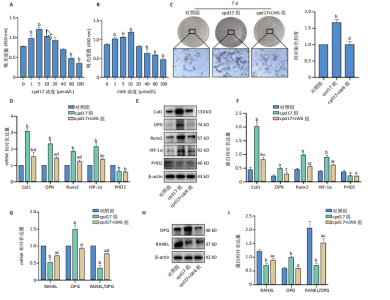
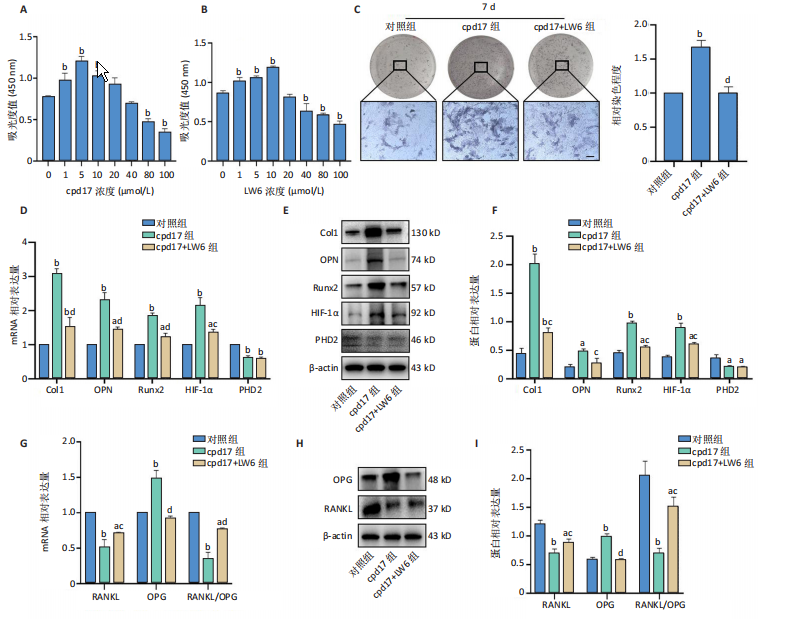
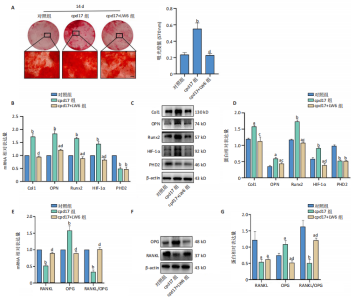
[1] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)[J].中国全科医学,2023,26(14):1671-1691.
[2] HUO S, TANG X, CHEN W, et al. Epigenetic regulations of cellular senescence in osteoporosis. Ageing Res Rev. 2024. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102235.
[3] 侯艳芳,刘建民.新型促骨形成剂Abaloparatide的研究进展[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2018,11(3):290-295.
[4] SEMENZA GL. Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3(10):721-732.
[5] WOLF D, MURALIDHARAN A, MOHAN S. Role of prolyl hydroxylase domain proteins in bone metabolism. Osteoporos Sarcopenia. 2022; 8(1):1-10.
[6] CORNER TP, TEO RZR, WU Y, et al. Structure-guided optimisation of N-hydroxythiazole-derived inhibitors of factor inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor-α. Chem Sci. 2023;14(43):12098-12120.
[7] 张怡婷.脯氨酸羟化酶抑制剂对肾性贫血患者铁蛋白的影响及其与微炎症状态的相关性研究[D].赣州:赣南医学院,2023.
[8] 商玲玲.脯氨酸羟化酶抑制剂DMOG在牙周组织再生中生物学效应的研究[D].济南:山东大学,2021.
[9] LIANG Y, WANG Y, SUN C, et al. Deferoxamine reduces endothelial ferroptosis and protects cerebrovascular function after experimental traumatic brain injury. Brain Res Bull. 2024;207:110878.
[10] XIE H, SMITH LJ, HOLMES AL, et al. The cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of soluble and particulate cobalt in human lung epithelial cells. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2016;57(4):282-287.
[11] ZHANG J, GUAN J, QI X, et al. Dimethyloxaloylglycine Promotes the Angiogenic Activity of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from iPSCs via Activation of the PI3K/Akt Pathway for Bone Regeneration. Int J Biol Sci. 2016 ;12(6):639-652.
