Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (18): 3948-3960.doi: 10.12307/2025.690
Association between plasma proteins and osteoporosis and identification of potential therapeutic targets: information analysis based on the UK Biobank database
Zhu Kai, Liu Wanxin, Luo Haobing, Feng Shengyi, Wang Qiugen
- Yueyang Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200437, China
-
Received:2024-07-23Accepted:2024-09-03Online:2025-06-28Published:2024-11-29 -
Contact:Wang Qiugen, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Yueyang Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200437, China -
About author:Zhu Kai, MD candidate, Physician, Yueyang Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200437, China -
Supported by:Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine Budgeted Project, No. KY110.01.423 (to FSY); Excellent Teaching Talent Cultivation Project of Yueyang Hospital, No. JY611.20.04.05 (to FSY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhu Kai, Liu Wanxin, Luo Haobing, Feng Shengyi, Wang Qiugen. Association between plasma proteins and osteoporosis and identification of potential therapeutic targets: information analysis based on the UK Biobank database[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3948-3960.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
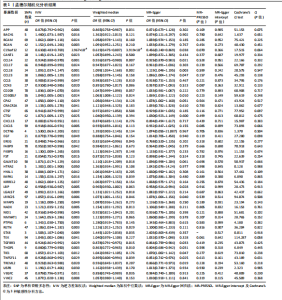
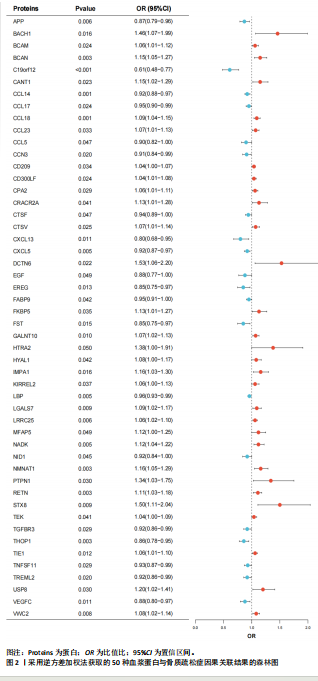
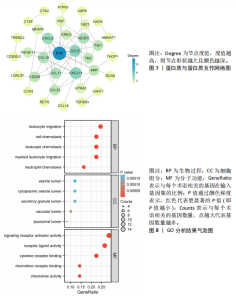
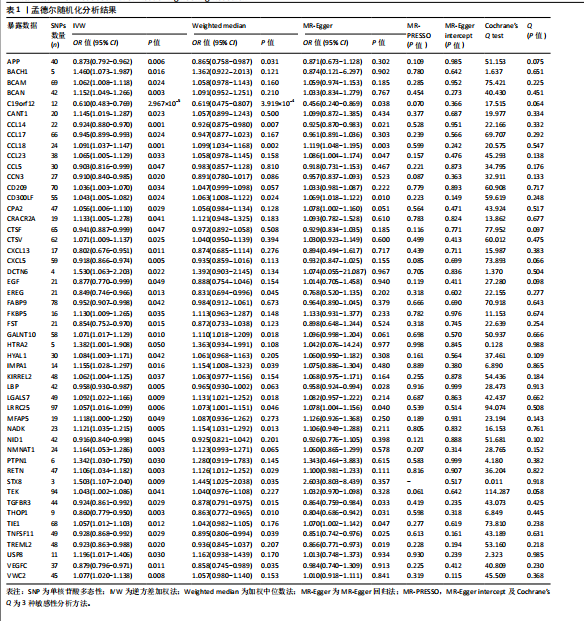
2.1 孟德尔随机化分析结果 在此文章中,基于工具变量的筛选标准,血浆蛋白共获得了2 279个pQTLs,所纳入单个单核苷酸多态性对应的F统计量均大于10,故研究避免了弱工具偏倚的影响。文章采用孟德尔随机化分析方法,探讨了1 001种血浆蛋白与骨质疏松症之间的关系。结果表明,有50种血浆蛋白与骨质疏松症存在因果关系(P < 0.05)。其中,OR < 1的血浆蛋白共有20种,包括淀粉样前体蛋白(amyloid precursor protein,APP)、染色体19开放阅读框12(chromosome 19 open reading frame 12,C19orf12)、CC基序趋化因子配体14(C-C motif chemokine ligand 14,CCL14)、CCL17、CCL5、细胞通讯网络因子3(cellular communication network factor 3,CCN3)、组织蛋白酶F(cathepsin F,CTSF)、CXC基序趋化因子配体13(C-X-C Motif chemokine ligand 13,CXCL13)、CXC基序趋化因子配体5(C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 5,CXCL5)、表皮生长因子(epidermal growth factOR,EGF)、上皮抑素(epiregulin,EREG)、脂肪酸结合蛋白9 (fatty acid bindingprotein 9,FABP9)、叶抑素(follistatin,FST)、脂多糖结合蛋白 (lipopolysaccharide binding protein,LBP)、巢蛋白1(nidogen 1,NID1)、转化生长因子β受体3(transforming growth factor beta receptor 3,TGFBR3)、Thimet寡肽酶1(thimet oligopeptidase 1,THOP1)、肿瘤坏死因子超家族成员11(tumor necrosis factor superfamily member 11,TNFSF11)、髓系细胞样触发受体2(triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells