are Able to Undergo Differentiation into Functional Islet-Like Cells in Type 2 Diabetic Tree Shrews. Mol Cell Probes. 2017;34:1-12. [83] LI B, CHENG Y, YIN Y, et al. Reversion of Early- and Late-Stage β-Cell Dedifferentiation by Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Cytotherapy. 2021;23(6):510-520. [84] WANG W, WU RD, CHEN P, et al. Liraglutide Combined with Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation Inhibits Beta-Cell Apoptosis Via Mediating the ASK1/JNK/BAX Pathway in Rats with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020;36(2):e3212. [85] YING W, LEE YS, DONG Y, et al. Expansion of Islet-Resident Macrophages Leads to Inflammation Affecting Beta Cell Proliferation and Function in Obesity. Cell Metab. 2019;29(2):457-474.e455. [86] MUKHUTY A, FOUZDER C, KUNDU R. Fetuin-a Secretion from Beta-Cells Leads to Accumulation of Macrophages in Islets, Aggravates Inflammation and Impairs Insulin Secretion. J Cell Sci. 2021;134(21): jcs258507. [87] ZHOU Y, LIU K, TANG W, et al. Beta-Cell miRNA-503-5p Induced by Hypomethylation and Inflammation Promotes Insulin Resistance and Beta-Cell Decompensation. Diabetes. 2024;73(1):57-74. [88] XIE T, HUANG Q, HUANG Q, et al. Dysregulated lncRNAs Regulate Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation into Insulin-Producing Cells by Forming a Regulatory Network with mRNAs. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024;15(1):22. |
| [1] | Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang. Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [2] | Wang Wentao, Hou Zhenyang, Wang Yijun, Xu Yaozeng. Apelin-13 alleviates systemic inflammatory bone loss by inhibiting macrophage M1 polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1548-1555. |
| [3] | Li Kaiying, Wei Xiaoge, Song Fei, Yang Nan, Zhao Zhenning, Wang Yan, Mu Jing, Ma Huisheng. Mechanism of Lijin manipulation regulating scar formation in skeletal muscle injury repair in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1600-1608. |
| [4] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [5] | Li Dijun, Jiu Jingwei, Liu Haifeng, Yan Lei, Li Songyan, Wang Bin. Three-dimensional gelatin microspheres loaded human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for chronic tendinopathy repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1356-1362. |
| [6] | Huang Ting, Zheng Xiaohan, Zhong Yuanji, Wei Yanzhao, Wei Xufang, Cao Xudong, Feng Xiaoli, Zhao Zhenqiang. Effects of macrophage migration inhibitory factor on survival, proliferation, and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1380-1387. |
| [7] | Chang Jinxia, Liu Yufei, Niu Shaohui, Wang Chang, Cao Jianchun. Visualization analysis of macrophage polarization in tissue repair process [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1486-1496. |
| [8] | Yu Ting, Lyu Dongmei, Deng Hao, Sun Tao, Cheng Qian. Icariin pretreatment enhances effect of human periodontal stem cells on M1-type macrophages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1328-1335. |
| [9] | Liu Lingyun, He Guixin, Qin Weibin, Song Hui, Zhang Liwen, Tang Weizhi, Yang Feifei, Zhu Ziyi, Ou Yangbin . Improvement of myocardial injury by traditional Chinese medicine: mitochondrial calcium homeostasis mediates macrophage autophagy and pyroptosis pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1276-1284. |
| [10] | Bai Jing, Zhang Xue, Ren Yan, Li Yuehui, Tian Xiaoyu. Effect of lncRNA-TNFRSF13C on hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in periodontal cells by modulation of #br# miR-1246 #br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 928-935. |
| [11] | Zhi Fang, Zhu Manhua, Xiong Wei, Lin Xingzhen. Analgesic effect of acupuncture in a rat model of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 936-941. |
| [12] | Wang Yuru, Li Siyuan, Xu Ye, Zhang Yumeng, Liu Yang, Hao Huiqin. Effects of wogonin on joint inflammation in collagen-induced arthritis rats via the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1026-1035. |
| [13] | Wang Sifan, He Huiyu, Yang Quan, Han Xiangzhen. miRNA-378a overexpression of macrophage cell line composite collagen sponge: anti-inflammation and tissue repair promotion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 789-799. |
| [14] | Zheng Yitong, Wang Yongxin, Liu Wen, Amujite, Qin Hu. Action mechanism of intrathecal transplantation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for repair of spinal cord injury under neuroendoscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7743-7751. |
| [15] | Yu Hui, Yang Yang, Wei Ting, Li Wenli, Luo Wenqian, Liu Bin. Gadd45b alleviates white matter damage in chronic ischemic rats by modulating astrocyte phenotype [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7797-7803. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||