Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (18): 3941-3947.doi: 10.12307/2025.679
Previous Articles Next Articles
Genetic causal relationship between gut microbiota and osteoporosis: analysis of 211 gut microbiota from the UK database
Fang Zhijie1, Ma Qiangping1, Dong Wantao2, Wu Junyuan1, Lu Yunlin1
- 1Clinical School of Chinese Medicine, Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China; 2Department of Sports Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China
-
Received:2024-07-06Accepted:2024-08-26Online:2025-06-28Published:2024-11-29 -
Contact:Dong Wantao, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Sports Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China -
About author:Fang Zhijie, Master candidate, Clinical School of Chinese Medicine, Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81960878 (to DWT); Key Research and Development Plan of Gansu Province, No. 21YF5FA017 (to DWT); Innovation and Entrepreneurship Project of Science and Technology Talents of Chengguan District of Lanzhou City, No. 2023-rc-7 (to DWT); Science and Technology Plan of Lanzhou City, No. 2023-2-83 (to DWT)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fang Zhijie, Ma Qiangping, Dong Wantao, Wu Junyuan, Lu Yunlin. Genetic causal relationship between gut microbiota and osteoporosis: analysis of 211 gut microbiota from the UK database[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3941-3947.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
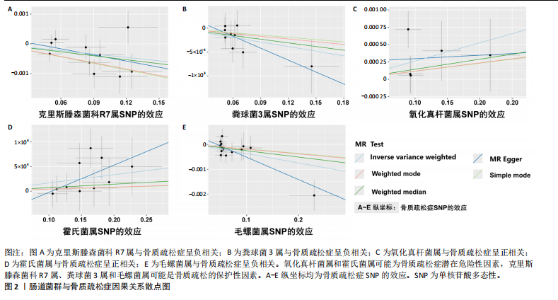
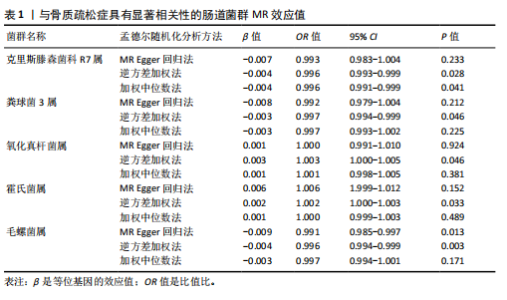
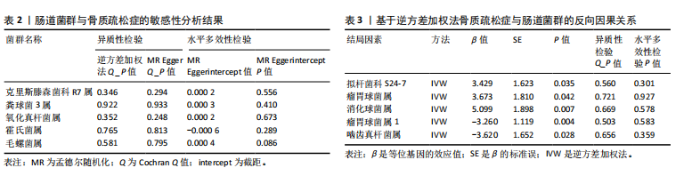
2.1 孟德尔随机化结果 首先,确定与肠道菌群在门、纲、目、科和属水平上相关的SNPs,经过一系列的筛选与检测,最终确定纳入5类菌,48个SNP,纳入分析的菌类其F值均> 10,选出的工具变量进行孟德尔随机化研究。基于MR Egger与IVW的β值,结果表明:霍氏菌属(MR Egger:β=0.006;IVW:β=0.002,P=0.033)和氧化真杆菌属(MR Egger:β=0.001;IVW:β=0.003,P=0.046)可能对骨质疏松症起到负向作用,这2个菌类为暴露因素分析所得综合效应值β均> 0,可见暴露因素是危险因素,随着暴露增加,结局的发病风险也随之增加。克里斯滕森菌科R7属(MR Egger:β=-0.007;IVW:β=-0.004,P=0.028)、粪球菌3属(MR Egger:β=-0.008;IVW:β=-0.003,P=0.046)和毛螺菌属(MR Egger:β=-0.009;IVW:β=-0.004,P=0.003)对骨质疏松症起到正面影响,这3个菌类为暴露因素所得综合效应值β均< 0,可见暴露因素是保护因素,随着暴露增加,结局的发病风险也随之减少。同时也运用MR Egger回归和加权中位数法对肠道菌群与骨质疏松症之间的关系进行分析,见图2和表1。"
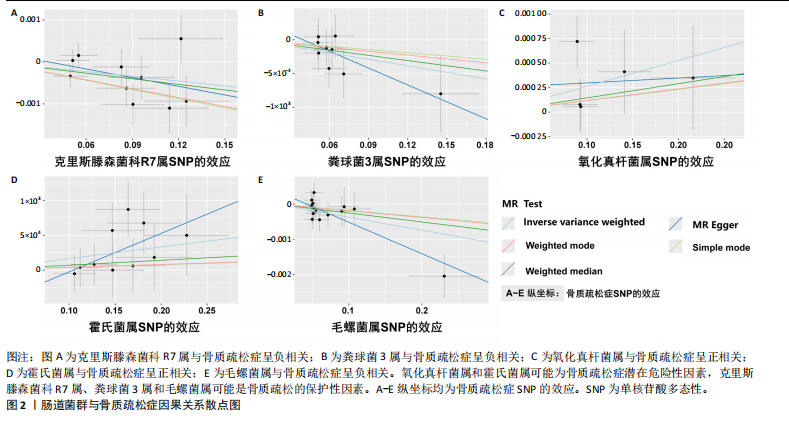
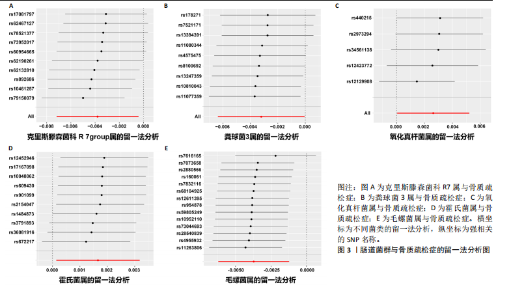
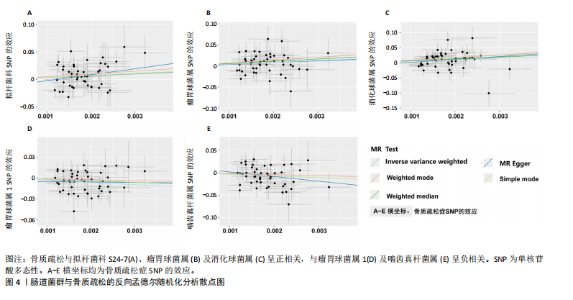
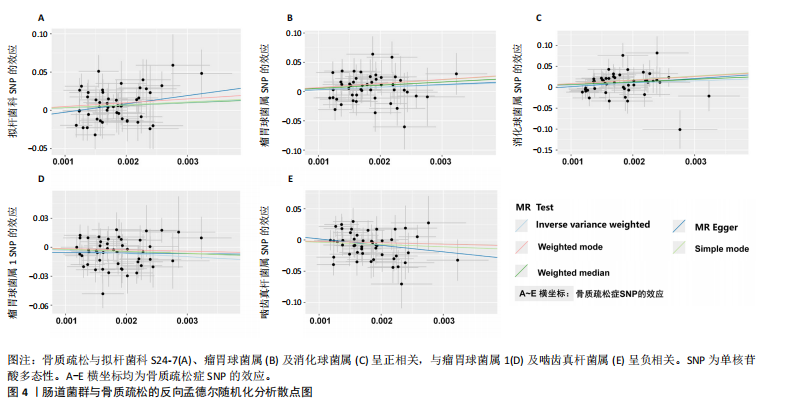
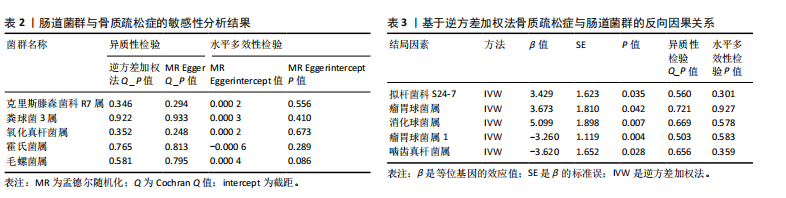
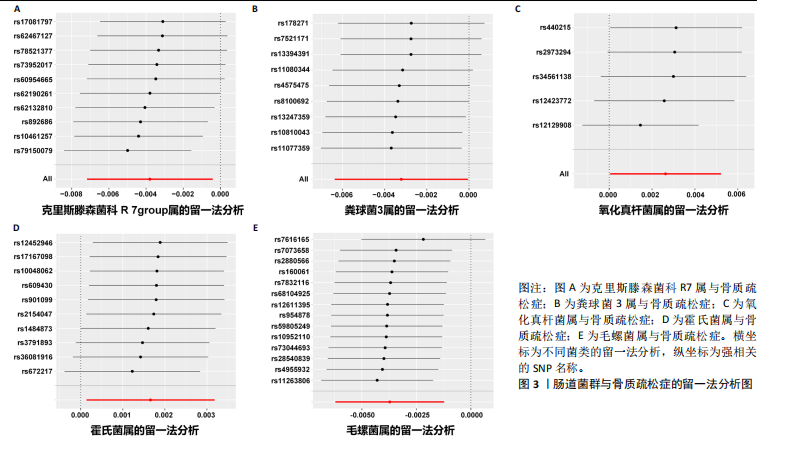
