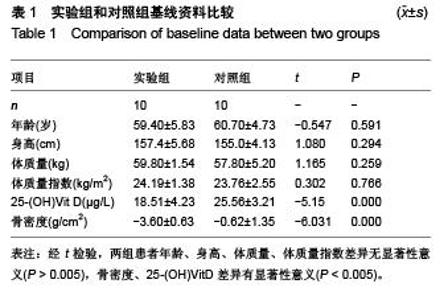
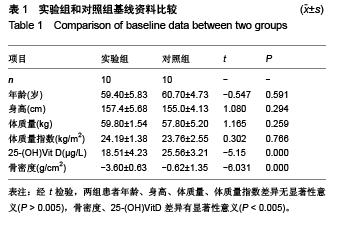
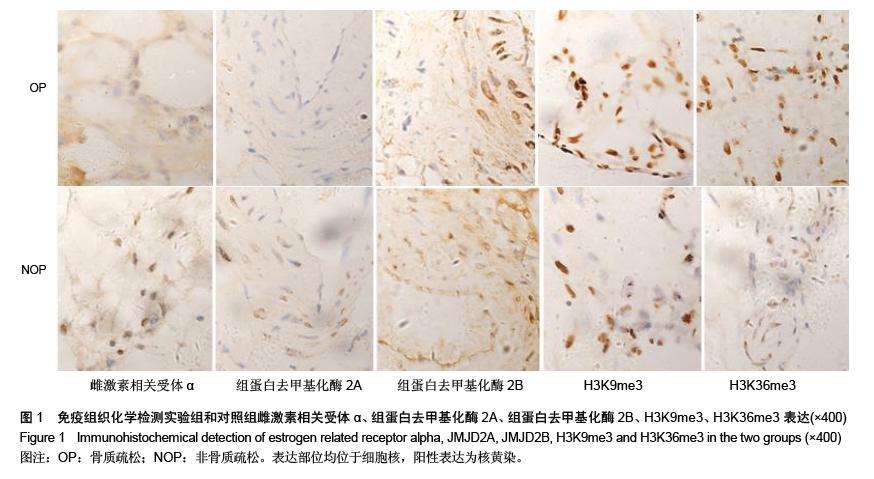
| [1] 李宁华,区品中,朱汉民,等.中国部分地区中老年人群原发性骨质疏松症患病率研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2001,21(5):275-278.
[2] Raisz MD. Pathogenesis of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Rev Endocr Metab Dis.2001;2:5-12.
[3] Gree EL,Shi Y.Histone methylation:a dynamic mark in health,disease and inheritance.Nat Rev Genet. 2012;5: 343-357.
[4] Bonnelye E,Merdad L,Kung V, et al. The orphan nuclear estrogen receptor- related receptor(ERRalpha) is expressed throughout osteoblast differentiation and regulates bone formation in vitro. J Cell Biol.2001;153(5):971-984.
[5] 钱云霞,钱凯先.雌激素相关受体ERR的功能及其调控[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2005,32(6):495-499.
[6] 石印玉.中西医结合骨伤科学[M].北京:中国中医药出版社,2007: 494.
[7] 张智海,刘忠厚,李娜,等.中国人骨质疏松症诊断标准专家共识(第三稿•2014版) [J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2014,9:1007-1010.
[8] Cummings SR, Melton LJ. Epidemiology and outcomes of osteoporotic fractures. Lancet.2002;939:1761-1767.
[9] 王海,冯涛涛,孙昊鹏,等.组蛋白去甲基化酶JMJD及其抑制剂的研究进展[J].药学进展,2013,37(11):565-573.
[10] Klose RJ,Yamane K,Bae Y,et al.The transcriptional repressor JHDM3A demethylates trimethyl histone H3 lysine 9 and lysine 36. Nature. Nature. 2006;442(7100):312-316.
[11] Chisamore MJ, Wilkinson HA, Flores O, et al. Estrogen-related receptor-alpha antagonist inhibits both estrogen receptor-positive and estrogen receptor-negative breast tumor growth in mouse xenografts. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009;8(3):672-681.
[12] Lu D, Kiriyama Y, Lee KY, et al. Transcriptional regulation of the estrogen- inducible pS2 beast cancer marker gene by the ERR family of orphan nuclear receptors.Cancer Res.2001; 61(18): 6755-6761.
[13] Yang J, Jubb AM, Pike L, et al.The histone demethylase JMJD2B is regulated by estrogen receptor alpha and hypoxia and is a key mediator of estrogen induced growth.Cancer Rs.2010;70(16):6456-6466.
[14] Kawazu M, Saso K, Tong KI, et al. Histone demethylase JMJD2B functions as a co-factor of estrogen receptor in breast cancer proliferation and mammary gland development. PLoS One.2011;6(3):e17830. |