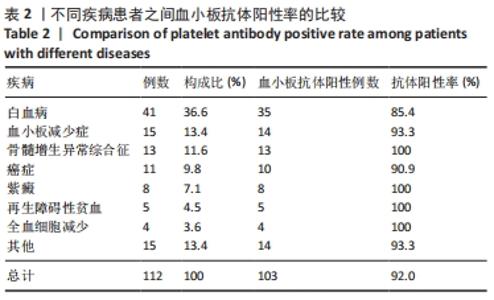
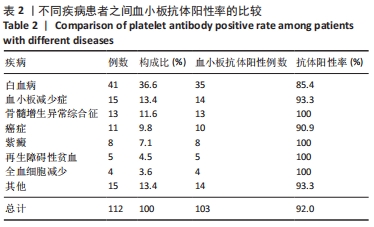
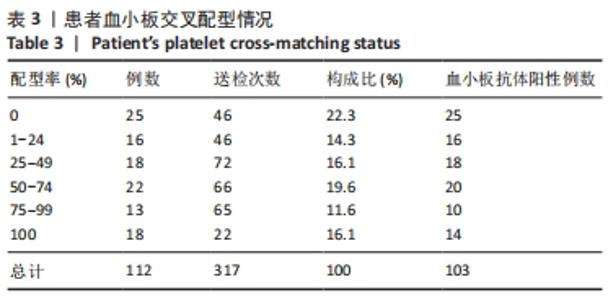
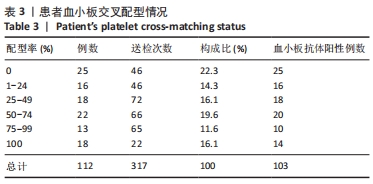
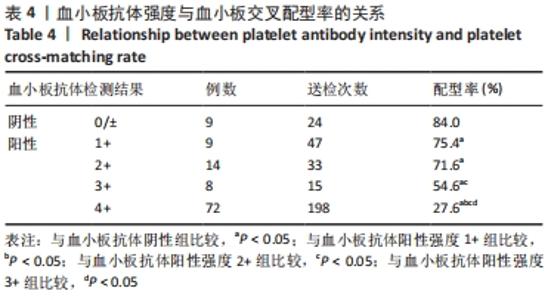
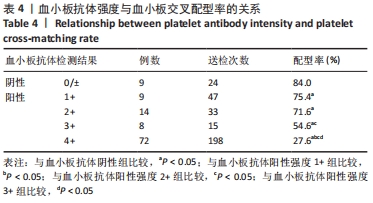
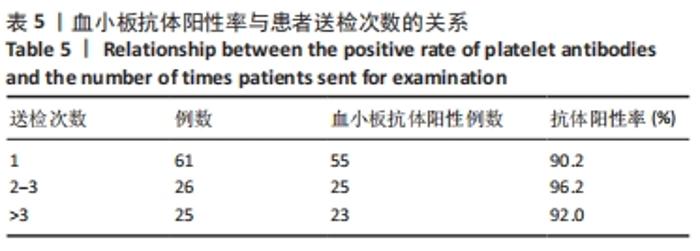
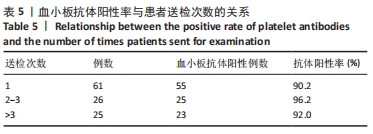
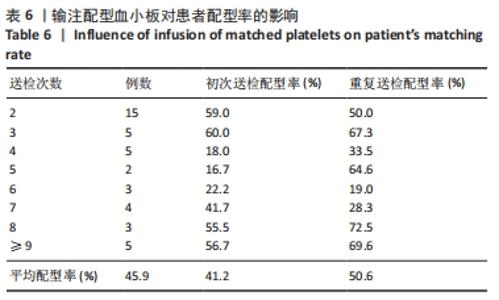
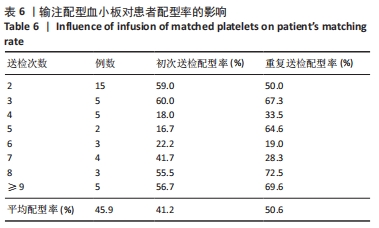
[1] 朱奕,伍昌林,党鑫堂.反复输血患者血小板抗体检测结果分析[J].国际检验医学杂志,2012,33(9):111-112.
[2] 任明,陈国安,沈钢.免疫性血小板输注无效血液病患者血小板抗体特异性检测及分析[J].中国输血杂志,2017,30(9):1021-1023.
[3] 杨小莉,余泽波.血小板输注无效原因及对策研究进展[J].检验医学与临床,2019,16(7):127-130.