基于IVW的OR,霍氏菌属(OR=1.002,95%CI:1.000-1.003,P=0.033)和氧化真杆菌属(OR=1.003,95%CI:1.000-1.005,P=0.046)2个菌类所得到的OR值均> 1,表明暴露是结局的危险因素。克里斯滕森菌科R7属(OR=0.996,95%CI:0.993-0.996,P=0.028)、粪球菌3属(OR=0.997,95%CI:0.994-0.999,P=0.046)和毛螺菌属(OR=0.996,95%CI:0.994-0.999,P=0.003)3个菌类所得到的OR值均< 1,表明暴露是结局的保护因素。以上5种菌类通过IVW得到的P值均< 0.05,表明暴露与结局存在因果关联。此外,留一法敏感性分析结果稳定,MR-Egger截距测试和MR-PRESSO全局检验无水平多效性,Cochran Q检验不存在异质性。 2.2 敏感性分析结果 在敏感性分析中,通过Cochran’s Q检验和MR Egger回归分析发现,文章中涉及的菌类P值均超过0.05的阈值,这说明所选工具变量SNPs之间未发现显著的异质性;使用MR-Egger截距测试和MR-PRESSO全局检验两种方法对工具变量进行水平多效性检验,结果显示:所纳入菌类P值均> 0.05,提示暴露因素的工具变量不存在水平多效性,见表2。留一法结果显示在逐一剔除SNP后,结果并没有发生改变,未见明显离群值,表明所得结果并非由单个SNP所导致,这些分析在一定程度上证明了文章结果的稳健性和可靠性,见图3。 2.3 反向孟德尔随机化结果 通过对骨质疏松症及196个肠道菌群进行反向孟德尔随机化分析,共得到了5个肠道菌群与骨质疏松症之间存在反向因果关系,敏感性分析显示,反向孟德尔随机化分析不存在异质性和水平多效性,见表3。反向孟德尔随机化分析结果显示,骨质疏松症与瘤胃球菌属1及啮齿真杆菌属呈负相关,与拟杆菌科S24-7、瘤胃球菌属及消化球菌属呈正相关,见图4。"
| [1] ARCEO-MENDOZA RM, CAMACHO PM. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: latest guidelines. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2021;50(2):167-178. [2] ZHIVODERNIKOV IV, KIRICHENKO TV, MARKINA YV, et al. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(21):15772. [3] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会,章振林.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)[J]. 中国全科医学,2023,26(14): 1671-1691. [4] DING K, HUA F, DING W. Gut microbiome and osteoporosis. Aging Dis. 2020;11(2): 438-447. [5] LI S, MAO Y, ZHOU F, et al. Gut microbiome and osteoporosis: a review. Bone Joint Res. 2020;9(8):524-530. [6] CASTANEDA M, STRONG JM, ALABI DA, et al. The Gut microbiome and bone strength. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020;18(6): 677-683. [7] XU Z, XIE Z, SUN J, et al. Gut microbiome reveals specific dysbiosis in primary osteoporosis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020;10:160. [8] XU J, ZHANG S, TIAN Y, et al. Genetic causal association between iron status and osteoarthritis: a two-sample mendelian randomization. Nutrients. 2022; 14(18):3683. [9] FERENCE BA, HOLMES MV, SMITH GD. Using mendelian randomization to improve the design of randomized trials. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2021;11(7):a040980. [10] KURILSHIKOV A, MEDINA-GOMEZ C, BACIGALUPE R, et al. Large scale association analyses identify host factors influencing human gut microbiome composition. Nat Genet. 2021;53(2):156-165. [11] LYON MS, ANDREWS SJ, ELSWORTH B, et al. The variant call format provides efficient and robust storage of GWAS summary statistics. Genome Biol. 2021;22(1):32. [12] DAVIES NM, HOLMES MV, DAVEY SMITH G. Reading Mendelian randomisation studies: a guide, glossary, and checklist for clinicians. BMJ. 2018;362:k601. [13] 梁家浩,杨舒龄,王海.