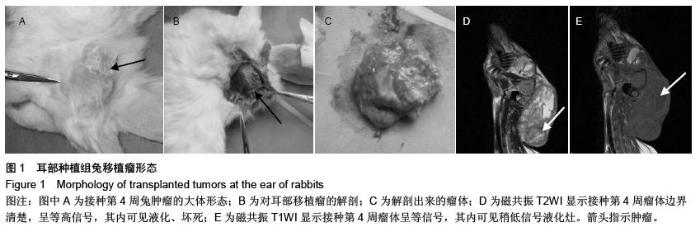
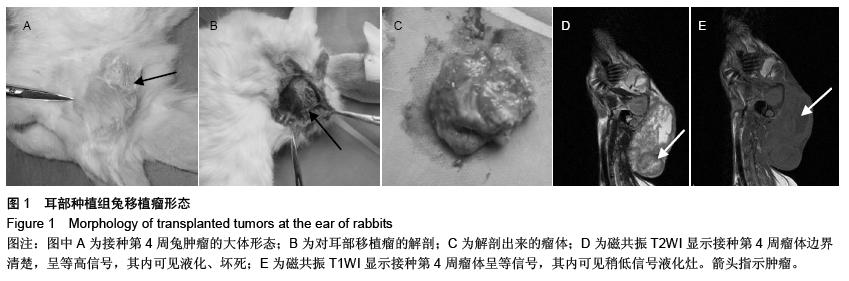
| [1] Mayne ST, Morse DE, Winn DM. Cancers of the oral cavity and pharynx. In: Schottenfeld D, Fraumeni JF Jr, eds. Cancer Epidemiology and Prevention. New York: Oxford University Press, 2006:674-696. [2] King M, Chatelain K, Farris D, et al. Oral squamous cell carcinoma proliferative phenotype is modulated by proanthocyanidins: a potential prevention and treatment alternative for oral cancer. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2007;7:22.[3] Ragin CC, Modugno F, Gollin SM. The epidemiology and risk factors of head and neck cancer: a focus on human papillomavirus. J Dent Res. 2007;86(2):104-114.[4] Gooden MJ, de Bock GH, Leffers N, et al. The prognostic influence of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Br J Cancer. 2011;105(1): 93-103. [5] Varilla V, Atienza J, Dasanu CA. Immune alterations and immunotherapy prospects in head and neck cancer. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2013;13(9):1241-1256. [6] Luo W, Zhou X, Zheng X, et al. Role of sonography for implantation and sequential evaluation of a VX2 rabbit liver tumor model. J Ultrasound Med. 2010;29(1):51-60.[7] Kidd JG, Rous P. Cancers deriving from the virus papillomas of wild rabbits under natural conditions. J Exp Med. 1940; 71(4): 469-494.[8] Sano D, Myers JN. Xenograft models of head and neck cancers. Head Neck Oncol. 2009;1:32.[9] Luo W, Zhou X, Zheng X, et al. Role of sonography for implantation and sequential evaluation of a VX2 rabbit liver tumor model. J Ultrasound Med. 2010;29(1):51-60.[10] Gaba RC, Baumgarten S, Omene BO, et al. Ethiodized oil uptake does not predict doxorubicin drug delivery after chemoembolization in VX2 liver tumors. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2012;23(2):265-273.[11] Xia X, Li X, Feng G, et al. Intra-arterial interleukin-12 gene delivery combined with chemoembolization: anti-tumor effect in a rabbit hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) model. Acta Radiol. 2013;54(6):684-689.[12] Dünne AA, Mandic R, Ramaswamy A, et al. Lymphogenic metastatic spread of auricular VX2 carcinoma in New Zealand white rabbits. Anticancer Res. 2002;22(6A):3273-3279.[13] Pascale F, Ghegediban SH, Bonneau M, et al. Modified model of VX2 tumor overexpressing vascular endothelial growth factor. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2012;23(6):809-817.e2.[14] Lee EW, Wong D, Tafti BA, et al. Irreversible electroporation in eradication of rabbit VX2 liver tumor. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2012; 23(6):833-840. [15] Chen YK, Huang AH, Lin LM. Sphere-forming-like cells (squamospheres) with cancer stem-like cell traits from VX2 rabbit buccal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oral Sci. 2014; 6(4):212-218.[16] Felthaus O, Ettl T, Gosau M, et al. Cancer stem cell-like cells from a single cell of oral squamous carcinoma cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;407(1):28-33.[17] Sun JH, Zhang YL, Nie CH, et al. Considerations for two inoculation methods of rabbit hepatic tumors: Pathology and image features. Exp Ther Med. 2012;3(3):386-390.[18] Suami H, Yamashita S, Soto-Miranda MA, et al. Lymphatic territories (lymphosomes) in a canine: an animal model for investigation of postoperative lymphatic alterations. PLoS One. 2013;8(7):e69222.[19] Zheng LF, Li YJ, Wang H, et al. Combination of vascular endothelial growth factor antisense oligonucleotide therapy and radiotherapy increases the curative effects against maxillofacial VX2 tumors in rabbits. Eur J Radiol. 