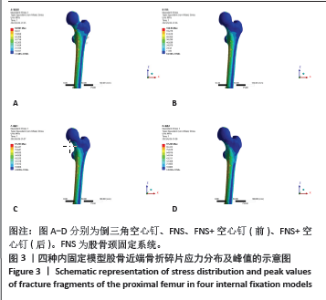
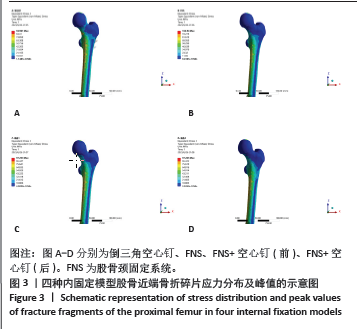
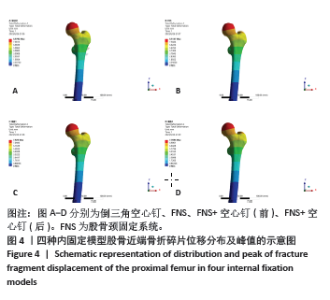
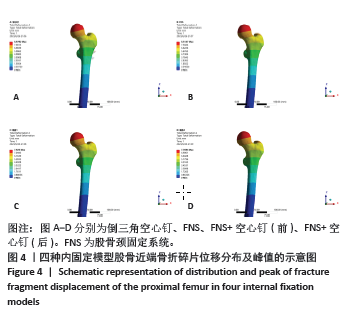
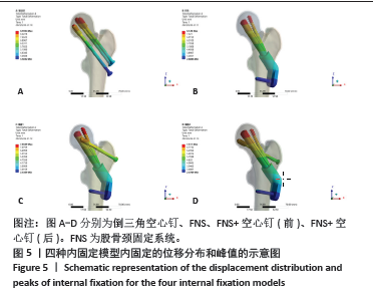
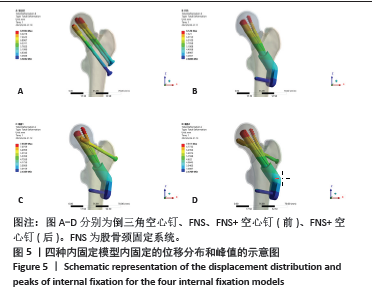
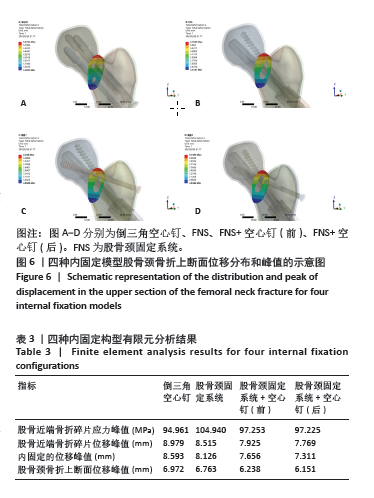
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (21): 4401-4406.doi: 10.12307/2025.153
Finite element analysis of four different internal fixation methods for treatment of Pauwels type III femoral neck fractures
Lu Jianpeng, Chen Long, Le Jiadi, Zhang Jianxiong
- Affiliated Second Hospital, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325000, Zhejiang Province, China
-
Received:2023-11-04Accepted:2024-03-09Online:2025-07-28Published:2024-12-04 -
Contact:Chen Long, MD, Chief physician, Affiliated Second Hospital, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325000, Zhejiang Province, China -
About author:Lu Jianpeng, Master, Physician, Affiliated Second Hospital, Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou 325000, Zhejiang Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lu Jianpeng, Chen Long, Le Jiadi, Zhang Jianxiong. Finite element analysis of four different internal fixation methods for treatment of Pauwels type III femoral neck fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(21): 4401-4406.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] 张少波, 刘芳, 彭岳文, 等. 中老年人维生素D、骨密度水平与髋部脆性骨折的相关性研究[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(6): 812-817+824. [2] FEI X, RONG L, MING L, et al. A New Random Forest Algorithm-Based Prediction Model of Post-operative Mortality in Geriatric Patients With Hip Fractures. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:829977. [3] ZHOU L, LIN J, HUANG A, et al. Modified cannulated screw fixation in the treatment of Pauwels type III femoral neck fractures: A biomechanical study. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2020;74:103-110. [4] FREITAS A, TOLEDO JÚNIOR JV, FERREIRA DOS SANTOS A, et al. Biomechanical study of different internal fixations in Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture - A finite elements analysis. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2021;14:145-150. [5] SHEN M, WANG C, CHEN H, et al. An update on the Pauwels classification. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11(1):161. [6] CHAN DS. Femoral Neck Fractures in Young Patients: State of the Art. J Orthop Trauma. 2019; 33 Suppl 1:S7-S11. [7] WANG Z, YANG Y, FENG G, et al. Biomechanical comparison of the femoral neck system versus InterTan nail and three cannulated screws for unstable Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture. Biomed Eng Online. 2022;21(1):34. [8] HACKL S, VON RÜDEN C, WEISEMANN F, et al. Internal Fixation of Garden Type III Femoral Neck Fractures with Sliding Hip Screw and Anti-Rotation Screw: Does Increased Valgus Improve Healing? Medicina (Kaunas). 2022;58(11):1573. [9] WANG J, GAO Y, SONG D, et al. Biomechanical study on parallel cannulated compression screw combined with medial buttress plate fixation and F-type cannulated compression screw fixation in Pauwels III femoral neck fracture: A finite element analysis. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022;47(8):1143-1153. [10] STOFFEL K, ZDERIC I, GRAS F, et al. Biomechanical Evaluation of the Femoral Neck System in Unstable Pauwels III Femoral Neck Fractures: A Comparison with the Dynamic Hip Screw and Cannulated Screws. