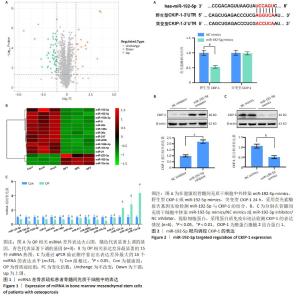
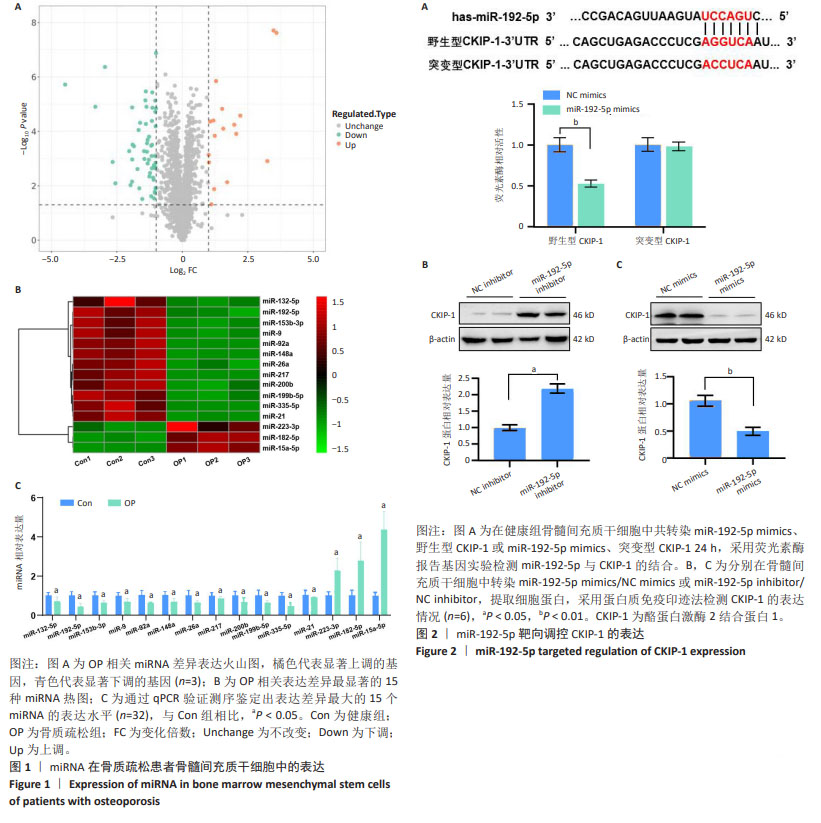
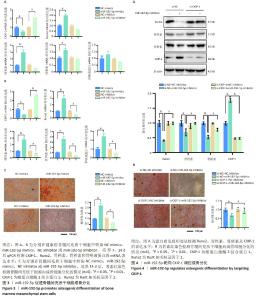
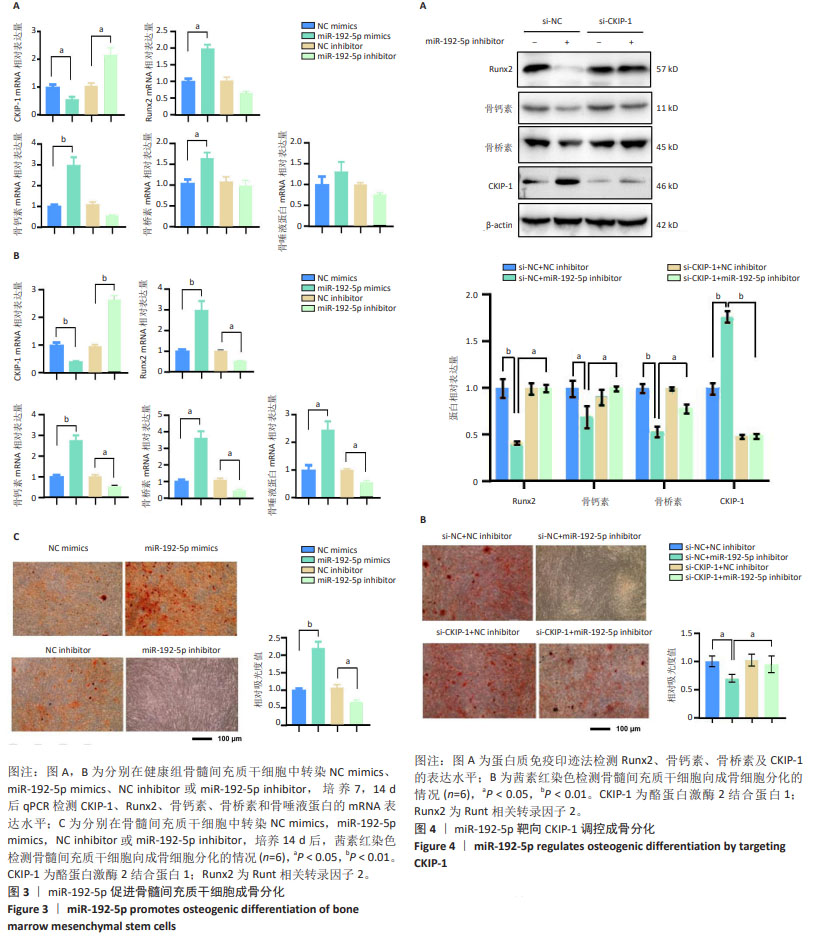
[1] VILACA T, EASTELL R, SCHINI M. Osteoporosis in men. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022;10(4):273-283.
[2] REID IR, BILLINGTON EO. Drug therapy for osteoporosis in older adults. Lancet. 2022;399(10329):1080-1092.
