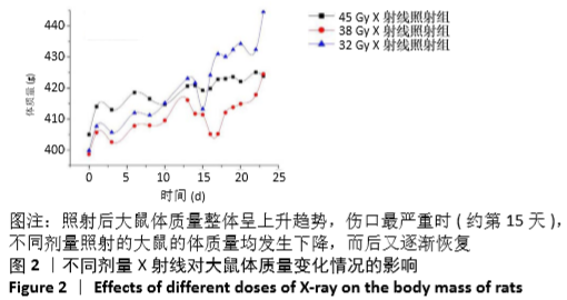
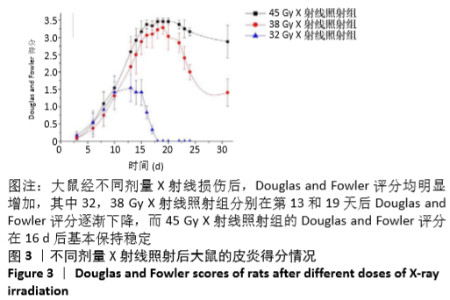
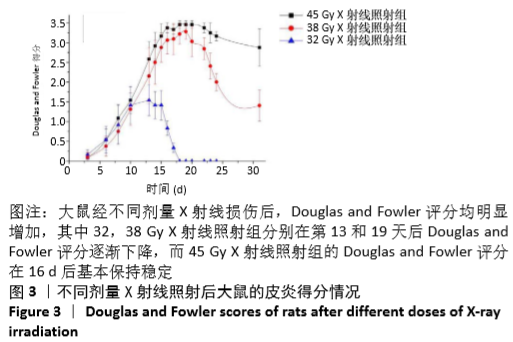
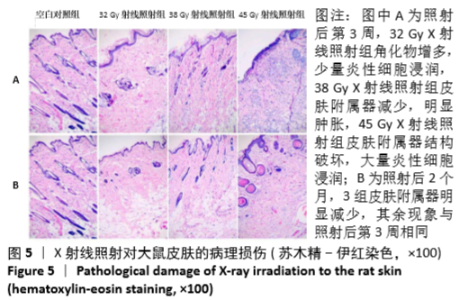
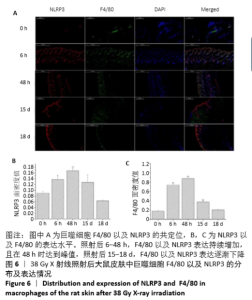
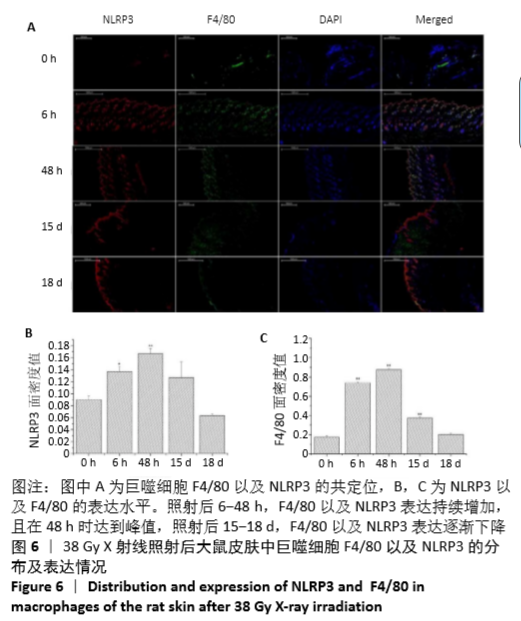
[1] BRODIN NP, VELCICH A, GUHA C, et al. A Model for Precise and Uniform Pelvic- and Limb-Sparing Abdominal Irradiation to Study the Radiation-Induced Gastrointestinal Syndrome in Mice Using Small Animal Irradiation Systems. Dose Response. 2017;15(1):1559325816685798.
[2] MCQUESTION M. Evidence-based skin care management in radiation therapy: clinical update. Semin Oncol Nurs. 2011;27(2):e1-17.
[3] GONG W, GUO M, HAN Z, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells stimulate intestinal stem cells to repair radiation-induced intestinal injury. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(9):e2387.
[4] 王帅.载血管生长因子壳聚糖纳米粒在防治放射性皮肤损伤中的应用及其作用机制的探讨[D].苏州:苏州大学,2016.
