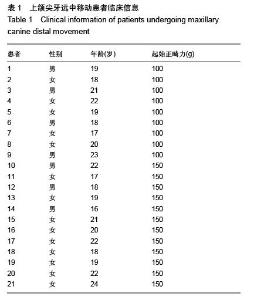
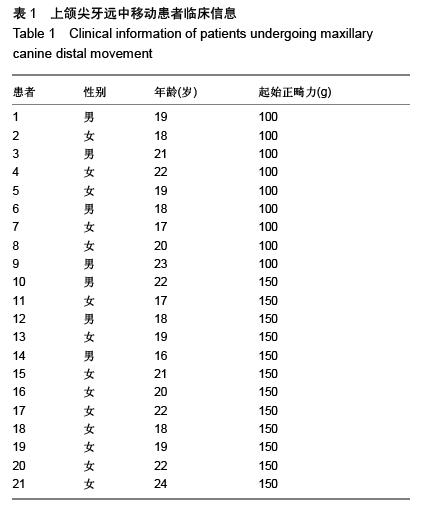
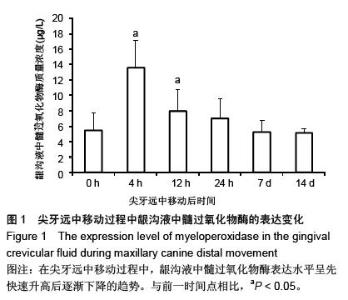
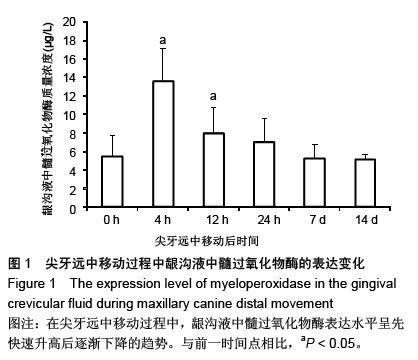
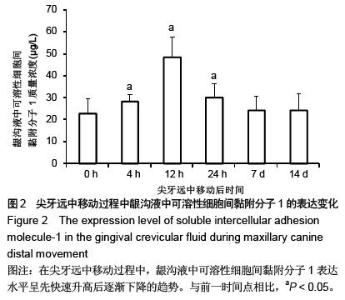
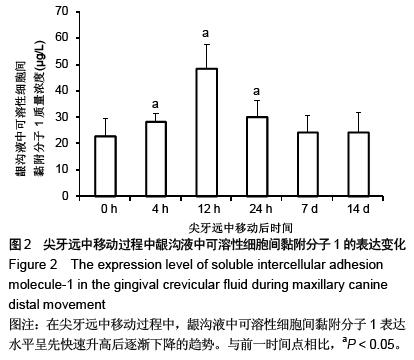
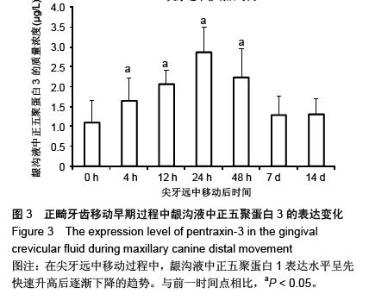
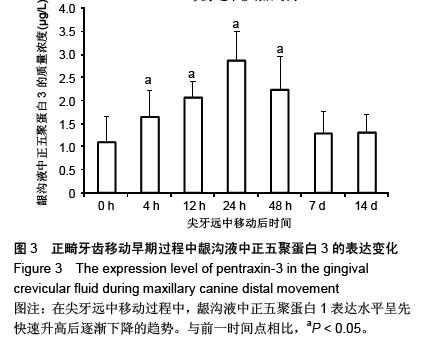
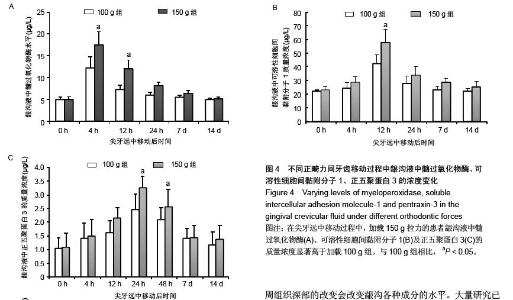
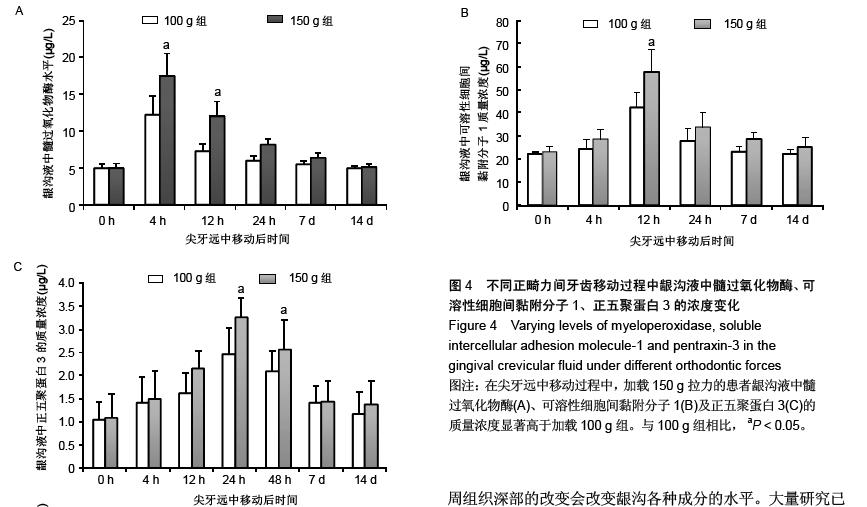
| [1] d'Apuzzo F, Cappabianca S, Ciavarella D, et al. Biomarkers of periodontal tissue remodeling during orthodontic tooth movement in mice and men: overview and clinical relevance. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013;2013:105873. [2] Nauseef WM. Myeloperoxidase in human neutrophil host defence. Cell Microbiol. 2014;16(8):1146-1155. [3] Rogowicz-Frontczak A, Pilacinski S, Araszkiewicz A, et al. C-Reactive protein and soluble intracellular adhesion molecule-1 are related to pulse wave reflection in type 1 diabetes 1C-1. J Diabetes. 2014;6(6):577-585. [4] Mantovani A1, Garlanda C, Bottazzi B. Pentraxin 3, a non-redundant soluble pattern recognition receptor involved in innate immunity. Vaccine. 2003;21 Suppl 2:S43-47.