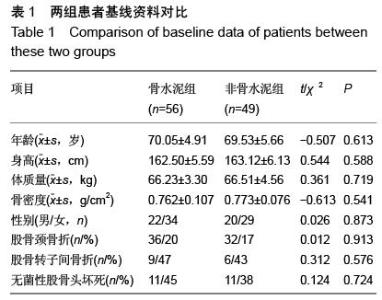
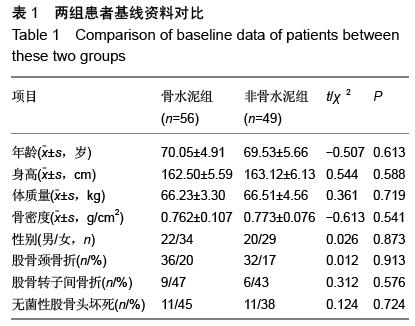
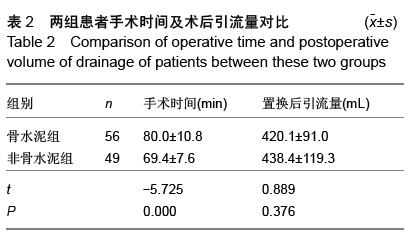
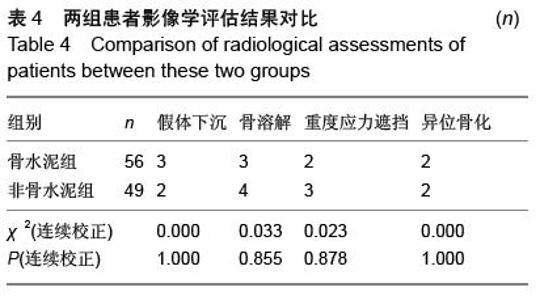
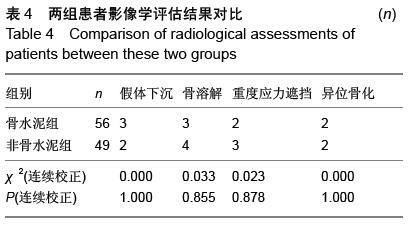
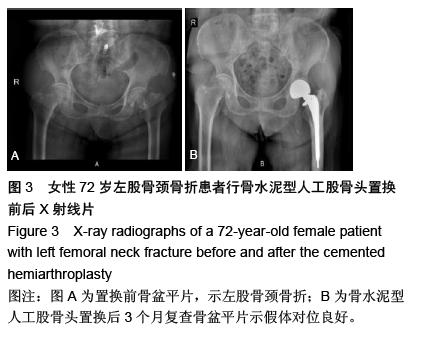
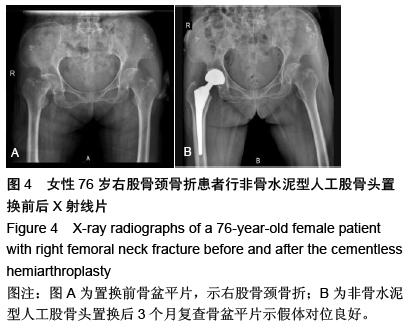
| [1] 王坤正,王岩.关节外科教程[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2014:127. [2] Zi-Sheng A, You-Shui G, Zhi-Zhen J, et al. Hemiarthroplasty vs primary total Hip arthroplasty for displaced fractures of the femoral neck in the elderly: a meta analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2012;4:583.[3] Bhandari M, Devereaux PJ, Tornetta III P, et al. Operative management of displaced femoral neck fractures in elderly patients. An international survey. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(9):2122.[4] Rogmark C, Fenstad AM, Leonardsson O,et al. Posterior approach and uncemented stems increases the risk of reoperation after hemiarthroplasties in elderly hip fracture patients. Acta Orthop. 2014;85(1): 18-25.[5] Gjertsen JE, Lie SA, Vinje T, et al. More re-operations after uncemented than cemented hemiarthroplasty used in the treatment of displaced fractures of the femoral neck: An observational study of 11116 hemiarthroplasties from a national register. J Bone Joint Surg (Br). 2012;8:1113.[6] Luo X, He S, Li Z, et al. Systematic review of cemented versus uncemented hemiarthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures in older patients. Arch Orthop Trauma. 2012; 132(4):455-463.[7] McGraw IW, Spence SC, Baird EJ, et al. Incidence of periprosthetic fractures after hip hemiarthroplasty:Are uncemented prostheses unsafe? Injury. 2013;44: 1945-1948.[8] Rogmark C, Carlsson A, Johnell O, et al. Primary hemiarthroplasty in old patients with displaced femoral neck fracture: a 1-year follow- up of 103 patients aged 80 years or more. Acta Orthop Scand. 2002;6:605.[9] Cankaya D, Ozkurt B, Tabak AY. Cemented calcar replacement versus cementless hemiarthroplasty for unstable intertrochanteric femur fractures in the elderly. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2013;19(6):548-553.[10] Lee YK, Ha YC, Chang BK, et al. Cementless Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty Using a Hydroxyapatite-Coated Long Stem for Osteoporotic Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures. J Arthroplasty. 2011;26(4):626-632. [11] Marya S, Thukral R, Hasan R, et al. Cementless bipolar hemiarthroplasty in femoral neck fractures in elderly. Indian J Orthop. 2011;45(3):236-242.[12] Richmond B.DXA scanning to diagnose osteoporosis: do you know what the results mean? Cleve Clin J Med. 2003;70(4):353-360.[13] 金超岭,王猛,李红磊,等.双能X线骨密度仪精密度和准确度的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2014,20(12):1425-1427.