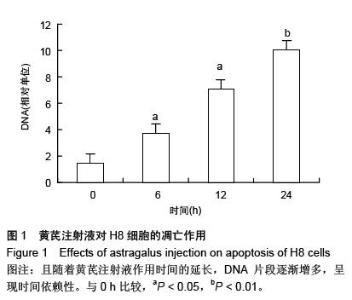
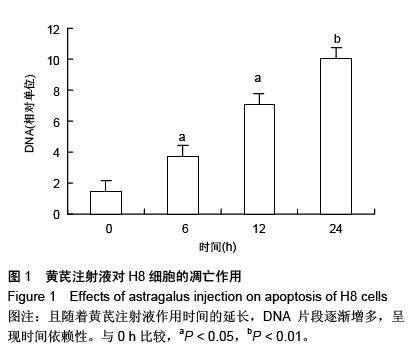
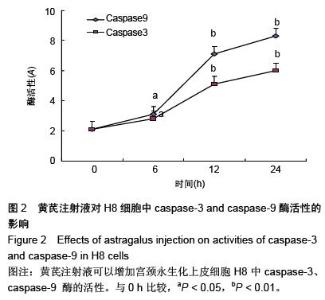
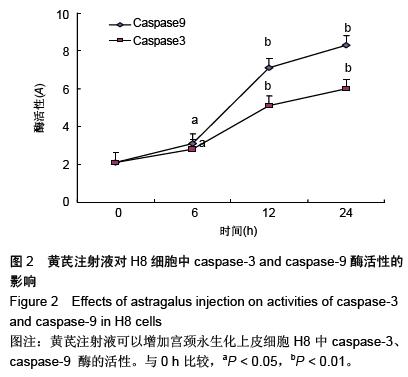
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (5): 743-747.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.05.023
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of astragalus injection on human immortalized cervical epithelial cell apoptosis in vitro
Lv Ling1, Xiao Chen-guang2, Liu Qing1, Zhang Li3, Li Neng-lian3, She Ya-li3
- 1Maternal and Child Health of Gansu Province, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, China; 2Lanzhou Uranium Worker Hospital of China National Nuclear Corporation, Lanzhou 730065, Gansu Province, China; 3Traditional Chinese Medical College of Gansu, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China