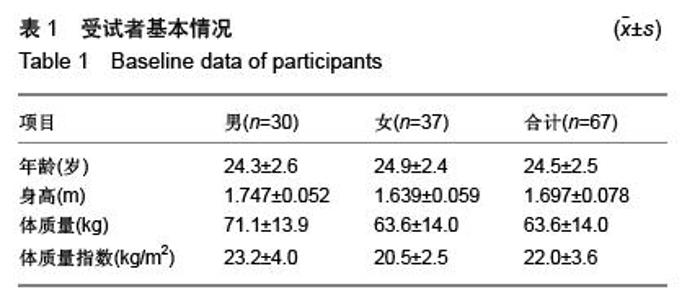
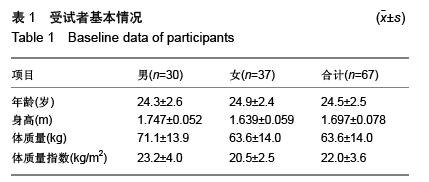
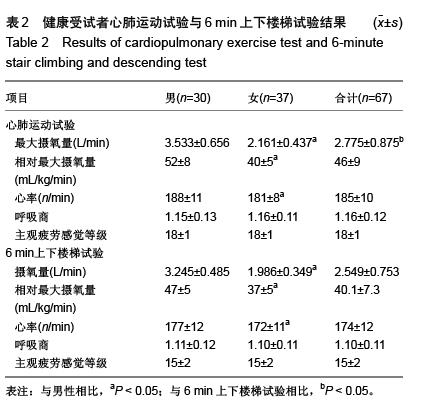
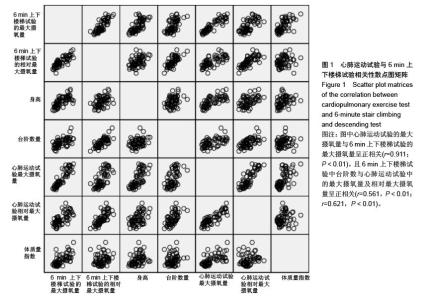
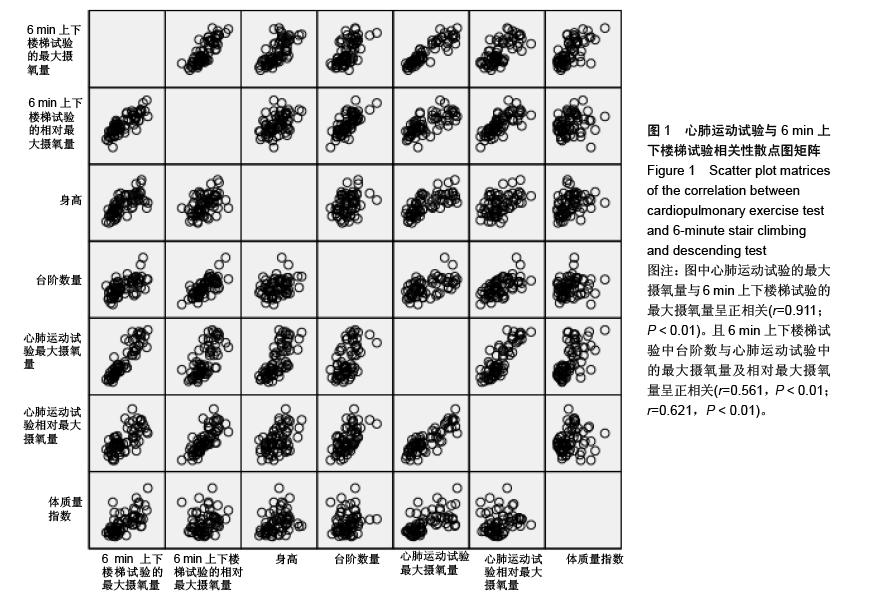
| [1] 刘前桂,李永杰,郑曦,等.6分钟步行试验在呼吸康复训练中的临床应用[J].临床肺科杂志,2010,15(1):129-131.[2] 留永健,韩江娜.临床常用肺功能检查项目及合理选择[J].中华临床免疫和变态反应杂志,2014,8(1):3-9.[3] 荆志成.六分钟步行距离试验的临床应用[J].中华心血管病杂志, 2006,34(4):381-384.[4] 张萍.六分钟步行试验及在心功能评价中的作用[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2007,1(4):10-11.[5] 崔冬清,王虹.六分钟步行试验评判慢性阻塞性肺疾病肺功能影响因素分析[J].中国全科医学,2010,13(16):1768-1770.[6] 邓国祥,王治明,王绵珍,等.心肺功能运动试验与静态肺功能判定肺损伤的比较[J].中国工业医学杂志,2005,18(5):269-272.[7] 郭志勇,滕志涛,蔡爱宁,等.心肺运动功能检查在冠心病诊断中的临床价值[J].中国医学工程,2013,(4):21-22.[8] 宁亮,孙兴国.心肺运动试验在医学领域的临床应用[J].中国全科医学,2013,16(33):3898-3902.[9] 郭志勇,滕志涛,江慧迪,等.心肺运动试验中功率递增方案的选择[J].中国医学工程,2011,(8):84-85.[10] 刘爱华.运动心肺功能试验的应用进展[J].医学综述,2013, 19(22): 4125-4128.[11] 杨德松,李旭,唐金明,等.心肺运动试验对预测肺癌患者术后呼吸衰竭的价值分析[J].临床医学工程,2015,22(6):731-732.[12] 李云峰,于松杨,崔峰鹤,等.心肺运动试验在老年人非心脏手术麻醉风险评估中的应用[J].山东医药,2015,(31):105-106. [13] 郭志勇,滕志涛.心肺运动试验在心肺疾病中的应用进展[J].山东医药,2011,51(3):107-108.[14] 林家仕,严翊,苏浩,等.体力活动?心肺耐力与心血管疾病风险因素之间的相关性研究[J].北京体育大学学报,2012,35(11):54-57.[15] 陈学伟,张娜,徐传香,等.最大摄氧量间接测量法-踏阶运动心率的变化特征[J].解放军预防医学杂志,2015,33(1):43-44.[16] 杨翼,黎敏,李章华.最大摄氧量及其相关和派生指标在运动训练中应用的研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2009,15(5): 445-448.[17] 王玉华,邹积丰,王凡,等.12分钟步行试验对糖尿病运动干预效果的评价[J].预防医学论坛,2008,14(9):769-770.[18] 李海燕,陈佩杰,庄洁.青少年体力活动摄氧量预测方法的实验研究[J].上海预防医学,2011,23(7):321-324.[19] 李俊勇,任晋军,曹峰锐.最大摄氧量?无氧阈和最大摄氧量平台同高校男生12min跑和1000m跑的相关性分析[J].北京体育大学学报,2010,(8):65-67.[20] Cataneo DC, Cataneo AJ. Accuracy of the stair climbing test using maximal oxygen uptake as the gold standard. J Bras Pneumol. 