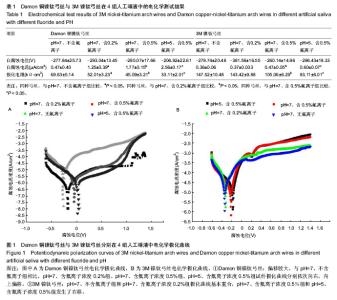
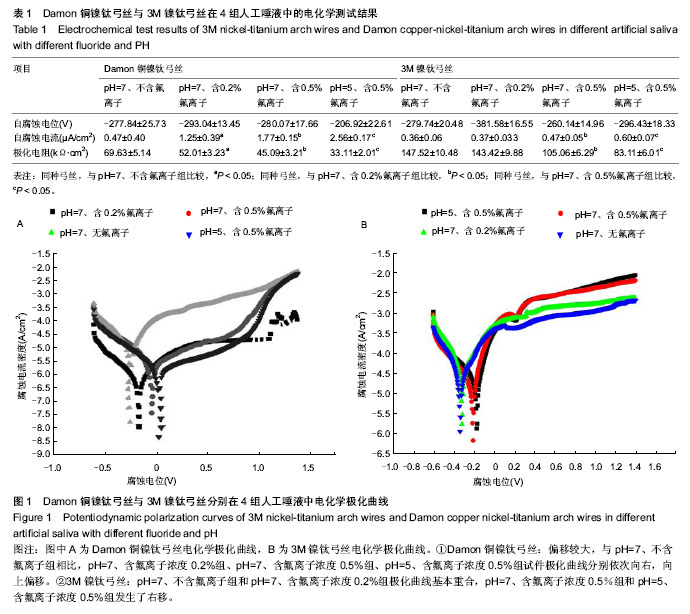
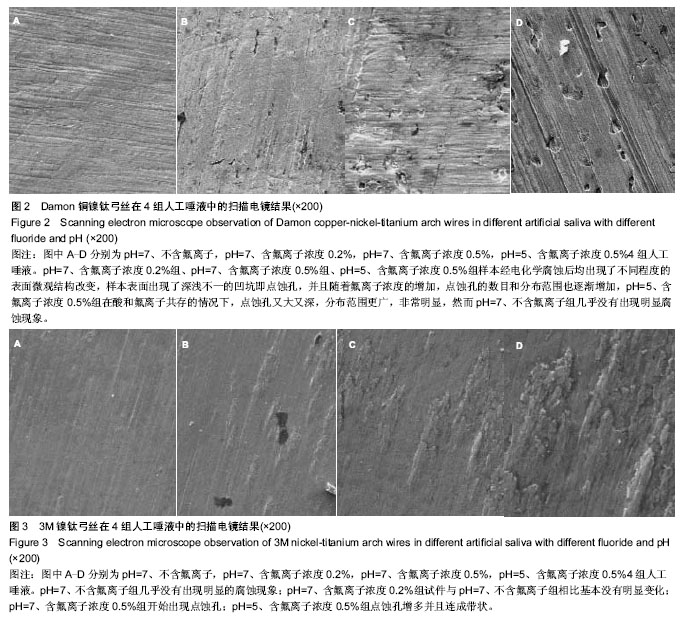
| [1] Queiroz GM,Silva LF,Ferreira JT,et al.Electrochemical behavior and pH stability of artificial salivas for corrosion tests.Braz Oral Res.2007;21(3):209-215.
[2] Shin JS, Oh KT, Hwang CJ.In vitro surface corrosion of stainless steel and NiTi orthodonticappliances.Aust Orthod J.2003;19(1):13-18.
[3] Wataha JC.Principles of biocompatibility for dental practitioners.J Prosthet Dent.2001;86(2):203-209.
[4] Kaneko K,Yokoyama K,Moriyama K,et al.Delayed fracture of betatitanium orthodontic wire in fluoride aqueous solutions. Biomaterials.2003; 24(18):2113-2116.
[5] Pun DK,Berzins DW.Corrosion behavior of shapememory, superelastic , and nonsuperelastic nickel-titanium-based orthodontic wires at various tem peratures.Dent Mater.2008;24(2):221-227.
[6] Horasawa N,Marek M.Effect of fluoride from glassionomer on discoloration and corrosion of titanium. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(2):662-666.
[7] Persson A,Lingstrom P,Bergdahl M,et al.Buffering effect of a prophylactic gel on dental plaque.Clin Oral Investig. 2006; 10(4): 289- 295.