like 2,TREML2)及血管内皮生长因子C(vascular endothelial growth factor C,VEGFC),可能与骨质疏松症的风险降低相关;OR > 1的血浆蛋白共30种,包括BTB结构域和CNC同源物1(BTB domain and CNC homolog 1,BACH1)、基底细胞黏附分子(basal cell adhesion molecule,BCAM)、短链蛋白聚糖(brevican,BCAN)、钙激活核苷酸酶1(calcium activated nucleotidase 1,CANT1)、CCL18、CCL23、CD209、CD300分子样家族成员F(CD300 molecule like family member F,CD300LF)、羧肽酶A2(carboxypeptidase A2,CPA2)、钙释放激活通道调节蛋白2A(calcium release activated channel regulator 2A,CRACR2A)、组织蛋白酶V(cathepsin V,CTSV)、动力蛋白复合物6亚基(dynactin subunit 6,DCTN6)、FK506结合蛋白5(FK506 binding protein 5,FKBP5)、多肽N-乙酰半乳糖胺转移酶10(polypeptide N-Acetylgalactosaminy ltransferase 10,GALNT10)、HtrA丝氨酸肽酶2(htrA serine peptidase 2,HTRA2)、透明质酸酶1(hyaluronidase 1,HYAL1)、肌醇单磷酸酶1(inositol monophosphatase 1,IMPA1)、IRRE类似家族2(kin of irre like 2,KIRREL2)、半乳糖凝集素7(galectin 7,LGALS7)、富含亮氨酸的重复序列25(leucine rich repeat containing 25,LRRC25)、微纤维相关蛋白5(microfibril associated protein 5,MFAP5)、NAD激酶(NAD kinase,NADK)、烟酰胺核苷酸腺苷酸转移酶1(nicotinamide nucleotide adenylyltransferase 1,NMNAT1)、蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶非受体型1(protein tyrosine phosphatase nonreceptor Type 1,PTPN1)、抵抗素(resistin,RETN)、突触融合蛋白8(syntaxin 8,STX8)、TEK受体酪氨酸激酶(tek receptor tyrosine kinase,TEK)、含免疫球蛋白样和EGF样结构域的酪氨酸激酶1 (tyrosine kinase with immunoglobulin like and EGF like domains 1,TIE1)、泛素特异性肽酶8(ubiquitin specific peptidase 8,USP8)及含von Willebrand因子C结构域2(Von willebrand factor C domain containing 2,VWC2),这可能与骨质疏松症的风险增加有关。经Bonferroni校正后,只有C19orf12 (P=2.967×10-5)与骨质疏松症存在显著因果关系,详见表1及图2。 2.2 敏感性分析结果 敏感性分析的相关结果详见表1。在多效性检验中,50种血浆蛋白的P值均大于0.05,同时MR-PRESSO也进一步表明文章结果不存在水平多效性。此外,经Cochrane’s Q检验,未发现异质性。留一法进一步提示分析结果较为稳健,见图3,4。漏斗图中呈现的因果效应分布基本具有对称性,未见明显偏倚,见图5,6。 2.3 网络分析及功能富集结果 文章将孟德尔随机化分析获取的50个蛋白上传到String数据库进行分析,并将String结果导入Cytoscape 3.9.0,去除孤立节点后构建了PPI网络,该网络由34个节点和49条边组成,平均节点度为1.96,其中节点度值位于前10的核心蛋白为EGF、CCL5、CXCL13、CXCL5、VEGFC、CCL18、CCL17、TEK、TIE1和CCL23,详见图7。GO分析如图8所示,在生物过程(biological process,BP)方面,主要富集于白细胞迁移(leukocyte migration)、细胞趋化(cell chemotaxis)过程;细胞组分(cellular component,CC)方面主要定位在囊泡腔(vesicle lumen)、分泌颗粒腔(secretory granule lumen)等;分子功能(molecular function,MF)方面主要涉及信号受体激活因子活性(signaling receptor activator activity)、细胞因子受体结合(cytokine receptor binding)、趋化因子受体结合(chemokine receptor binding)等。KEGG分析结果显示,显著富集的通路包括细胞因子-细胞因子受体相互作用(cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction)、趋化因子信号通路(chemokine signaling pathway)、肿瘤坏死因子信号通路(TNF signaling pathway)、溶酶体(Lysosome)和细胞凋亡(Apoptosis),详见图9。这些通路强调了蛋白靶标在细胞因子介导的信号传导和免疫系统调节中的核心作用。"