[5] MEI K, ZHAO S, QIAN L, et al. Hydrogen protects rats from dermatitis caused by local radiation. J Dermatolog Treat. 2014;25(2):182-188.
[6] 倪晨,王贵均,赵爱国.β射线致皮肤放射性损伤动物模型的建立[J].中药新药与临床药理,2011,22(2):224-225.
[7] 周迎会,仇灏,徐岚,等.电子射线局部辐照大鼠Ⅰ/Ⅲ型胶原表达及基质金属蛋白酶改变的研究[J].实验动物与比较医学,2006,26(4):227-230.
[8] OKUNIEFF P, XU J, HU D, et al. Curcumin protects against radiation-induced acute and chronic cutaneous toxicity in mice and decreases mRNA expression of inflammatory and fibrogenic cytokines. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;65(3): 890-898.
[9] 周迎会,吴士良,王秀珍,等.β和γ射线放射性皮肤损伤动物模型的初步研究[J].辐射防护,2005,25(6):39-43,73.
[10] DOUGLAS BG, FOWLER JF. The effect of multiple small doses of x rays on skin reactions in the mouse and a basic interpretation. Radiat Res. 1976;66(2):401-426.
[11] 王红光,曹卫红,邹晓防,等.酸性成纤维细胞生长因子表达对急性放射性皮肤溃疡创面修复的影响[J].中国临床康复,2005,9(30):107-109,275.
[12] 佘毅敏,杨善民,洪金省,等.小鼠高能X射线放射性皮炎动物模型的建立[J].菏泽医学专科学校学报,2014,26(2):10-11,68.
[13] 高红林,张玉民,褚丽萍,等.不同剂量X射线对BALB/c小鼠放射性皮肤损伤程度比较[J].中国辐射卫生,2016,25(2):161-162,166.
[14] SONG B, ZHOU T, YANG WL, et al. Programmed cell death in periodontitis: recent advances and future perspectives. Oral Dis. 2017;23(5):609-619.
[15] FORCHERON F, AGAY D, SCHERTHAN H, et al. Autologous adipocyte derived stem cells favour healing in a minipig model of cutaneous radiation syndrome. PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31694.
[16] HOLLER V, BUARD V, GAUGLER MH, et al. Pravastatin limits radiation-induced vascular dysfunction in the skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129(5):1280-1291.
[17] DOCTROW SR, LOPEZ A, SCHOCK AM, et al. A synthetic superoxide dismutase/catalase mimetic EUK-207 mitigates radiation dermatitis and promotes wound healing in irradiated rat skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2013;133(4):1088-1096.
[18] JOURDAN MM, LOPEZ A, OLASZ EB, et al. Laminin 332 deposition is diminished in irradiated skin in an animal model of combined radiation and wound skin injury. Radiat Res. 2011;176(5):636-648.
[19] ZHANG S, SONG C, ZHOU J, et al. Amelioration of radiation-induced skin injury by adenovirus-mediated heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) overexpression in rats. Radiat Oncol. 2012;7:4.
[20] 谷庆阳,王德文,赵梅兰,等.EGF和EGFR在急性放射性皮肤溃疡组织中的表达水平:与单纯伤口愈合的对比研究[J].辐射研究与辐射工艺学报, 2003,21(2):135-138.
[21] 沈国良,陆兴安,唐俊,等.大鼠急性β射线皮肤损伤动物模型的建立与应用[J].中华放射医学与防护杂志,2006,26(6):577-579.
[22] 王晶.γ-H2AX用于辐射生物剂量计研究的动物模型评价[J].中华放射医学与防护杂志,2015,35(5):329-333.
[23] 刘秀芳,李凤玉,王舒琦,等.大鼠电子射线皮肤损伤动物模型的建立[J].山西医药杂志,2012,41(4):336-337.
[24] 陈强,程岩,任淑萍,等.放射性皮肤损伤病变规律初探[J].中国实验诊断学,2008,12(5):676-677.
[25] 龚震宇,童亚林,万友华,等.高能X射线放射性皮肤损伤动物模型的建立[J].中华烧伤杂志,2010,26(5):379-381.
[26] HARPER JL, FRANKLIN LE, JENRETTE JM, et al. Skin toxicity during breast irradiation: pathophysiology and management. South Med J. 2004;97(10):989-993.
[27] 李洋,薛洪范,闫荣,等.水凝胶对大鼠Ⅱ度放射性皮炎创面愈合影响机制探讨[J].社区医学杂志,2018,16(14):38-42.
|