Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (17): 3724-3731.doi: 10.12307/2025.645
Previous Articles Next Articles
Types and contents of fatty acids and the risk of knee osteoarthritis
Tang Xiran1, Chen Weijian1, 2, Jiang Tao2, Tan Xianyun1, Liu Wengang2
- 1Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 2Guangdong Second Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital (Guangdong Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine Engineering Technology), Guangzhou 510095, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2024-06-14Accepted:2024-08-01Online:2025-06-18Published:2024-11-07 -
Contact:Liu Wengang, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Guangdong Second Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital (Guangdong Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine Engineering Technology), Guangzhou 510095, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Tang Xiran, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Guangdong Provincial Fund for Basic and Applied Basic Research - Natural Science Foundation General Program, No. 2023A1515012615 (to LWG); Guangdong Provincial Fund for Basic and Applied Basic Research - Provincial Enterprises Joint Fund General Project, No. 2022A1515220157 (to LWG); Guangdong Second Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital Scientific Research and Innovation Fund - Excellence Team Project, No. SEZYY2023B16 (to LWG)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tang Xiran, Chen Weijian, Jiang Tao, Tan Xianyun, Liu Wengang . Types and contents of fatty acids and the risk of knee osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3724-3731.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

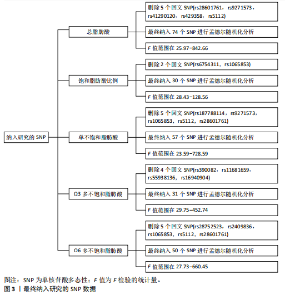
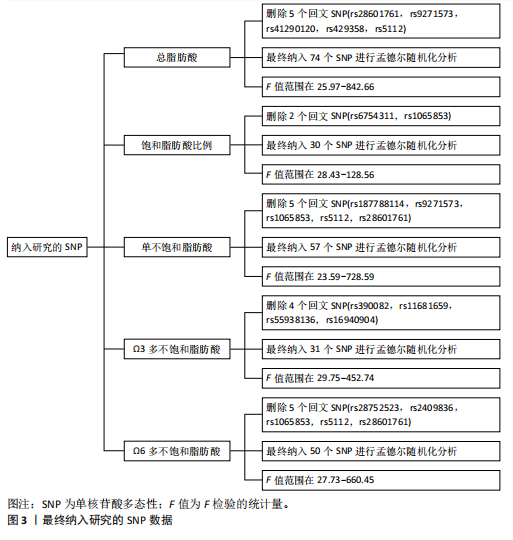
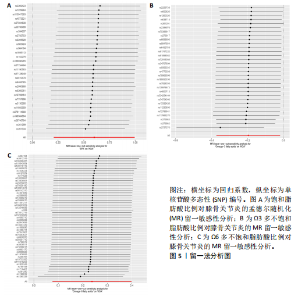
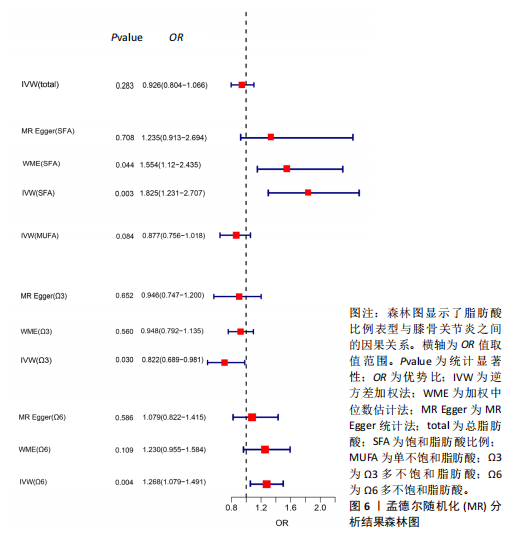
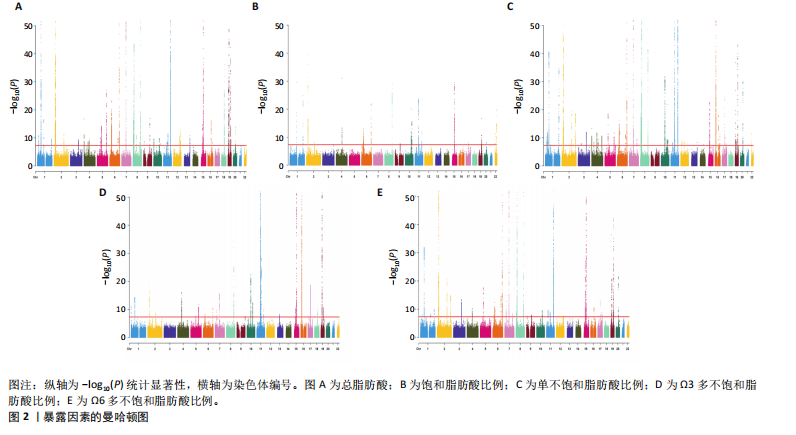
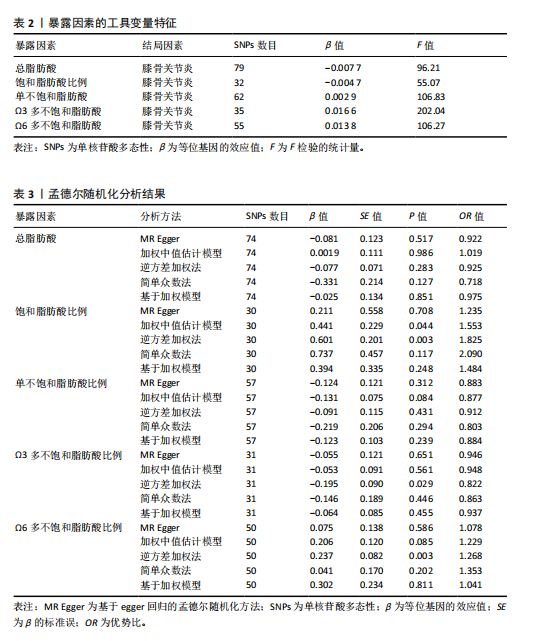
2.1 工具变量选取结果 根据筛选条件,得出与各个暴露表型具有强关联性SNPs,曼哈顿图表示在红线以上的SNPs具有强关联性,见图2。去除连锁不平衡现象、5种暴露表型的F值均大于10表明不存在弱工具变量以及删除混杂因素后,进一步得到筛选的SNP数目,见表2。再分别与提取的结局数据集合并,最终纳入研究的SNP数目见图3。根据MR-Egger截距测试表明数据均不存在水平多效性(P > 0.05),可进行孟德尔随机化分析。 2.2 脂肪酸比例对膝骨关节炎的因果效应 逆方差加权法分析表明,膝骨关节炎作为结局数据集,共有3种脂肪酸比例表型对膝骨关节炎具有显著因果关系(P < 0.05),其中饱和脂肪酸比例(OR=1.825,95%CI:1.230-2.706),Ω6多不饱和脂肪酸比例(OR=1.268,95%CI:1.079-1.491)与膝骨关节炎呈正向因果效应,对膝骨关节炎具"
