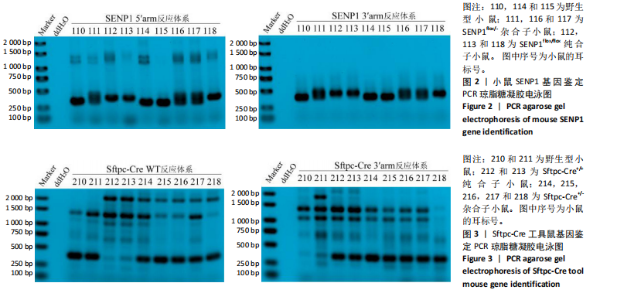
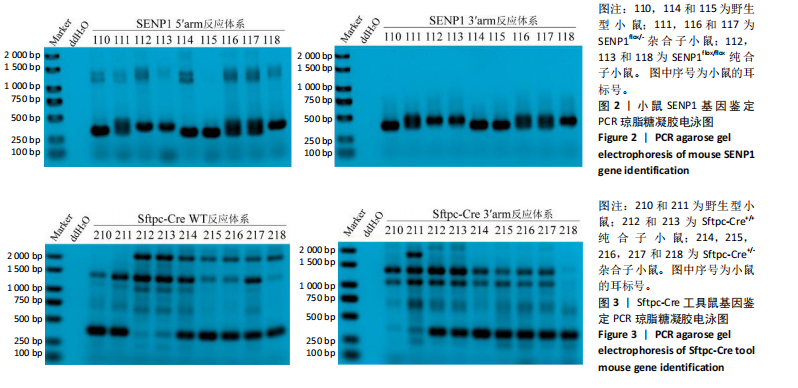
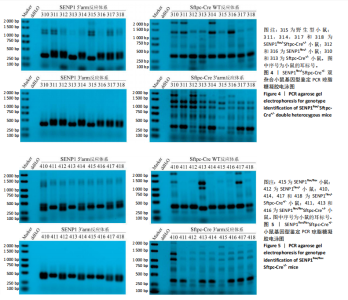
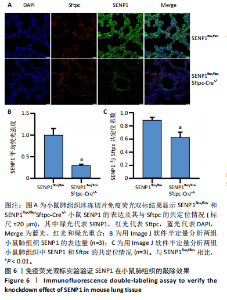
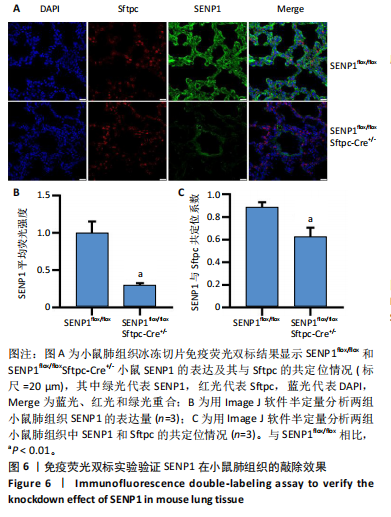
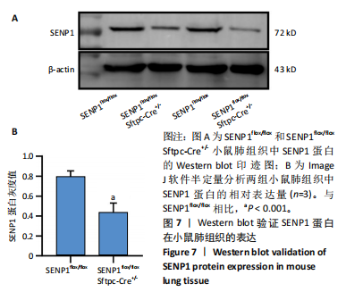
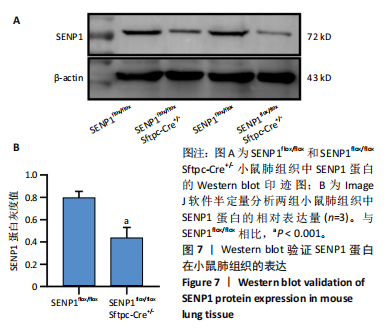
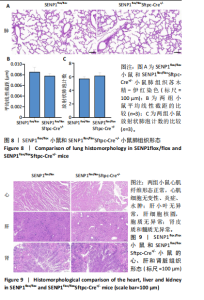
[1] YAU TY, SANDER W, EIDSON C, et al. SUMO Interacting Motifs: Structure and Function. Cells. 2021;10(11):2825.
[2] FERGANI IF, FRICK LR. Wrestling and Wrapping: A Perspective on SUMO Proteins in Schwann Cells. Biomolecules. 2021;11(7):1055.
[3] HOTZ PW, MÜLLER S, MENDLER L. SUMO-specific Isopeptidases Tuning Cardiac SUMOylation in Health and Disease. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:786136.
[4] LI P, JING H, WANG Y, et al. SUMO modification in apoptosis. J Mol Histol. 2021;52(1):1-10.
[5] 王嵘.SENP1的生理功能研究进展[J].军事医学,2015,39(10):805-807.
[6] 马禕文,吕翔.抑制SUMO特异性蛋白酶1在小鼠急性肺损伤中的保护作用[J].中国临床医学,2015,22(6):738-740.
[7] 万雪晴,卢红艳,万峰云,等.SUMO1和SENP1在新生大鼠肺发育过程中的表达[J].基础医学与临床,2019,39(2):225-229.
