Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (30): 4770-4776.doi: 10.12307/2024.624
Previous Articles Next Articles
Finite element analysis of reamed versus undreamed proximal femoral nail antirotation-II in treatment of 31-A3 intertrochanteric femur fracture
Liu Zemin, Wang Dong, Li Yan, Liu Min, Chen Bin, Wang Caoqi, Lyu Xin, Zhang Yonghong
- Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2023-07-05Accepted:2023-08-16Online:2024-10-28Published:2023-12-23 -
Contact:Zhang Yonghong, MD, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Liu Zemin, Doctoral candidate, Physician, Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82172439 (to ZYH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Zemin, Wang Dong, Li Yan, Liu Min, Chen Bin, Wang Caoqi, Lyu Xin, Zhang Yonghong. Finite element analysis of reamed versus undreamed proximal femoral nail antirotation-II in treatment of 31-A3 intertrochanteric femur fracture[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(30): 4770-4776.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
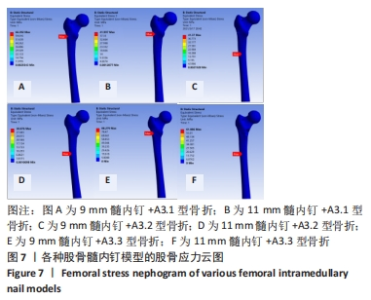
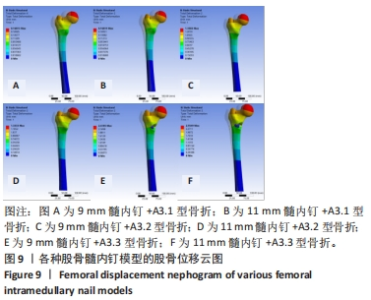
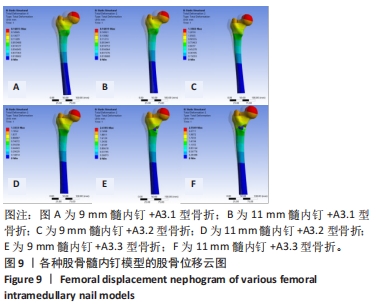
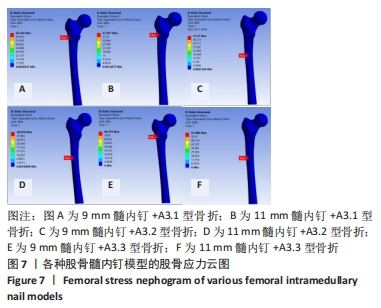
2.2 股骨的von Mises应力分布 3组不同骨折分型的股骨-内固定模型中,股骨最大应力值出现的位置各有不同,见图7。不论采用9 mm或11 mm髓内钉固定,A3.1型股骨应力集中均出现于股骨近端外侧壁与内固定接触处,9 mm髓内钉固定股骨最大应力值66.39 MPa,大于11 mm髓内钉固定时的42 MPa。A3.2型股骨应力集中部位与固定的髓内钉直径无关,均出现在远端锁钉与股骨外侧皮质接触处,9 mm髓内钉固定时股骨最大应力值41.37 MPa,大于11 mm髓内钉固定时股骨的30.88 MPa。A3.3型股骨应力集中部位与髓内钉固定直径有关,9 mm髓内钉固定时股骨最大应力值为88.28 MPa,位于股骨近端外侧壁与内固定接触处;11 mm髓内钉固定时股骨最大应力值位于远端锁钉与股骨外侧皮质接触处,其值61.89 MPa小于9 mm髓内钉固定时股骨最大应力值。"
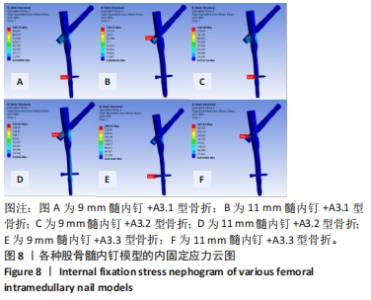
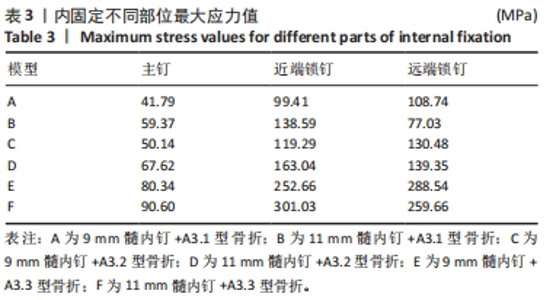
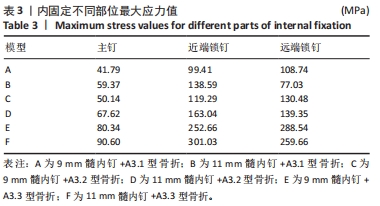
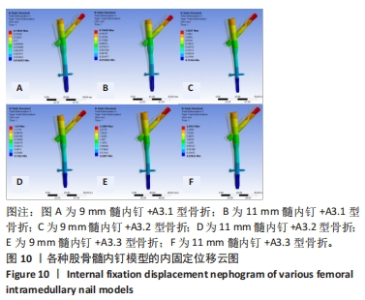
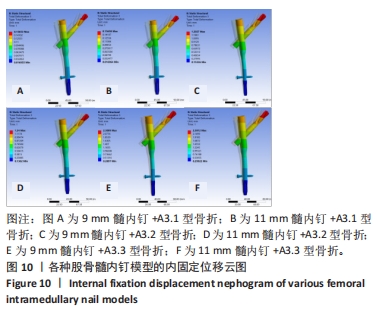
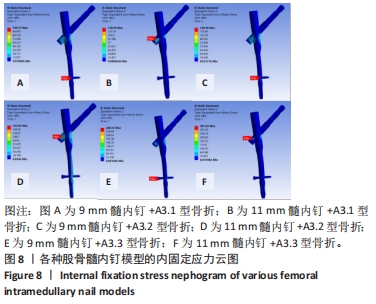
2.3 内固定的von Mises应力分布 3组不同骨折分型的股骨-内固定模型中,9 mm髓内钉固定时内固定应力主要集中于远端锁钉,11 mm髓内钉固定时内固定应力主要集中于近端锁钉与主钉接触处,见图8。A3.1型骨折采用9 mm髓内钉固定时内固定的最大应力值108.74 MPa小于11 mm髓内钉固定时的138.59 MPa。A3.2型骨折采用9 mm髓内钉固定时内固定的最大应力值130.48 MPa小于11 mm髓内钉固定时的163.04 MPa。A3.3型骨折采用9 mm髓内钉固定时内固定的最大应力值288.54 MPa小于11 mm髓内钉固定时的421.45 MPa。6个模型内固定不同部位最大应力值,见表3,可见A3.1到A3.3型,内固定各部位最大应力值呈现增大趋势。同一分型内,随着髓内钉直径增大,主钉和近端锁钉最大应力值增大,远端锁钉最大应力值减小。"
| [1] BRAUER CA, COCA-PERRAILLON M, CUTLER DM, et al. Incidence and mortality of hip fractures in the United States. JAMA. 2009;302(14): 1573-1579. [2] 王璞. 老年髋部骨折流行病学特征及致伤因素分析[D].西安:中国人民解放军空军军医大学,2022. [3] 葛迅, 陈小虎, 吴成玉, 等. 股骨转子间骨折的治疗进展[J]. 锦州医科大学学报,2019,40(4):109-112. [4] 冯俊超,高明暄,骆文远.股骨转子间骨折外侧壁与内侧壁的意义[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2023,31(5):436-440. [5] HAN L, LIU JJ, HU YG, et al. Controlled Study On Gamma Nail and Proximal Femoral Locking Plate for Unstable Intertrochanteric Femoral Fractures with Broken Lateral Wall. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):11114. [6] 吴钟汉,王景坤,李涛,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗外侧壁完整型和外侧壁危险型股骨转子间骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2024, 28(6):911-916. [7] 陈心敏, 罗斯嘉, 夏卓伟, 等. 