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31(3):131-137. [11] WANG K, LIN D, CHEN P, et al. Incidence and factors influencing neck shortening after screw fixation of femoral neck fractures with the femoral neck system. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):317. [12] AUGAT P, BLIVEN E, HACKL S. Biomechanics of Femoral Neck Fractures and Implications for Fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 2019;33 Suppl 1: S27-S32. [13] 李英周, 叶锋, 万蕾, 等. 改良经皮加压钢板治疗Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折的疗效分析 [J]. 中国骨伤,2018,31(2):120-123. [14] HAMIDI S, KHOSRAVIFARD A, HEMATIYAN MR, et al. A comparative mechanical study of two types of femur bone implant using the finite element method. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng. 2021; 37(6):e3459. [15] HUANG Q, ZHANG C, BAI H, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of two modified intramedullary fixation system for treating unstable femoral neck fractures: A finite element analysis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1116976. [16] JIANG D, ZHAN S, WANG L, et al. Biomechanical comparison of five cannulated screw fixation strategies for young vertical femoral neck fractures. J Orthop Res. 2021;39(8):1669-1680. [17] TENG Y, ZHANG Y, GUO C. Finite element analysis of femoral neck system in the treatment of Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture. Medicine. 2022;101(28):e29450. [18] YANG JJ, LIN LC, CHAO KH, et al. Risk factors for nonunion in patients with intracapsular femoral neck fractures treated with three cannulated screws placed in either a triangle or an inverted triangle configuration. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(1):61-69. [19] CHEN ZM, YANG F, YU S, et al. [Finite element analysis of optimal selection of cannulated threaded screw for the prevention of femoral neck shortening after internal fixation for femoral neck fracture]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2022;35(11):1042-1048. [20] JOHNSON JP, BORENSTEIN TR, WARYASZ GR, et al. Vertically Oriented Femoral Neck Fractures: A Biomechanical Comparison of 3 Fixation Constructs. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31(7):363-368. [21] JI R, LU X, CONG R, et al. [Comparison of full thread compression cannulated screw and partial thread cannulated screw in treatment of femoral neck fracture]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023;37(1):19-24. [22] SU ZH, TAN HL, XU ZH, et al. [Biomechanical analysis of four internal fixations for Pauwels Ⅲ femoral neck fractures with defects]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2023;36(3):255-261. [23] YANG J, ZHOU X, LI L, et al. [Comparison of femoral neck system and inverted triangle cannulated screws fixations in treatment of Pauwels typle Ⅲ femoral neck fractures]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021;35(9):1111-1118. [24] CHA Y, CHUNG JY, JUNG CH, et al. Pre-sliding of femoral neck system improves fixation stability in pauwels type III femoral neck fracture: a finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):506. [25] ZHOU Y, LI Z, LAO K, et al. Femoral neck system vs. cannulated screws on treating femoral neck fracture: a meta-analysis and system review. Front Surg. 2023;10:1224559. [26] JIANG X, LIANG K, DU G, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of different internal fixation methods based on finite element analysis for Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture. Injury. 2022;53(10):3115-3123. [27] SU M, HE Z, HUANG N, et al. Superior short-term outcomes of FNS in combination with a cannulated screw in treating femoral neck fractures. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):823. |