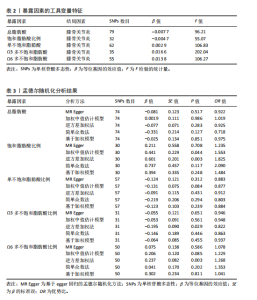
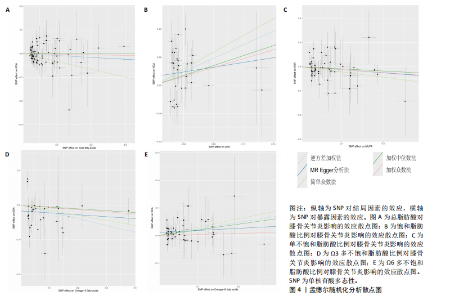
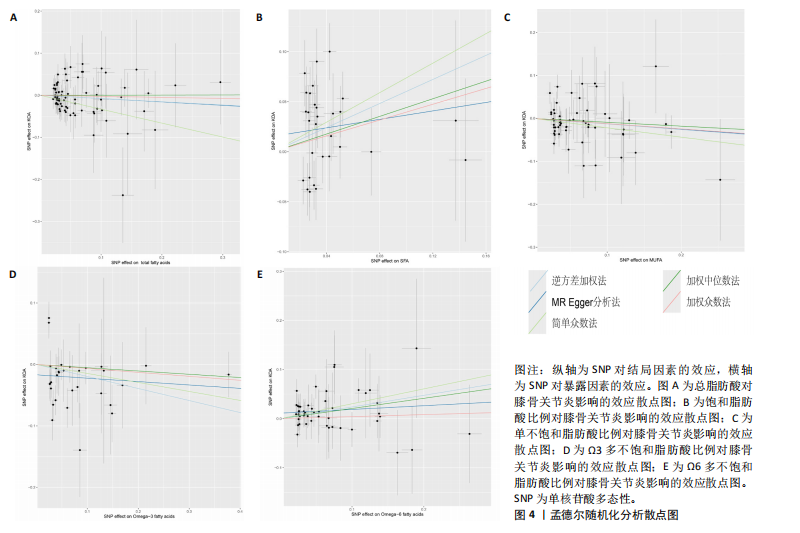
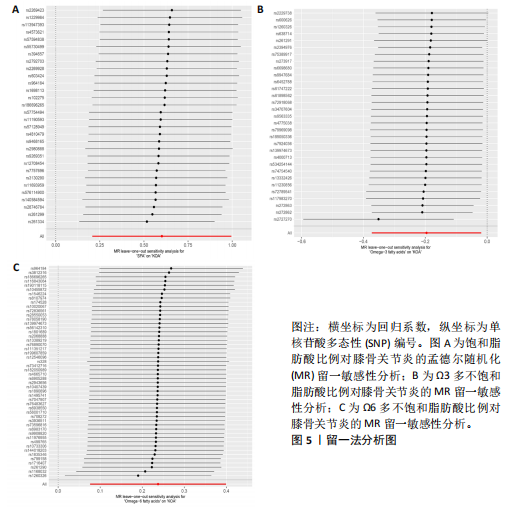
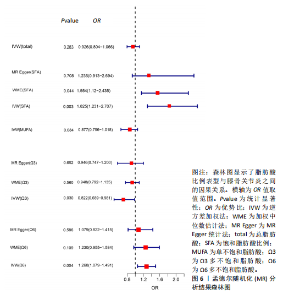
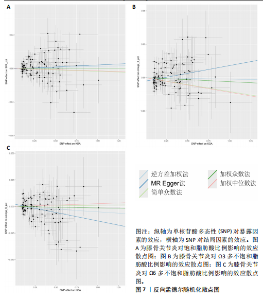
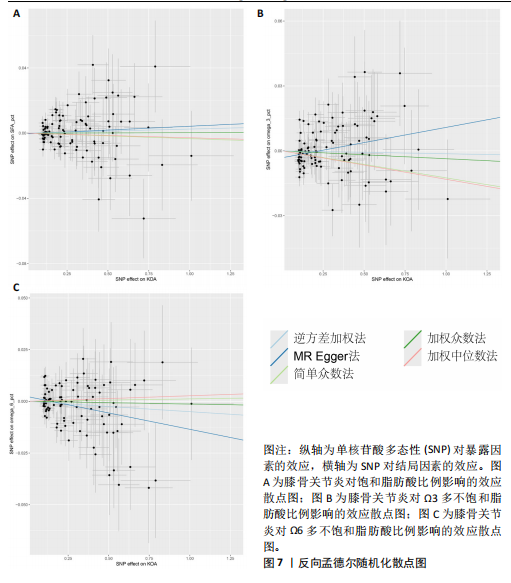
有危险性;Ω3多不饱和脂肪酸比例(OR=0.822,95%CI:0.689-0.981)与膝骨关节炎呈负向因果效应,对膝骨关节炎具有保护作用。总脂肪酸(P=0.283)、单不饱和脂肪酸(P=0.08)与膝骨关节炎无因果关系,见表3。 2.3 敏感性分析结果 散点图显示遗传预测的回归线基本一致,见图4。对饱和脂肪酸比例进行异质性检验,结果提示存在一定的异质性(Q_Pval=0.14),但并不意味着多效性的存在[27],来自不同的数据库、实验及人群等的工具变量就可能存在异质性,其他4种脂肪酸比例表型的异质性检验结果均大于0.05。MR-PRESSO方法进行敏感性分析均未发现对因果关联影响较大的SNP,根据MR-Egger截距测试结果提示均不存在水平多效性(P > 0.05)。留一法分析结果表明,消除任何一个SNP都不会显著影响因果相关的估计,提示孟德尔随机化分析结果稳健[28],见图5。敏感性分析结果的森林图,见图6。 2.4 膝骨关节炎对脂肪酸比例的因果效应 结局数据为饱和脂肪酸比例,逆方差加权法显示(OR=1.002,95%CI:0.995-1.011,P=0.513);当结局为Ω3多不饱和脂肪酸比例,逆方差加权法显示(OR=0.998,95%CI:0.990-1.006,P=0.745);当结局为Ω6"
| [1] 朱治龙,黄国鑫,艾金伟,等.全球膝关节骨性关节炎发病率和患病率分析与趋势预测[J].湖北医药学院学报,2023,42(6):647-654. [2] HEIDARI B. Knee osteoarthritis prevalence, risk factors, pathogenesis and features: Part I. Caspian J Intern Med. 2011;2(2):205-212. [3] 周峻,刘晓雨,王萍,等.社区膝骨关节炎患者非手术治疗现状:多中心横断面研究[J].中国全科医学,2024,27(24):2969-2975. [4] 伍琪瑶,李鑫.退行性膝骨关节炎的康复治疗现状与思考[J].光明中医,2024,39(12):2517-2520. [5] 许成燕,陈军香,王教明,等.中国人群膝骨关节炎危险因素的Meta分析[J].中国循证医学杂志,2021,21(7):772-778. [6] KLEIN S, GASTALDELLI A, YKI-JÄRVINEN H, et al. Why does obesity cause diabetes? Cell Metab. 2022;34(1):11-20. [7] 于晨,李双,袁勇军,等.基于脂肪酸指标的调和植物油品质评析[J].食品安全质量检测学报, 2021,12(6):2073-2079. [8] 谷雪妹,李智强,高仁元,等.YAP甲基化修饰促进肥胖发生的机制研究[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2021,43(6):1193-1201. [9] TAKEUCHI T, KAMEYAMA K, MIYAUCHI E, et al. Fatty acid overproduction by gut commensal microbiota exacerbates obesity. Cell Metab. 2023; 35(2):361-375. [10] 孙桂菊,柳和春,许登峰,等.n-3多不饱和脂肪酸的抗炎作用和2型糖尿病[J].健康教育与健康促进,2020,15(2):116-119. [11] KOYAMA T, UCHIDA K, FUKUSHIMA K, et al. Elevated levels of TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and IL-6 in the synovial tissue of patients with labral tear: a comparative study with hip osteoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):33. [12] INNES JK, CALDER PC. Omega-6 fatty acids and inflammation. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2018;132:41-48. [13] 郭浩阳,汪伟,常鑫,等.类风湿关节炎与2型糖尿病风险的两样本孟德尔随机化研究[J].