钉道强化股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗老年A3.3型股骨转子间骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020,24(27):4265-4271. [8] 杨大威. 股骨转子间骨折的研究进展[J]. 创伤外科杂志,2020, 22(12):959-961. [9] AUDIGÉ L, HANSON B, SWIONTKOWSKI MF. Implant-Related Complications in the Treatment of Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures: Meta-Analysis of Dynamic Screw-Plate Versus Dynamic Screw-Intramedullary Nail Devices. Int Orthop. 2003;27(4):197-203. [10] 刘泽民, 吕欣, 刘晋元, 等. 髋部骨折2342例流行病学分布特点的单中心分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(32):5085-5091. [11] 罗先正, 张薇. 髓内钉的生物力学设计[J]. 中华骨科杂志,1997, 10(4):272-276. [12] ROSA N, MARTA M, VAZ M, et al. Intramedullary Nailing Biomechanics: Evolution and Challenges. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2019;233(3):295-308. [13] YANG S, YANG Y, HUO Y, et al. Effect of the degree of displacement of the third fragment on healing of femoral shaft fracture treated by intramedullary nailing. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):380. [14] JUNG O, LINDNER C, PANTERMEHL S, et al. Heat Development During Medical Drilling: Influencing Factors and Examination Methods - Overview and First Results. In Vivo. 2021;35(6):3011-3017. [15] GIANNOUDIS PV, SNOWDEN S, MATTHEWS SJ, et al. Temperature rise during reamed tibial nailing. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(395):255-261. [16] OCHSNER PE, BAUMGART F, KOHLER G. Heat-induced segmental necrosis after reaming of one humeral and two tibial fractures with a narrow medullary canal. Injury. 1998;29(Suppl S2):B1-B10. [17] ROMAN PFEIFER MD, BARKATALI BM, PETER GIANNOUDIS MD, et al. Physiologic Effects Associated with Intramedullary Reaming. Springer London, 2015. [18] BREKELMANS WAM, POORT HW, SLOOFF TJJH. A New Method to Analyse the Mechanical Behaviour of Skeletal Parts. Acta Orthop Scand. 1972;43(5):301-317. [19] GHOSH R, CHANDA S, CHAKRABORTY D. Application of finite element analysis to tissue differentiation and bone remodelling approaches and their use in design optimization of orthopaedic implants: A review. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng. 2022;38(10):e3637. [20] 冯卫. 三种股骨近端髓内固定系统(PFNA、PFNA-II、InterTan)与中国人股骨近端形态学匹配性研究及其固定股骨转子间骨折的有限元分析[D]. 广州:南方医科大学,2012. [21] 乔文, 吕欣, 刘晋元, 等. 有限元评估尖顶距与股距尖顶距对股骨转子间骨折髓内钉内固定术后稳定性的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(36):5755-5763. [22] 张世民, 余斌. Ao/Ota-2018版股骨转子间骨折分类的解读与讨论[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,20(7):583-587. [23] 袁高翔, 张伟滨. 有限元分析在骨骼肌肉系统模型材料特性研究中的应用[J]. 国际骨科学杂志,2011,32(6):352-355. [24] 张国栋, 廖维靖, 陶圣祥, 等. 股骨颈有限元分析的赋材料属性方法探讨及有效性验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(52):10263-10268. [25] 徐锴, 李开南. 三种内固定固定股骨转子间六部分骨折各分型稳定性的有限元分析[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2019,21(4):345-352. [26] 蔡群斌, 邹霞, 胡剑涛, 等. 有限元法分析尖顶距与股骨近端防旋髓内钉固定股骨转子间骨折稳定性的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021,25(6):831-836. [27] 武建超. 内外侧壁损伤及小转子骨折模式对股骨粗隆间骨折生物力学影响的有限元分析[D]. 兰州:兰州大学,2020. [28] 虎群盛. 改良股骨近端髓内钉固定Evans ⅳ型股骨转子间骨折的有限元分析[D]. 广州:广州中医药大学,2017. [29] KEYAK JH, KANEKO TS, TEHRANZADEH J, et al. Predicting Proximal Femoral Strength Using Structural Engineering Models. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;(437):219-228. [30] 杜育任. 股骨转子间骨折形态特点对内固定效果的影响[D]. 天津:天津医科大学,2019. [31] 胡慧婷. 股骨有限元建模及相应的生物力学分析[D]. 太原:太原理工大学,2014. [32] HELLER MO. Finite element analysis in orthopedic biomechanics[M].Human orthopaedic biomechanics. Academic Press, 2022:637-658. [33] MISHRA RN, SINGH MK, KUMAR V. Biomechanical analysis of human femur using finite element method: A review study. Mater Today Proc. 2022;56:384-389. [34] GOTFRIED Y. The lateral trochanteric wall: a key element in the reconstruction of unstable pertrochanteric hip fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(425):82-86. [35] MUSTAFA MA, LI S, BANO S, et al. Advances in the Restoration and Fixation of Lateral Femoral Wall Fracture. Proc Ant Res. 2023;7(1):30-40. [36] 林荣侯, 刘勇, 隋丽娟, 等. InterTAN、PFNA、DHS治疗不稳定性股骨粗隆间骨折的比较[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(6):507-511. [37] HUANG C, WU X. Surgical Selection of Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures: PFNA Combined with or without Cerclage Cable. Biomed Res Int. 2021;1:1-12. [38] TIAN Z, CHEN J, ZHANG Y, et al. A Retrospective Study of 98 Elderly Patients with High-Risk Lateral Femoral Wall Intertrochanteric Hip Fractures to Compare Outcomes Following Surgery with Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA) Versus Dynamic Hip Screw (DHS). Med Sci Monit. 2022;28:e936923. [39] MUKHERJEE K, PRASHANTH KR, KUMAR RD. Mismatch of short straight proximal femur nails with anterior bow of femur in Indian population- A radiological and functional analysis. J Orthop. 2022;29:65-70. [40] BONG MR, KOVAL KJ, EGOL KA. The history of intramedullary nailing. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2006;64(3-4):94-97. [41] TUCKER SM, WEE H, FOX E, et al. Parametric Finite Element Analysis of Intramedullary Nail Fixation of Proximal Femur Fractures. J Orthop Res. 2019;37(11):2358-2366. [42] 徐绍勇. 交锁髓内钉扩髓与否在治疗胫骨骨折中的临床比较研究[D]. 福州:福建中医药大学,2010. [43] CLAES L. Improvement of clinical fracture healing-What can be learned from mechano-biological research? J Biomech. 2021;115:110148. [44] 何祥鑫, 林梓凌, 李鹏飞, 等. 基于Hypermesh 14.0和LS-DYNA的老年转子间骨折有限元建模分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018, 22(11):1725-1730. [45] 陈心敏, 李文标, 熊凯凯, 等. 钉道强化股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗老年A3.3型股骨转子间骨折:最佳骨水泥量有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(9):1404-1409. [46] 何祥鑫. 内收肌主动响应对脾虚型老年髋部骨折断裂行为影响的有限元研究[D]. 广州:广州中医药大学,2018. |
| [1] | Li Liangkui, Huang Yongcan, Wang Peng, Yu Binsheng. Effect of anterior controllable anteriodisplacement and fusion on vertebrae-ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament complex and implants: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1761-1767. |
| [2] | Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao. Xu Biao, Lu Tan, Jiang Yaqiong, Yin Yujiao [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1768-1774. |
| [3] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [4] | Chen Xi, Tang Tao, Chen Tongbing, Li Qing, Zhang Wen. Mechanical stability of intertrochanteric fracture of femur with different internal fixation systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1783-1788. |