[3] KENDLER DL, COSMAN F, STAD RK, et al. Denosumab in the treatment of osteoporosis: 10 years later: a narrative review. Adv Ther. 2022; 39(1):58-74.
[4] FU L, ZHANG L. Physiological functions of CKIP-1: from molecular mechanisms to therapy implications. Ageing Res Rev. 2019;53:100908.
[5] ZHANG X, WANG Q, WAN Z, et al. CKIP-1 knockout offsets osteoporosis induced by simulated microgravity. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2016;122(2): 140-148.
[6] HO PT, CLARK IM, LE L. MicroRNA-based diagnosis and therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(13):7167.
[7] CORREIA SM, GJORGJIEVA M, DOLICKA D, et al. Deciphering miRNAs’ action through miRNA editing. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(24):6249.
[8] HILL M, TRAN N. miRNA interplay: mechanisms and consequences in cancer. Dis Model Mech. 2021;14(4):dmm047662.
[9] WANG H, ALARCON CN, LIU B, et al. Genetically engineered and enucleated human mesenchymal stromal cells for the targeted delivery of therapeutics to diseased tissue. Nat Biomed Eng. 2022; 6(7):882-897.
[10] GAO F, NAN F, FENG J, et al. Discovery of conserved and novel microRNAs in galdieria sulphuraria. Iran J Biotechnol. 2021;19(2):e2671.
[11] KIM DS, LEE SY, LEE JH, et al. MicroRNA-103a-3p controls proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived stromal cells. Exp Mol Med. 2015;47(7):e172.
[12] ZHANG Z, XIE X, YAO Q, et al. PPARdelta agonist prevents endothelial dysfunction via induction of dihydrofolate reductase gene and activation of tetrahydrobiopterin salvage pathway. Br J Pharmacol. 2019;176(16):2945-2961.
[13] WEI C, WANG B, PENG D, et al. Pan-cancer analysis shows that ALKBH5 is a potential prognostic and immunotherapeutic biomarker for multiple cancer types including gliomas. Front Immunol. 2022;13:849592.
[14] UENAKA M, YAMASHITA E, KIKUTA J, et al. Osteoblast-derived vesicles induce a switch from bone-formation to bone-resorption in vivo. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):1066.
[15] MARCHESONI A, CAPORALI R, LUBRANO E. Clinical implications of peripheral new bone formation in psoriatic arthritis: a literature-based review. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019;37(2):310-317.
[16] LIU J, LU C, WU X, et al. Targeting osteoblastic casein kinase-2 interacting protein-1 to enhance Smad-dependent BMP signaling and reverse bone formation reduction in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Sci Rep. 2017;7:41295.
[17] PIACENTINO ML, BRONNER ME. Intracellular attenuation of BMP signaling via CKIP-1/Smurf1 is essential during neural crest induction. PLoS Biol. 2018;16(6):e2004425.
[18] ZHU Q, FU Y, CUI CP, et al. OTUB1 promotes osteoblastic bone formation through stabilizing FGFR2. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):142.
[19] WANG Y, NIR J, WANG Y, et al. CKIP-1 couples Smurf1 ubiquitin ligase with Rpt6 subunit of proteasome to promote substrate degradation. EMBO Rep. 2012;13(11):1004-1011.
[20] NIE J, LIU L, XING G, et al. CKIP-1 acts as a colonic tumor suppressor by repressing oncogenic Smurf1 synthesis and promoting Smurf1 autodegradation. Oncogene. 2014;33(28):3677-3687.
[21] YANG Y, YUJIAO W, FANG W, et al. The roles of miRNA, lncRNA and circRNA in the development of osteoporosis. Biol Res. 2020; 53(1):40.
[22] DIENER C, KELLER A, MEESE E. Emerging concepts of miRNA therapeutics: from cells to clinic. Trends Genet. 2022;38(6):613-626.
[23] HE B, ZHAO Z, CAI Q, et al. miRNA-based biomarkers, therapies, and resistance in cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(14):2628-2647.
[24] SUN Z, SHI K, YANG S, et al. Effect of exosomal miRNA on cancer biology and clinical applications. Mol Cancer. 2018;17(1):147.
[25] SU X, LIAO L, SHUAI Y, et al. MiR-26a functions oppositely in osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs and ADSCs depending on distinct activation and roles of Wnt and BMP signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2015; 6(8):e1851.
[26] HUANG K, FU J, ZHOU W, et al. MicroRNA-125b regulates osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by targeting cbfbeta in vitro. Biochimie. 2014;102:47-55.
[27] ZHANG Y, CHENG W, HAN B, et al. Let-7i-5p functions as a putative osteogenic differentiation promoter by targeting CKIP-1. Cytotechnology. 2021;73(1):79-90.
[28] LOU L, TIAN M, CHANG J, et al. MiRNA-192-5p attenuates airway remodeling and autophagy in asthma by targeting MMP-16 and ATG7. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;122:109692.
[29] ZOU P, ZHU M, LIAN C, et al. miR-192-5p suppresses the progression of lung cancer bone metastasis by targeting TRIM44. Sci Rep. 2019; 9(1):19619.
[30] VAJEN B, GREIWE L, SCHAFFER V, et al. MicroRNA-192-5p inhibits migration of triple negative breast cancer cells and directly regulates Rho GTPase activating protein 19. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2021;60(11):733-742.
[31] ZHOU S, XIONG M, DAI G, et al. MicroRNA-192-5p suppresses the initiation and progression of osteosarcoma by targeting USP1. Oncol Lett. 2018;15(5):6947-6956.
|