| [1] COMPSTON JE, MCCLUNG MR, LESLIE WD. Osteoporosis. Lancet. 2019;393(10169): 364-376. [2] BORGSTRÖM F, KARLSSON L, ORTSÄTER G, et al. Fragility fractures in Europe: burden, management and opportunities. Arch Osteoporos. 2020;15(1):59. [3] ANAM AK, INSOGNA K. Update on Osteoporosis Screening and Management. Med Clin North Am. 2021;105(6):1117-1134. [4] SALARI N, GHASEMI H, MOHAMMADI L, et al. The global prevalence of osteoporosis in the world: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):609. [5] CHEN P, LI Z, HU Y. Prevalence of osteoporosis in China: a meta-analysis and systematic review. BMC Public Health. 2016;16(1):1039. [6] LEE K, JANG Y, LEE H, et al. Transcriptome analysis reveals that Abeliophyllum distichum Nakai extract inhibits RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis mainly through suppressing Nfatc1 expression. Biology (Basel). 2020;9(8):212. [7] ZHANG Y, XIE J, WEN S, et al. Evaluating the causal effect of circulating proteome on the risk of osteoarthritis-related traits. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023;82(12):1606-1617. [8] 芦晶晶,李星,娄萍萍,等.血清铁蛋白水平与骨密度的相关性研究[J].中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2020,6(2):111-116. [9] 郑淑蓓,郑育,李占园,等.成纤维细胞生长因子23、Klotho蛋白与血液透析患者骨密度改变的关系[J].中华肾脏病杂志,2016,32(5):321-326. [10] 谭娟,刘媛媛,朱永芳,等.2型糖尿病患者血红蛋白水平与骨密度及骨质疏松之间的关系[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2024,40(2):98-103. [11] WU Y, WANG Z, YANG Y, et al. Exploration of potential novel drug targets and biomarkers for small cell lung cancer by plasma proteome screening. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1266782. [12] CHEN L, PETERS JE, PRINS B, et al. Systematic Mendelian randomization using the human plasma proteome to discover potential therapeutic targets for stroke. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):6143. [13] YUAN S, XU F, LI X, et al. Plasma proteins and onset of type 2 diabetes and diabetic complications: proteome-wide Mendelian randomization and colocalization analyses. Cell Rep Med. 2023;4(9):101174. [14] SANDERSON E, GLYMOUR MM, HOLMES MV, et al. Mendelian randomization. Nat Rev Methods Primers. 2022;2:6. [15] SUHRE K. Genetic associations with ratios between protein levels detect new pQTLs and reveal protein-protein interactions. Cell Genom. 2024;4(3):100506. [16] YAZDANPANAH N, YAZDANPANAH M, WANG Y, et al. Clinically relevant circulating protein biomarkers for type 1 diabetes: evidence from a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Diabetes Care. 2022; 45(1):169-177.