[12] CHAN MC, HOLT-MARTYN JP, SCHOFIELD CJ, et al. Pharmacological targeting of the HIF hydroxylases--A new field in medicine development. Mol Aspects Med. 2016;47-48:54-75.
[13] CHEN N, HAO C, LIU BC, et al. Roxadustat Treatment for Anemia in Patients Undergoing Long-Term Dialysis. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(11): 1011-1022.
[14] ZHANG X, LEI Y, HU T, et al. Discovery of Clinical Candidate (5-(3-(4-Chlorophenoxy)prop-1-yn-1-yl)-3-hydroxypicolinoyl)glycine, an Orally Bioavailable Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Anemia. J Med Chem. 2020;63(17):10045-10060.
[15] FAN L, LI J, YU Z, et al. The hypoxia-inducible factor pathway, prolyl hydroxylase domain protein inhibitors, and their roles in bone repair and regeneration. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:239356.
[16] LI L, LI A, ZHU L, et al. Roxadustat promotes osteoblast differentiation and prevents estrogen deficiency-induced bone loss by stabilizing HIF-1α and activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):286.
[17] YELLOWLEY CE, GENETOS DC. Hypoxia Signaling in the Skeleton: Implications for Bone Health. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2019;17(1):26-35.
[18] LIU X, TU Y, ZHANG L, et al. Prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors protect from the bone loss in ovariectomy rats by increasing bone vascularity. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014;69(1):141-149.
[19] LI L, LI A, GAN L, et al. Roxadustat improves renal osteodystrophy by dual regulation of bone remodeling. Endocrine. 2023;79(1):180-189.
[20] RUNDLE CH, GOMEZ GA, POURTEYMOOR S, et al. Sequential application of small molecule therapy enhances chondrogenesis and angiogenesis in murine segmental defect bone repair. J Orthop Res. 2023;41(7):1471-1481.
[21] TAYLOR SE, SHAH M, ORRISS IR. Generation of rodent and human osteoblasts. Bonekey Rep. 2014;3:585.
[22] LEE K, KANG JE, PARK SK, et al. LW6, a novel HIF-1 inhibitor, promotes proteasomal degradation of HIF-1alpha via upregulation of VHL in a colon cancer cell line. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010;80(7):982-989.
[23] HAO Q, LIU Z, LU L, et al. Both JNK1 and JNK2 Are Indispensable for Sensitized Extracellular Matrix Mineralization in IKKβ-Deficient Osteoblasts. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11:13.
[24] DEMPSTER DW, COMPSTON JE, DREZNER MK, et al. Standardized nomenclature, symbols, and units for bone histomorphometry: a 2012 update of the report of the ASBMR Histomorphometry Nomenclature Committee. J Bone Miner Res. 2013;28(1):2-17.
[25] JAHANGIR S, HOSSEINI S, MOSTAFAEI F, et al. 3D-porous β-tricalcium phosphate-alginate-gelatin scaffold with DMOG delivery promotes angiogenesis and bone formation in rat calvarial defects. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2018;30(1):1.
[26] CHEN C, YAN S, QIU S, et al. HIF/Ca2+/NO/ROS is critical in roxadustat treating bone fracture by stimulating the proliferation and migration of BMSCs. Life Sci. 2021;264:118684.
[27] HULLEY PA, PAPADIMITRIOU-OLIVGERI I, KNOWLES HJ. Osteoblast-Osteoclast Coculture Amplifies Inhibitory Effects of FG-4592 on Human Osteoclastogenesis and Reduces Bone Resorption. JBMR Plus. 2020;4(7):e10370.
[28] 王永炫,李梅,章振林,等.《原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)》要点解读[J].协和医学杂志,2023,14(6):1203-1207.
[29] TAKPRADIT C, VIPRAKASIT V, NARKBUNNAM N, et al. Using of deferasirox and deferoxamine in refractory iron overload thalassemia. Pediatr Int. 2021;63(4):404-409.
[30] TANG X, LIU F, LI Q, et al. Roxadustat for Patients with Posttransplant Anemia: A Narrative Review. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2023;10(1):32-38.
|