基于孟德尔随机化探讨肠道菌群与儿童哮喘的因果关联[J].华西医学,2024,39(4):553-560. [14] LI P, WANG H, GUO L, et al. Association between gut microbiota and preeclampsia-eclampsia: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. BMC Med. 2022;20(1): 443. [15] CAO Y, LU H, XU W, et al. Gut microbiota and Sjögren’s syndrome: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1187906. [16] PIERCE BL, AHSAN H, VANDERWEELE TJ. Power and instrument strength requirements for Mendelian randomization studies using multiple genetic variants. Int J Epidemiol. 2011;40(3):740-752. [17] HARTWIG FP,DAVIES NM,HEMANI G, et al. Two-sample Mendelian randomization: avoiding the downsides of a powerful,widely applicable but potentially fallible technique. Int J Epidemiol. 2016;45(6):1717-1726. [18] YUAN S, CHEN J, RUAN X, et al. Smoking, alcohol consumption, and 24 gastrointestinal diseases: Mendelian randomization analysis. Elife. 2023;12:e84051. [19] BURGESS S, THOMPSON SG. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur J Epidemiol. 2017;32(5):377-389. [20] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, HAYCOCK PC, et al. Consistent estimation in mendelian randomization with some invalid instruments using a weighted median estimator. Genet Epidemiol. 2016;40(4): 304-314. [21] 马玮玮,陈虹谷,李彤彤,等.基于孟德尔随机化分析肠道菌群与骨密度的因果关系[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(12): 1780-1785. [22] LARSSON SC, BUTTERWORTH AS, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization for cardiovascular diseases: principles and applications. Eur Heart J. 2023;44(47): 4913-4924. [23] YANG M, WAN X, ZHENG H, et al. No evidence of a genetic causal relationship between ankylosing spondylitis and gut microbiota: a two-sample mendelian randomization study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(4):1057. [24] KANG L, LI P, WANG D, et al. Alterations in intestinal microbiota diversity, composition, and function in patients with sarcopenia.Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):4628. [25] DAS M, CRONIN O, KEOHANE DM, et al. Gut microbiota alterations associated with reduced bone mineral density in older adults. Rheumatology(Oxford). 2019;58(12):2295-2304. [26] COSTEA PI, HILDEBRAND F, ARUMUGAM M. Enterotypes in the landscape of gut microbial community composition. Nat Microbiol. 2018;3(1):8-16. [27] RAFII F. The role of colonic bacteria in the metabolism of the natural isoflavone daidzin to equol. Metabolites. 2015;5(1):56-73. [28] 何姣姣,陈玉林,张敏,等.