[17] GHANBARI F, YAZDANPANAH N, YAZDANPANAH M, et al. Connecting genomics and proteomics to identify protein biomarkers for adult and youth-onset type 2 diabetes: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Diabetes. 2022;71(6):1324-1337. [18] WINGO TS, LIU Y, GERASIMOV ES, et al. Brain proteome-wide association study implicates novel proteins in depression pathogenesis. Nat Neurosci. 2021;24(6):810-817. [19] YANG H, CHEN L, LIU Y. Novel causal plasma proteins for hypothyroidism: a large-scale plasma proteome Mendelian randomization analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023; 108(2):433-442. [20] BURGESS S, SMALL DS, THOMPSON SG. A review of instrumental variable estimators for Mendelian randomization. Stat Methods Med Res. 2015;26(5):2333-2355. [21] BURGESS S, BUTTERWORTH A, THOMPSON SG. Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data. Genet Epidemiol. 2013;37(7):658-665. [22] ZHOU S, TAO B, GUO Y, et al. Integrating plasma protein-centric multi-omics to identify potential therapeutic targets for pancreatic cancer. J Transl Med. 2024; 22(1):557. [23] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44(2):512-525. [24] ZHOU S, WEI T, LIU X, et al. Causal effects of COVID-19 on structural changes in specific brain regions: a Mendelian randomization study. BMC Med. 2023;21(1):261. [25] KLINGELHUBER F, FRENDO-CUMBO S, OMAR-HMEADI M, et al. A spatiotemporal proteomic map of human adipogenesis. Nat Metab. 2024;6(5):861-879. [26] SHAO C, ZHU J, MA X, et al. C19orf12 ablation causes ferroptosis in mitochondrial membrane protein-associated neurodegeneration. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022;182:23-33. [27] VENCO P, BONORA M, GIORGI C, et al. Mutations of C19orf12, coding for a transmembrane glycine zipper containing mitochondrial protein, cause mis-localization of the protein, inability to respond to oxidative stress and increased mitochondrial Ca2+. Front Genet. 2015; 6:185. [28] CAI W, ZHANG J, YU Y, et al. Mitochondrial transfer regulates cell fate through metabolic remodeling in osteoporosis. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(4):e2204871. [29] YAN C, SHI Y, YUAN L, et al. Mitochondrial quality control and its role in osteoporosis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14: 1077058. [30] GENETOS DC, RAO RR, VIDAL MA. Betacellulin inhibits osteogenic differentiation and stimulates proliferation through HIF-1alpha. Cell Tissue Res. 2010; 340(1):81-89. [31] MIYABE Y, LIAN J, MIYABE C, et al. Chemokines in rheumatic diseases: pathogenic role and therapeutic implications. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019; 15(12):731-746. [32] LIU W, WANG P, XIE Z, et al. Abnormal inhibition of osteoclastogenesis by mesenchymal stem cells through the miR-4284/CXCL5 axis in ankylosing spondylitis. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(3):188. [33] ACHUDHAN D, LAI YL, LIN YY, et al. CXCL13 promotes TNF-α synthesis in rheumatoid arthritis through activating ERK/p38 pathway and inhibiting miR-330-3p generation. Biochem Pharmacol. 2024;221:116037. [34] LEE J, HOSHINO A, INOUE K, et al. The HIV co-receptor CCR5 regulates osteoclast function. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):2226. [35] WINTGES K, BEIL FT, ALBERS J, et al. Impaired bone formation and increased osteoclastogenesis in mice lacking chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5 (Ccl5). J Bone Miner Res. 2013;28(10):2070-2080. [36] BRYLKA LJ, SCHINKE T. Chemokines in physiological and pathological bone remodeling. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2182. [37] PENG R, DONG Y, KANG H, et al. Identification of genes with altered methylation in osteoclast differentiation and its roles in osteoporosis. DNA Cell Biol. 2022;41(6):575-589. [38] VOTTA BJ, WHITE JR, DODDS RA, et al. CKbeta-8 [CCL23], a novel CC chemokine, is chemotactic for human osteoclast precursors and is expressed in bone tissues. J Cell Physiol. 2000;183(2):196-207. [39] HUANG M, XU S, LIU L, et al. m6A methylation regulates osteoblastic differentiation and bone remodeling. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:783322. [40] RAJASUNDARAM S, ZEBARDAST N, MEHTA P, et al. TIE1 and TEK signalling, intraocular pressure, and primary open-angle glaucoma: a Mendelian randomization study. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):847. [41] CAO X, LI T, XU B, et al. Endothelial TIE1 restricts angiogenic sprouting to coordinate vein assembly in synergy with its homologue TIE2. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2023;43(8):e323-e338. [42] NOH J, YANG Y, JUNG H. Molecular mechanisms and emerging therapeutics for osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(20):7623. [43] OKAMOTO K, NAKASHIMA T, SHINOHARA M, et al. Osteoimmunology: the conceptual framework unifying the immune and skeletal systems. Physiol Rev. 2017;97(4):1295-1349. [44] ZHANG W, GAO R, RONG X, et al. Immunoporosis: role of immune system in the pathophysiology of different types of osteoporosis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:965258. [45] WANG T, HE C. TNF-α and IL-6: the link between immune and bone system. Curr Drug Targets. 2020;21(3):213-227. [46] FISCHER V, HAFFNER-LUNTZER M. Interaction between bone and immune cells: Implications for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022; 123:14-21. [47] BRUNETTI G, D’AMELIO P, MORI G, et al. Editorial: Updates on osteoimmunology: what’s new on the crosstalk between bone and immune cells. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11:74. [48] AMARASEKARA DS, YUN H, KIM S, et al. Regulation of osteoclast differentiation by cytokine networks. Immune Netw. 2018; 18(1):e8. [49] XU J, YU L, LIU F, et al. The effect of cytokines on osteoblasts and osteoclasts in bone remodeling in osteoporosis: a review. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1222129. [50] AMARASEKARA DS, KIM S, RHO J. Regulation of osteoblast differentiation by cytokine networks. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(6):2851. [51] ZHAO Z, DU Y, YAN K, et al. Exercise and osteoimmunology in bone remodeling. FASEB J. 2024;38(7):e23554. [52] Wu Z, Yang KG, Lam TP, et al. Genetic insight into the putative causal proteins and druggable targets of osteoporosis: a large-scale proteome-wide mendelian randomization study. Front Genet. 2023; 14:1161817. |
| [1] | Chen Jiayong, Tang Meiling, Lu Jianqi, Pang Yan, Yang Shangbing, Mao Meiling, Luo Wenkuan, Lu Wei, Zhou Jiatan. Based on Mendelian randomization, the causal relationship between 1400 metabolites and sarcopenia and the correlation analysis of cardiovascular disease were investigated [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-11. |
| [2] | Li Jiagen, Chen Yueping, Huang Keqi, Chen Shangtong, Huang Chuanhong. The construction and validation of a prediction model based on multiple machine learning algorithms and the immunomodulatory analysis of rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of mitophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-15. |
| [3] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [4] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [5] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [6] | Dong Tingting, Chen Tianxin, Li Yan, Zhang Sheng, Zhang Lei. Causal relationship between modifiable factors and joint sports injuries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1953-1962. |
| [7] | Deng Keqi, Li Guangdi, Goswami Ashutosh, Liu Xingyu, He Xiaoyong. Screening and validation of Hub genes for iron overload in osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1972-1980. |
| [8] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [9] | Liu Lin, Liu Shixuan, Lu Xinyue, Wang Kan. Metabolomic analysis of urine in a rat model of chronic myofascial trigger points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1585-1592. |
| [10] | Zhao Jiacheng, Ren Shiqi, Zhu Qin, Liu Jiajia, Zhu Xiang, Yang Yang. Bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers for primary osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1741-1750. |
| [11] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [12] | Li Jialin, Zhang Yaodong, Lou Yanru, Yu Yang, Yang Rui. Molecular mechanisms underlying role of mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1512-1522. |
| [13] | Li Yueyao, Zhang Min, Yang Jiaju. Cistanoside A mediates p38/MAPK pathway to inhibit osteoclast activity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1144-1151. |
| [14] | Zheng Lin, Jin Wenjun, Luo Shanshan, Huang Rui, Wang Jie, Cheng Yuting, An Zheqing, Xiong Yue, Gong Zipeng, Liao Jian. Eucommia ulmoides promotes alveolar bone formation in ovariectomized rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1159-1167. |
| [15] |
Huang Xiaobin, Ge Jirong, Li Shengqiang, Xie Lihua, Huang Jingwen, He Yanyan, Xue Lipeng.
Mechanisms of different yin nourishing and kidney tonifying methods on osteoclastysis pathway in ovariectomized rats #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1214-1219.
|
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||