[8] DONG W, ZHU X, LIU X, et al. Role of the SENP1-SIRT1 pathway in hyperoxia-induced alveolar epithelial cell injury. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;173:142-150.
[9] DU FL, DONG WB, ZHANG C, et al. Budesonide and Poractant Alfa prevent bronchopulmonary dysplasia via triggering SIRT1 signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(24):11032-11042.
[10] CALKOVSKA A, KOLOMAZNIK M, CALKOVSKY V. Alveolar type II cells and pulmonary surfactant in COVID-19 era. Physiol Res. 2021;70(S2): S195-S208.
[11] PARIMON T, YAO C, STRIPP BR, et al. Alveolar Epithelial Type II Cells as Drivers of Lung Fibrosis in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(7):2269.
[12] LU HY, WANG MY, ZHU SX, et al. ILC2 influence the differentiation of alveolar type II epithelial cells in bronchopulmonary dysplasia mice. J Leukoc Biol. 2023;114(6):604-614.
[13] 赵许,董文斌,雷小平,等.SENP1基因沉默的人Ⅱ型肺泡上皮细胞系构建[J].山东医药,2017,57(3):16-19.
[14] YANG K, YANG M, SHEN Y, et al. Resveratrol Attenuates Hyperoxia Lung Injury in Neonatal Rats by Activating SIRT1/PGC-1α Signaling Pathway. Am J Perinatol. 2024;41(8):1039-1049.
[15] 李靖飞,张小鹃,徐艺心,等.基于Cre-LoxP系统的高尔基体蛋白73胰腺特异性敲除小鼠模型建立与鉴定[J].军事医学,2023,47(7): 487-492.
[16] 黄庆,甄兰,赵桂霖,等.巨噬细胞条件性GP73基因敲除小鼠的构建及鉴定[J].中国癌症防治杂志,2023,15(6):630-636.
[17] 吴孟瑶,张雪婷,程倩倩,等.基于Cre-LoxP系统的B细胞特异性荧光报告基因小鼠模型的构建及鉴定[J].中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2023,37(5):361-367.
[18] 熊锐,李国瑞,邹诗施,等.利用Cre-loxP系统构建AT2细胞特异性敲除HDAC3基因小鼠[J].医学研究杂志,2023,52(2):24-29+148.
[19] 王肖,赖舒畅,叶艳诗,等.利用Cre/lox P系统构建胰岛β细胞特异性敲除PDHA1基因的小鼠模型[J].中国组织工程研究,2019, 23(31):5023-5029.
[20] 袁涛,王勇卓,黄远章,等.基于Cre/LoxP系统建立软骨组织特异性印第安刺猬蛋白基因敲除小鼠模型[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(19):3013-3018.
[21] CHEN YD, LIU JY, LU YM, et al. Functional roles of C/EBPα and SUMO‑ modification in lung development. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40(4):1037-1046.
[22] ZHU Y, CHEN X, MI L, et al. Sumoylation of CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein α inhibits lung differentiation in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia model rats. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(12):7067-7071.
[23] HE S, FAN C, JI Y, et al. SENP3 facilitates M1 macrophage polarization via the HIF-1α/PKM2 axis in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Innate Immun. 2023;29(1-2):25-34.
[24] ZHOU F, DAI A, JIANG Y, et al. SENP‑1 enhances hypoxia‑induced proliferation of rat pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells by regulating hypoxia‑inducible factor‑1α. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(4):3482-3490.
[25] KANG L, WANG X, WANG J, et al. SENP1 knockdown-mediated CTCF SUMOylation enhanced its stability and alleviated lipopolysaccharide-evoked inflammatory injury in human lung fibroblasts via regulation of FOXA2 transcription. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2024;1868(1): 130500.
[26] PANDEY D, NOMURA Y, ROSSBERG MC, et al. Hypoxia Triggers SENP1 (Sentrin-Specific Protease 1) Modulation of KLF15 (Kruppel-Like Factor 15) and Transcriptional Regulation of Arg2 (Arginase 2) in Pulmonary Endothelium. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018;38(4):913-926.
[27] SUN W, YANG X, CHEN L, et al. FSTL1 promotes alveolar epithelial cell aging and worsens pulmonary fibrosis by affecting SENP1-mediated DeSUMOylation. Cell Biol Int. 2023;47(10):1716-1727.
[28] WAN XQ, CAI JY, ZHU Y, et al. SENP1 has an important role in lung development and influences the differentiation of alveolar type 2 cells. Int J Mol Med. 2019;43(1):371-381.
[29] ZHANG D, ZHAO X, ZHANG D, et al. Hyperoxia reduces STX17 expression and inhibits the autophagic flux in alveolar type II0 epithelial cells in newborn rats. Int J Mol Med. 2020;46(2):773-781.
[30] CONFALONIERI P, VOLPE MC, JACOB J, et al. Regeneration or Repair? The Role of Alveolar Epithelial Cells in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF). Cells. 2022;11(13):2095. |