肠道菌群在骨质疏松症发病机制中的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(8):1197-1202. [29] SEELY KD, KOTELKO CA, DOUGLAS H, et al. The human Gut microbiota: a key mediator of osteoporosis and osteogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(17):9452. [30] XU Q, LI D, CHEN J, et al. Crosstalk between the gut microbiota and postmenopausal osteoporosis: mechanisms and applications. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;110:108998. [31] HE J, XU S, ZHANG B, et al. Gut microbiota and metabolite alterations associated with reduced bone mineral density or bone metabolic indexes in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Aging. 2020;12(9):8583-8604. [32] GUAN Z, LUO L, LIU S, et al. The role of depletion of gut microbiota in osteoporosis and osteoarthritis: a narrative review. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:847401. [33] WALDBAUM JDH, XHUMARI J, AKINSUYI OS, et al. Association between dysbiosis in the gut microbiota of primary osteoporosis patients and bone loss. Aging Dis. 2023; 14(6):2081-2095. [34] WANG N, MA S, FU L. Gut microbiota dysbiosis as one cause of osteoporosis by impairing intestinal barrier function. Calcif Tissue Int. 2022;110(2):225-235. [35] LOCANTORE P, DEL GATTO V, GELLI S, et al. The interplay between immune system and microbiota in osteoporosis. Mediators Inflamm. 2020;2020:3686749. [36] YAN J, CHARLES JF. Gut microbiome and bone: to build, destroy, or both? Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2017;15(4):376-384. [37] D’AMELIO P, SASSI F. Gut microbiota, immune system, and bone. Calcif Tissue Int. 2018;102(4):415-425. [38] GUO M, LIU H, YU Y, et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG ameliorates osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats by regulating the Th17/Treg balance and gut microbiota structure. Gut Microbes. 2023;15(1):2190304. [39] ZHAO F, GUO Z, KWOK LY, et al. Bifidobacterium lactis Probio-M8 improves bone metabolism in patients with postmenopausal osteoporosis, possibly by modulating the gut microbiota. Eur J Nutr. 2023;62(2):965-976. [40] JIANG X, QI X, XIE C. Lactobacillus plantarum LP45 inhibits the RANKL/OPG signaling pathway and prevents glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Food Nutr Res. 2023. doi: 10.29219/fnr.v67.9064 |
| [1] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [2] | Dong Tingting, Chen Tianxin, Li Yan, Zhang Sheng, Zhang Lei. Causal relationship between modifiable factors and joint sports injuries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1953-1962. |