[4] 聂锋,练正秋,李玲.血小板抗体检测分析与探讨[J].中国实验诊断学,2019,23(12):2052-2054.
[5] 张秋会,张婧,刘丽娜.多次输血后患者血小板输注无效的血小板抗体检测与分析[J].临床输血与检验,2015,17(5):35-38.
[6] 芦凤亮,李鑫,颜廷宇.哈尔滨地区血小板输注无效患者的抗体鉴定与分析[J].中国输血杂志,2019,32(8):27-28.
[7] HAYASHI T, HIRAYAMA F. Advances in alloimmune thrombocytopenia: perspectives on current concepts of human platelet antigens, antibody detection strategies, and genotyping. Blood Transfus. 2015;13(3): 380-390.
[8] 周燕,李丽兰,钟周琳,等.造血干细胞移植术后抗-CD36抗体介导的血小板输注无效症和相关病例的实验研究[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2018,26(2):541-546.
[9] 周燕,李丽兰,钟周琳.南宁地区血小板输注无效患者血小板同种抗体检测及特异性分析[J].临床输血与检验,2015,17(2):103-106.
[10] 梁静,刘雯,叶海燕.血小板输注无效患者血小板抗体阳性的相关因素研究[J].新疆医科大学学报,2020,43(6):738-740.
[11] 张桂芬,闫萌. 反复输血后血小板输注无效患者抗体阳性率、特异性及影响因素分析[J].临床血液学杂志,2020,33(6):391-393.
[12] Bertrand G, Danger Y, Croisille L, et al. A new platelet alloantigen (Efsa, HPA-35bw) on glycoprotein IIIa leading to neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia. Transfusion. 2019;59(7):2463-2464.
[13] 赵凤春,李淑萍,张芃,等.血小板输注无效与血小板抗原(HPA)多态性的相关性[J].现代生物医学进展,2020,20(3):103-106.
[14] 李茵,苏蔓,何路军,等.石家庄汉族血小板捐献者HPA1-17基因多态性分析[J].中国输血杂志,2019,32(5):427-429.
[15] 冯治伟,邓素容,何翠.46名血小板输注无效患者HPA基因分型及多态性研究[J].中国输血杂志,2014,27(2):179-181.
[16] 顾萍,王静,张帆.血小板膜糖蛋白Ⅱb/Ⅲa基因多态性与血小板输注疗效的关系[J].检验医学,2013,28(9):770-774.
[17] SCHUH AC, WATKINS NA, NGUYEN Q, et al. A tyrosine703serine polymorphism of CD109 defines the Gov platelet alloantigens. Blood. 2002;99(5):1692-1698.
[18] BERTRAND G, JALLU V, BERANGER T, et al. HPA-5 typing discrepancy reveals an Ile503Leu substitution in platelet GPIa (α2 integrin). Vox Sang. 2013;105(1):73-76.
[19] 许云波,张静.血液病反复输血患者血小板抗体,交叉配型结果与血小板输注效果的相关性分析[J].国际检验医学杂志,2020,41(3): 323-326.
[20] KIEFEL V. Platelet antibodies in immune thrombocytopenia and related conditions. Journal of Laboratory Medicine. 2020; 44(5): 273-284.
[21] TAO S, CHEN S, HONG X, et al. Novel method for simultaneously detecting HPA and HLA antibodies using Luminex microbeads. J Transl Med. 2019;17(1):249.
[22] 吴红,唐绮,李国良,等.血小板交叉配型技术在免疫性血小板输注无效患者中的应用[J].实验与检验医学,2019,37(5):959-961.
[23] 江灵,王洁,王雨涵,等.血小板抗体检测及交叉配型在血小板输注患者中的运用[J].中国输血杂志,2019,32(3):263-266.
[24] 王晓伟,邵春燕,张菁,等.北京地区HPA1-6,15基因库的建立与应用[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2020,28(1):296-299.
[25] 张坤莲,陈阳,李晓丰.血小板捐献者HLA资料库的建立[J].中国输血杂志,2011,24(4):331-333.
[26] 邱芳. HLA-Ⅰ抗体、HPA抗体与血小板输注疗效的相关性研究[D].南昌:南昌大学,2015.
[27] 李晓丰,李剑平.辽宁地区血小板志愿捐献者HPA基因资料库的建立[J].中国输血杂志,2009,22(12):997-998.
[28] 林凤秋,李晓丰,邵超鹏.血小板CD36新等位基因1142T>G序列分析及确认[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(5):8184-8189.
[29] LIN FQ, LI XF, LI WW, et al. A string of 12 mutations in Intron 3 is a new clue associated with Type II CD36 deficiency. Transfusion. 2019;59(3): 1159-1161.
|