2011; 78(2):272-276. [20] Molinari AJ, Aromando RF, Itoiz ME, et al. Blood vessel normalization in the hamster oral cancer model for experimental cancer therapy studies. Anticancer Res. 2012;32(7):2703-2709.[21] Okuma T, Matsuoka T, Okamura T, et al. 18F-FDG small-animal PET for monitoring the therapeutic effect of CT-guided radiofrequency ablation on implanted VX2 lung tumors in rabbits. J Nucl Med. 2006;47(8):1351-1358.[22] Guo Y, Zhang Y, Jin N, et al. Electroporation-mediated transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in the rabbit VX2 liver tumor model. Invest Radiol. 2012;47(2):116-120. [23] Qian T, Chen M, Gao F, et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging to evaluate microvascular density after transarterial embolization ablation in a rabbit VX2 liver tumor model. Magn Reson Imaging. 2014;32(8):1052-1057. [24] Tanaka T, Nishiofuku H, Hukuoka Y, et al. Pharmacokinetics and antitumor efficacy of chemoembolization using 40 µm irinotecan-loaded microspheres in a rabbit liver tumor model. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014;25(7):1037-1044.e2. [25] Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55(2):74-108.[26] Oliveira LR, Oliveira-Costa JP, Araujo IM, et al. Cancer stem cell immunophenotypes in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med. 2011;40(2):135-142. [27] Lim YC, Oh SY, Cha YY, et al. Cancer stem cell traits in squamospheres derived from primary head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Oral Oncol. 2011;47(2):83-91.[28] Sankaranarayanan R, Black RJ, Swaminathan R, et al. An overview of cancer survival in developing countries. IARC Sci Publ. 1998;(145):135-173.[29] Sapundzhiev N, Dünne AA, Ramaswamy A, et al. The auricular VX2 carcinoma: feasibility of complete tumor resection. Anticancer Res. 2005;25(6B):4209-4214.[30] Lee KC, Moon WK, Chung JW, et al. Assessment of lymph node metastases by contrast-enhanced MR imaging in a head and neck cancer model. Korean J Radiol. 2007;8(1): 9-14.[31] Jefferis AF, Berenbaum MC. The rabbit VX2 tumour as a model for carcinomas of the tongue and larynx. Acta Otolaryngol. 1989;108(1-2):152-160.[32] Chikui T, Yuasa K, Maemura S, et al. Change of angiostructure and hemodynamics in lymph node metastases in rabbits. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002;93(3):350-357.[33] 沈毅,孙坚,周晓健,等.兔舌不同部位VX-2鳞癌与颈淋巴结转移模型的生物学特性[J].上海口腔医学,2007,16(5):497-501.[34] Zhang YW, Ao J, Liu Y, et al. Pharmacokinetics of gelatin sponge microparticles in a rabbit VX2 liver tumor model of hepatic arterial chemoembolization. Tumour Biol. 2014; 35(11):10905-10910. [35] Jiang XY, Zhang XP, Huang JH, et al. Effects of intra-arterial infusion of 3-bromopyruvate on metastases and survival benefit of hepatic VX2 tumor in rabbits. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013;93(39):3139-3142.[36] Oshiro H, Fukumura H, Nagahama K, et al. Establishment of successively transplantable rabbit VX2 cancer cells that express enhanced green fluorescent protein. Med Mol Morphol. 2015;48(1):13-23.[37] Soto-Miranda MA, Suami H, Chang DW. Mapping superficial lymphatic territories in the rabbit. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2013;296(6):965-970.[38] 李文晋,牛金亮,金慧兰,等.头颈部肿瘤颈部淋巴结隐匿性转移的病理实验研究[J].中国药物与临床,2012,12(12):1533-1535.[39] 蓝美红,牛金亮,李文晋,等.相对表观弥散系数与钆喷替酸葡甲胺增强MRI诊断兔头颈转移淋巴结的对比研究[J].中国中西医结合影像学杂志,2012,10(2):105-108. [40] Parvinian A, Casadaban LC, Gaba RC. Development, growth, propagation, and angiographic utilization of the rabbit VX2 model of liver cancer: a pictorial primer and "how to" guide. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2014;20(4):335-340. |