[14] Callaghan JJ, Dysart SH, Savory CG. The uncemented porous-coated anatomic total hip prosthesis. Two-year results of a prospective consecutive series. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998; 70:337.[15] Gruen TA, McNeice GM, Amstuz HC. ‘Modes of failure’ of cemented stem-type femoral components: a radiographic analysis of loosening. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979;141:17.[16] Engh CA, Bobyn JD. The influence of stem size and extent of porous coating on femoral bone resorption after primary cementless hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988;231:7. [17] Nicholas A, Bedard BS, John J, et al. Cementless THA for the Treatment of Osteonecrosis at 10-Year Follow-Up: Have We Improved Compared to Cemented THA? J Arthroplasty. 2013;28: 1192-1199.[18] 胥少汀,葛宝丰,徐印坎.实用骨科学[M].北京:人民军医出版社,2012:2539.[19] Parvizi J, Ereth MH, Lewallen DG. Thirty-day mortality following hip arthroplasty for acute fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;9:1983-1988.[20] Byrick RJ. Cement implantation syndrome: a time limited embolic phenomenon. Can J Anaesth. 1997;44(2):107.[21] 吕厚山.现代人工关节外科学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2006:32.[22] 沈国平,王正,罗从风,等.老年骨质疏松症对人工髋关节置换影响的实验研究[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2005, 20(7): 462-464.[23] Bottner F, Zawadsky M, Su EP, et al. Implant migration after early weightbearing in cementless hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;436:132.[24] Engh CA, Hooteh JP, Schaffer KFZ,et al. Evaluation of bone ingrowth in Proximally and extensively Porous- coated anatomic medullary locking prostheses retrieved at autopsy. J Bone Joint Surg(Am).1995;77:903-910.[25] Lee YK, Joung HY, Kim SH, et al. Cementless Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty Using a Micro-Arc Oxidation Coated Stem in Patients with Displaced Femoral Neck Fractures. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29: 2388-2392.[26] Berend KR, Lombardi AV, Mallory TH, et al. Cementless Double-Tapered Total Hip Arthroplasty in Patients 75 Years of Age and Older. J Arthroplasty. 2004;19(3):288-295.[27] Rhyu KH, Lee SM, Chun YS, et al. Does osteoporosis increase early subsidence of cementless double-tapered femoral stem in hip arthroplasty? J Arthroplasty. 2012;7:1305.[28] Sangiorgio SN, Ebramzadeh E, Knutsen AR, et al. Fixation of Non-Cemented Total Hip Arthroplasty Femoral Components in a Simulated Proximal Bone Defect Model. J Arthroplasty.2013;28: 1618-1624.[29] Meftah M, John M, Lendhey M, et al. Safety and Efficacy of Non-Cemented Femoral Fixation in Patients 75 Years of Age and Older. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28:1378-1380.[30] Vidovic D, Matejcic A. Periprosthetic bone loss following hemiarthroplasty: a comparison between cemented and cementless hip prosthesis. Injury. 2013; 44: S62-S66. |