| [5] | Li Shuai, Liu Hua, Shang Yonghui, Liu Yicong, Zhao Qihang, Liu Wen. Stress distribution on the maxilla when wearing the Twin-block appliance for Class II malocclusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 881-887. |
| [6] | Zhou Zonghao, Luo Siyang, Chen Jiawen, Chen Guangneng, Feng Hongchao. Finite element analysis of bioabsorbable plates versus miniature titanium plates in mandibular fracture fixation in different bone qualities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 818-826. |
| [7] | Chen Yilong, Zhang Xu, Li Hong. Mechanical analysis of fiber post combined with different crown restorations for endodontically treated non-carious cervical lesions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 866-871. |
| [8] | Su Dejun, Dong Wanpeng, Dong Yuefu, Zhang Jichao, Zhang Zhen. Design of asymmetric prosthesis and mechanical analysis of total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 510-516. |
| [9] | Wang X, Wang Hm, Chen Sh, Feng Tx, Bu Hm, Zhu Lg, Chen Dd, Wei X. Stress and morphological characteristics of intervertebral foramen of cervical rotation-traction manipulation for treating cervical spondylotic radiculopathy: a three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 441-447. |
| [10] | Zhao Yuxin, Liang Liang, Jin Feng, Xu Yangyang, Kang Zhijie, Fang Yuan, He Yujie, Wang Xing, Wang Haiyan, Li Xiaohe. Establishment and stress analysis of a finite element model for adolescent cervical disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 448-454. |
| [11] | Li Zhenggang, Shang Xuehong, Wu Zhang, Li Hong, Sun Chaojun, Chen Huadong, Sun Zhe, Yang Yi. Finite element analysis of three internal fixation modalities for treatment of Pauwels type III femoral neck fractures under different loading conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 455-463. |
| [12] | Liu Mengfei, Chen Gang, Shi Yihan, Zeng Lin, Jiang Kan, Yilihamujiang•Wusiman. Finite element analysis of optimization of femoral prosthesis implantation position in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in osteoporotic patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 464-470. |
| [13] | Xue Guangming, Muhetaer · Kelimu, Li Hong. Preparation and radial support mechanical behavior of new mixed braided stents [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3440-3448. |
| [14] | Mawulanjiang · Abudurenmu, Zilalai · Julaiti, Baibujiafu · Yelisi, Gulizainu · Yibulayin, Nijiati · Tuerxun. Stress analysis of angled abutments of maxillary central incisor implant crown in different implant spacing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3351-3359. |
| [15] | Cao Yilin, Wang Xinyu, Zhuang Yan, Wang Yaru Jiang Zhixiu, Liu Danyu, Men Jiuxu, Ding Yuansheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of three-dimensional printed personalized orthodontic appliances for vertical movement of single teeth [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3360-3368. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||