[5] Jeyraj Y, Katta AK, Vannala V, et al. Estimation of alkaline phosphatase in the gingival crevicular fluid during orthodontic tooth movement in premolar extraction cases to predict therapeutic progression. J Nat Sci Biol Med. 2015;6(2):343-346.[6] Jung GB, Kim KA, Han I, et al. Biochemical characterization of human gingival crevicular fluid during orthodontic tooth movement using Raman spectroscopy. Biomed Opt Express. 2014;5(10):3508-3520.[7] Yamaguchi M, Yoshii M, Kasai K. Relationship between substance P and interleukin-1beta in gingival crevicular fluid during orthodontic tooth movement in adults. Eur J Orthod. 2006;28(3):241-246.[8] Kapoor P, Kharbanda OP, Monga N, et al. Effect of orthodontic forces on cytokine and receptor levels in gingival crevicular fluid: a systematic review. Prog Orthod. 2014;15:65.[9] 苏林杰.40例慢性牙周炎患者龈沟液中CRP、sICAM-1水平测定[J].山东医药,2011,51(51):49-50.[10] Garlanda C, Jaillon S1, Doni A, et al. PTX3, a humoral pattern recognition molecule at the interface between microbe and matrix recognition. Curr Opin Immunol. 2015;38:39-44.[11] Surlin P, Rauten AM, Silosi I, et al. Pentraxin-3 levels in gingival crevicular fluid during orthodontic tooth movement in young and adult patients. Angle Orthod. 2012;82(5):833-838. |