| [1] | Xu Hao, Ding Lu, Li Xiao. Investigating the effect of the mechanical wear on abutment screw in Morse taper connection implant implant system by using finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Sun Xiaojun, Wang Huaming, Zhang Dehong, Song Xuewen, Huang Jin, Zhang Chen, Pei Shengtai. Effect of finite element method in treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1897-1904. |
| [3] | Li Liangkui, Huang Yongcan, Wang Peng, Yu Binsheng. Effect of anterior controllable anteriodisplacement and fusion on vertebrae-ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament complex and implants: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1761-1767. |
| [4] | Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao. Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1768-1774. |
| [5] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [6] | Chen Xi, Tang Tao, Chen Tongbing, Li Qing, Zhang Wen. Mechanical stability of intertrochanteric fracture of femur with different internal fixation systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1783-1788. |
| [7] | Fu Enhong, Yang Hang, Liang Cheng, Zhang Xiaogang, Zhang Yali, Jin Zhongmin. OpenSim-based prediction of lower-limb biomechanical behavior in adolescents with plantarflexor weakness [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1789-1795. |
| [8] | Lu Jieming, Li Yajing, Du Peijie, Xu Dongqing. Effects of artificial turf versus natural grass on biomechanical performance of the lower limbs in young females during jump-landing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1101-1107. |
| [9] | Li Shuai, Liu Hua, Shang Yonghui, Liu Yicong, Zhao Qihang, Liu Wen. Stress distribution on the maxilla when wearing the Twin-block appliance for Class II malocclusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 881-887. |
| [10] | Zhou Zonghao, Luo Siyang, Chen Jiawen, Chen Guangneng, Feng Hongchao. Finite element analysis of bioabsorbable plates versus miniature titanium plates in mandibular fracture fixation in different bone qualities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 818-826. |
| [11] | Chen Yilong, Zhang Xu, Li Hong. Mechanical analysis of fiber post combined with different crown restorations for endodontically treated non-carious cervical lesions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 866-871. |
| [12] | Yang Yicheng, Zheng Zhizhen, Liang Shuangxue, Wu Chengliang, Du Yunyun. Influence and implications of basketball shoes' functional parameters on human biomechanics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7620-7628. |
| [13] | Wang Lei, Li Chengsong, Zhang Shenshen, Wang Qing. Finite element analysis of biomechanical characteristics of three internal fixation methods in treatment of inferior patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7048-7054. |
| [14] | Xu Xin, Wurikaixi·Aiyiti, Lyu Gang, Maimaiaili·Yushan, Ma Zhiqiang, Ma Chao. Finite element analysis of four different internal fixation methods for complex acetabular double-column fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7063-7071. |
| [15] | Liang Cheng, Zhuo Chuanchuan, Zhang Xiaogang, Wang Guan, Duan Ke, Li Zhong, Lu Xiaobo, Zhuo Naiqiang, Jin Zhongmin. Biomechanical characteristics of a novel sacroiliac lag screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7080-7086. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||