山东第一医科大学(山东省医学科学院)学报, 2022,43(9):703-706. [14] CLAYTON GL, GONCALVES A, SOARES, et al. A framework for assessing selection and misclassification bias in mendelian randomisation studies: an illustrative example between body mass index and covid-19. BMJ. 2023;381:e072148. [15] SEKULA P, DEL GRECO M F, PATTARO C, et al. Mendelian randomization as an approach to assess causality using observational data. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;27(11):3253-3265. [16] 王惠达,张智,王晗宇,等.代谢综合征组成部分与膝关节骨性关节炎的因果关系:孟德尔随机化研究[J].中国循证医学杂志,2023, 23(11):1241-1246. [17] QIU S, ZHENG K, HU Y, et al. Genetic correlation, causal relationship, and shared loci between vitamin D and COVID-19: a genome-wide cross-trait analysis. J Med Virol. 2023;95(5):e28780. [18] LYON MS, ANDREWS SJ, ELSWORTH B, et al. The variant call format provides efficient and robust storage of GWAS summary statistics. Genome Biol. 2021;22(1):32. [19] LUO X, RUAN Z, LIU L. Causal relationship between telomere length and epilepsy: a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Epilepsia Open. 2023;8(4):1432-1439. [20] HAN Y, ZHANG Y, ZENG X. Assessment of causal associations between uric acid and 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:1024675. [21] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SG, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44(2):512-525. [22] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SG, HAYCOCK PC, et al. Consistent estimation in mendelian randomization with some invalid instruments using a weighted median estimator. Genet Epidemiol. 2016;40(4): 304-314. [23] DOBRIJEVIC E, VAN ZWIETEN A, KIRYLUK K, et al. Mendelian randomization for nephrologists. Kidney Int. 2023;104(6):1113-1123. [24] HEMANI G, TILLING K, DAVEY SMITH G. Correction: orienting the causal relationship between imprecisely measured traits using GWAS summary data. PLoS Genet. 2017;13(12):e1007149. [25] 李镇圻,杜宁,和红阳.两样本孟德尔随机化分析原发性硬化性胆管炎与结直肠癌发生风险的关系[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2023,39(3):567-572. [26] 谭文岳,韦柏安,王树声,等.甲状腺功能障碍与前列腺癌的因果关联:两样本孟德尔随机化研究[J].重庆医科大学学报,2023,48(8):935-939. [27] BOWDEN J, HOLMES MV. Meta-analysis and Mendelian randomization: a review. Res Synth Methods. 2019;10(4):486-496. [28] 陈继鑫,余伟杰,郭天赐,等.睡眠特征与骨关节炎发病风险:两样本与多变量孟德尔随机化分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(32):5203-5209. [29] 宋秉娜,胡翔,彭子涵,等.膝骨关节炎病人运动康复的研究进展[J].护理研究,2022,36(10): 1827-1830. [30] HALL M, VAN DER ESCH M, HINMAN RS, et al. How does hip osteoarthritis differ from knee osteoarthritis? Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022; 30(1):32-41. [31] JIANG L, XIE X, WANG Y, et al. Body mass index and hand osteoarthritis susceptibility: an updated meta-analysis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016;19(12): 1244-1254. [32] BROUWER GM, VAN TOL AW, BERGINK AP, et al. Association between valgus and varus alignment and the development and progression of radiographic osteoarthritis of the knee. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(4):1204-1211. [33] ANDRIACCHI TP, MUNDERMANN A. The role of ambulatory mechanics in the initiation and progression of knee osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2006;18(5):514-518. [34] 石银朋,奚阳,张志毅,等.血脂对骨关节炎影响研究进展[J].中国实用内科杂志,2020,40(1): 67-69. [35] DENG W, YI Z, YIN E, et al. Effect of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids supplementation for patients with osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):381. [36] 吴松,王鑫,张彦,等.高糖高脂饮食对兔膝关节软骨形态的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(33):6433-6438. [37] BAO M, ZHANG K, WEI Y, et al. Therapeutic potentials and modulatory mechanisms of fatty acids in bone. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(2):e12735. [38] BARAN P, HANSEN S, WAETZIG GH, et al. The balance of interleukin (IL)-6, IL-6.soluble IL-6 receptor (sIL-6R), and IL-6.sIL-6R.sgp130 complexes allows simultaneous classic and trans-signaling. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(18):6762-6775. [39] ROGERO MM, CALDER PC. Obesity, inflammation, Toll-like receptor 4 and fatty acids. Nutrients. 2018;10(4):432. [40] SEKAR S, SHAFIE SR, PRASADAM I, et al. Saturated fatty acids induce development of both metabolic syndrome and osteoarthritis in rats. Sci Rep. 2017;7:46457. [41] HWANG DH, KIM JA, LEE JY. Mechanisms for the activation of Toll-like receptor 2/4 by saturated fatty acids and inhibition by docosahexaenoic acid. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016;785:24-35. [42] NA HS, PARK JS, CHO KH, et al. Interleukin-1-interleukin-17 signaling axis induces cartilage destruction and promotes experimental osteoarthritis. Front Immunol. 2020;11:730. [43] Du X, LIU ZY, TAO XX, et al. Research progress on the pathogenesis of knee osteoarthritis. Orthop Surg. 2023;15(9):2213-2224. [44] FIELDS JK, GUNTHER S, SUNDBERG EJ. Structural basis of IL-1 family cytokine signaling. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1412. [45] WESTACOTT CI, BARAKAT AF, WOOD L, et al. Tumor necrosis factor alpha can contribute to focal loss of cartilage in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2000;8(3):213-221. [46] MUSTONEN AM, NIEMINEN P. Fatty acids and oxylipins in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis-a complex field with significant potential for future treatments. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2021; 23(6):41. [47] ELAGIZI A, LAVIE CJ, O’KEEFE E, et al. An update on omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and cardiovascular health. Nutrients. 2021;13(1):204. [48] GHEITA T, KAMEL S, HELMY N, et al. Omega-3 fatty acids in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: effect on cytokines (IL-1 and TNF-α), disease activity and response criteria. Clin Rheumatol. 2012;31(2):363-366. [49] 芦玲,白琳,武猛,等.PUFA对LPS致ALI大鼠的氧化应激及TLR4、TNF-α的影响[J].国际检验医学杂志,2017,38(24):3383-3385. [50] DENNIS EA, NORRIS PC. Eicosanoid storm in infection and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015;15(11):724. [51] CORDINGLEY DM, CORNISH SM. Omega-3 fatty acids for the management of osteoarthritis: a narrative review. Nutrients. 2022;14(16):3362. [52] SIMONETTO M, INFANTE M, SACCO RL, et al. A novel anti-inflammatory role of omega-3 pufas in prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis and vascular cognitive impairment and dementia. Nutrients. 2019;11(10):2279. [53] SKRIVANKOVA VW, RICHMOND RC, WOOLF BAR, et al. Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology using mendelian randomization: the STROBE-MR statement. JAMA. 2021;326(16):1614-1621. |
| [1] | Chen Jiayong, Tang Meiling, Lu Jianqi, Pang Yan, Yang Shangbing, Mao Meiling, Luo Wenkuan, Lu Wei, Zhou Jiatan. Based on Mendelian randomization, the causal relationship between 1400 metabolites and sarcopenia and the correlation analysis of cardiovascular disease were investigated [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-11. |
| [2] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [3] | Dong Tingting, Chen Tianxin, Li Yan, Zhang Sheng, Zhang Lei. Causal relationship between modifiable factors and joint sports injuries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1953-1962. |