[8] Amini F,Rakhshan V,Pousti M,et al.Variations in surface roughness of seven orthodontic archwires:an SEM-profilometry studyKorean.J Orthod.2012;42(3):129-137.
[9] 苏俭生,韩雯斐,田芝娟,等.不同浓度茶多酚人工唾液溶液对牙科铸造合金腐蚀行为的影响[J].中华口腔医学研究杂志(电子版), 2010,4(3):254-260.
[10] 曹楚南.腐蚀电化学原理[M].北京:工业化学出版社,2004:69-74.
[11] 曹楚南,张鉴清.电化学阻抗谱导论[M].北京:科学出版社, 2002: 2-3.
[12] 张鉴清,张昭,王建明,等.电化学噪声的分析与应用-电化学噪声的分析原理[J].中国腐蚀与防护学报,2001,21(5):310-320.
[13] Huang HH.Effect of chemical composition on the corrosion behavior of Ni -Cr- Mo dental casting alloys.J Biomed Mater Res.2002;60(3):458-465.
[14] Abalos C,Paúl A ,Mendoza A,Solano E.In?uence of topographical features on the ?uoride corrosion of Ni–Ti orthodontic archwires.J Mater Sci.2011;22:2813-2821.
[15] Willershausen B,Callaway A,Ernst CP,et al.Influenceof oral bacteria on the surface morphology of various dental materials under conditions.Int Dent J.1995; 45(5):298-301.
[16] 马长柏,刘新强,李金华.氟对镍钛弓丝色泽的影响[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2009,27(6):645-648.
[17] 王强,那莹,战德松,等.模拟人体口腔环境中比较镍钛弓丝的腐蚀性能[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(42): 7855- 7858.
[18] 周群,余和东,苗磊,等.Vitallium 2000+钴铬钼合金和纯钛在不同人工唾液中耐腐蚀性的评价[J].口腔医学,2013,33(1):28-31.
[19] Weine FS.The C-shaped mandibular second molar:Incidence and other considerations. Members of the Arizona Endodontic Association.J Endod.1998;2(5):372-375.
[20] Hadded GY,Nehem WB,Ounsi HF.Diagnosis, classification, and frequency of C-shaped canals in mandibular second molars in the Lebanese population.J Endod. 1999;25(4): 268-271.
[21] Zheng YF,Wang QY,Li L.The electrochemical behavior and surface analysis of Ti49.6Ni45.1Cu5Cr0.3 alloy for orthodontic usage.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2008;86B(2):335-340.
[22] 麻健丰,刘劲松,张大风,等.3种牙科铸造金属模拟唾液浸泡后粗糙度的变化[J].上海口腔医学,2007,16(3):307-310.
[23] Ahn HS,Kim MJ,Seol HJ,et al.Effect of pH and temperature on orthodontic NiTi wir es immersed in acidic fluoride solution.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2006; 79(1): 7-15.
[24] Mane PP,Pawar R,Ganiger C,et al.Effect of fluoride prophylactic agents on the surface topography of NiTi and CuNiTi wires.J Contemp Dent Pract.2012;13(3):285-288.
[25] Kusy RP.A review of contemporary archwires: their properties and characteristics.Angle Orthod.1997;67(3):197-207.
[26] Ren CC,Bai YX,Wang HM,et al.Phase transformation analysis of varied nickel-titanium orthodontic wires.Chin Med J (Engl).2008;121(20):2060-2064.
[27] Boyer R,Welhch G,Collings EW.Materials properties handbook:Titanium alloys.Materials Park,Ohio: ASM International, 1994:1035-1044,1065-1073.
[28] Toumelin-Chamela F,Rouelle F,Burdairon G.Corrosive properties of fluoride containing odontologic gels against titanium.J Dent.1996;24:109-115.
[29] Yokoyama K,Kaneko K,Moriyama K,et al.Hydrogen embrittlement of NiTi superelastic alloy in fluoride solution.J Biomed Mater Res.2003;65:182-187.
[30] Fragou S, Eliades T.Effect of topical fluoride application on titanium alloys: A review of effects and clinical implications. Pediatr Dent.2010;32(2):99-105.
[31] Walker MP,White RJ,Kula KS.Effect of fluoride prophylactic agents on the mechanical properties of nickel-titanium-based orthodontic wires.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2005; 127(6): 662-669. |