2007;33(2):128-133.[21] Bassett DR, Vachon JA, Kirkland AO, et al. Energy cost of stair climbing and descending on the college alumnus questionnaire. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1997;29(9):1250-1254.[22] eh KC, Aziz AR. Heart rate, oxygen uptake, and energy cost of ascending and descending the stairs. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2002;34(4):695-699.[23] 鲁葆春,任培土.登楼梯耐力试验在术前评估80岁以上胆道病人心肺功能的作用[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2010,16(4):426- 429.[24] 王欢,郑迎东,张彦峰,等.登楼梯能量消耗的测量与统计方法研究[J].中国体育科技,2010,46(2):11-13.[25] 马良赟,伍硕允,叶敏,等.登楼梯试验在预测老年肺癌患者术后心肺并发症中的作用[J].中国医师进修杂志,2006,29(26):24-25.[26] 刘建华,丸山仁司,胜平纯司.上下台阶方法的生物力学研究[J].中国康复理论与实践,2003,9(10):32-33.[27] 杨文兰.运动心肺试验的安全性及注意事项[J].中国实用内科杂志,2014,(S1):27-29.[28] Boreham CA, Wallace WF, Nevill A. Training effects of accumulated daily stair-climbing exercise in previously sedentary young women. Prev Med. 2000;30(4):277-281.[29] 李文慧,姚明焰.登阶运动对大学男生体质未达标群体的体质干预研究[J].北京体育大学学报,2009(4):75-78.[30] 李镒冲,李晓松.两种测量方法定量测量结果的一致性评价[J].现代预防医学,2007,34(17):3263-3266.[31] 苏远力.健康年轻人功率自行车与平板运动心肺功能试验比较研究[D].广州:广州医学院,2009.[32] 陈嵘,王健,杨红春.四种运动负荷试验评价运动心肺功能比较研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2014,(9):917-920.[33] 吕莉.天津市大学生12 min跑评分标准及评价等级制订研究[J].山东体育学院学报,2015,31(3):105-109.[34] 袁林,宋应华,刘心伟,等.不同体重人群爬楼梯过程中能量消耗的测定[J].中国体育科技,2012,48(3):104-107.[35] 王新本,周新春,滕志涛,等.运动心肺功能参数对轻度慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者康复治疗的指导作用[J].山东医药,2013,53(13): 29-31.[36] 孙景权,苏浩,严翊,等.高强度间歇运动改善心肺耐力的线粒体合成机制[J].中国运动医学杂志.2015,34(10):1022-1027. |