| [3] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [4] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [5] | Zhao Jiacheng, Ren Shiqi, Zhu Qin, Liu Jiajia, Zhu Xiang, Yang Yang. Bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers for primary osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1741-1750. |
| [6] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [7] | Li Yueyao, Zhang Min, Yang Jiaju. Cistanoside A mediates p38/MAPK pathway to inhibit osteoclast activity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1144-1151. |
| [8] | Zheng Lin, Jin Wenjun, Luo Shanshan, Huang Rui, Wang Jie, Cheng Yuting, An Zheqing, Xiong Yue, Gong Zipeng, Liao Jian. Eucommia ulmoides promotes alveolar bone formation in ovariectomized rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1159-1167. |
| [9] |
Huang Xiaobin, Ge Jirong, Li Shengqiang, Xie Lihua, Huang Jingwen, He Yanyan, Xue Lipeng.
Mechanisms of different yin nourishing and kidney tonifying methods on osteoclastysis pathway in ovariectomized rats #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1214-1219.
|
| [10] | Qian Kun, Li Ziqing, Sun Shui . Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the occurrence and development of common degenerative bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1285-1295. |
| [11] |
Zhao Wensheng, Li Xiaolin, Peng Changhua, Deng Jia, Sheng Hao, Chen Hongwei, Zhang Chaoju, He Chuan.
Gut microbiota and osteoporotic fractures #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1296-1304.
|
| [12] | Li Jiatong, Jin Yue, Liu Runjia, Song Bowen, Zhu Xiaoqian, Li Nianhu . Association between thyroid function levels and phenotypes associated with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1312-1320. |
| [13] | Lan Shuangli, Xiang Feifan, Deng Guanghui, Xiao Yukun, Yang Yunkang, Liang Jie. Naringin inhibits iron deposition and cell apoptosis in bone tissue of osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 888-898. |
| [14] |
Sun Guanghan, Xie Zhencong, Sun Mi, Xu Yang, Guo Dong.
Therapeutic effect and mechanism by which Trichosanthis Fructus-Allii Macrostemonis Bulbus regulates gut microbiota in a rat model of coronary heart disease #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 917-927.
|
| [15] | Wang Dongyang, Yang Qiaohui, Lin Xinchao. Relationship between vitamin D levels and reproductive characteristics and exercise dietary situation in postmenopausal women [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1021-1025. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||