| [4] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [5] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [6] |
Zhao Wensheng, Li Xiaolin, Peng Changhua, Deng Jia, Sheng Hao, Chen Hongwei, Zhang Chaoju, He Chuan.
Gut microbiota and osteoporotic fractures #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1296-1304.
|
| [7] | Ma Haoyu, Qiao Hongchao, Hao Qianqian, Shi Dongbo. Causal effects of different exercise intensities on the risk of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1305-1311. |
| [8] | Li Jiatong, Jin Yue, Liu Runjia, Song Bowen, Zhu Xiaoqian, Li Nianhu . Association between thyroid function levels and phenotypes associated with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1312-1320. |
| [9] | Wu Guangtao, Qin Gang, He Kaiyi, Fan Yidong, Li Weicai, Zhu Baogang, Cao Ying . Causal relationship between immune cells and knee osteoarthritis: a two-sample bi-directional Mendelian randomization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1081-1090. |
| [10] | Fang Ying, Zhang Yanwei, Li Xi, Yan Peidong, Bi Miao. Improvements in automatic diagnosis methods for knee osteoarthritis based on deep learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7511-7518. |
| [11] | Ji Long, Chen Ziyang, , Jin Pan, Kong Xiangkui, Pu Rui, . Lipophagy, exercise intervention and prevention and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7611-7619. |
| [12] | Wang Xuepeng, , He Yong, . Effect of insulin-like growth factor family member levels on inflammatory arthritis: a FinnGen biobank-based analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7656-7662. |
| [13] | Wang Tao, Wang Shunpu, Min Youjiang, Wang Min, Li Le, Zhang Chen, Xiao Weiping. Causal relationship between gut microbiota and rheumatoid arthritis: data analysis in European populations based on GWAS data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7663-7668. |
| [14] | Han Jie, Pan Chengzhen, Shang Yuzhi, Zhang Chi. Identification of immunodiagnostic biomarkers and drug screening for steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7690-7700. |
| [15] | Wu Zhenhua, Zhang Xiwei, Wang Yipin, Li Qianqian. Relationship between seven serum lipid traits and osteoarthritis: a large sample analysis of European population in IEU OPEN GWAS database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 7004-7014. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||