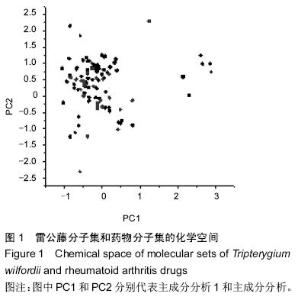
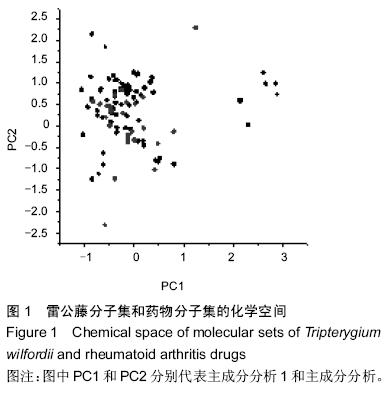
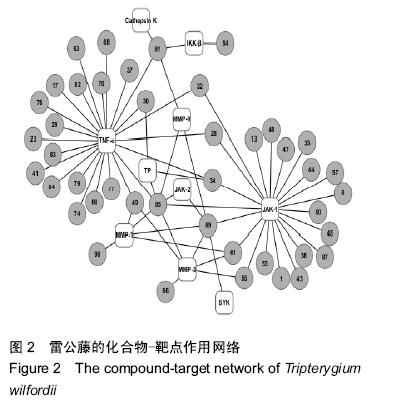
| [1] 刘献祥,林燕萍.中西医结合骨伤科学[M].北京:科学出版社,2011:239-241.[2] 施文,王永铭.非甾体类抗炎药的不良反应研究进展[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2003,19(1): 57-62.[3] 穆荣,栗占国.糖皮质激素在类风湿关节炎治疗中的应用[J].中华全科医师杂志,2005,4(3): 143-145.[4] 兰芬,阳凌燕,管剑龙.类风湿关节炎治疗药物的研究进展[J].药学服务与研究,2013, 13(1):38-42.[5] Zimmermann GR,Lehár J,Keith CT.Multi-target therapeutics: when the whole is greater than the sum of the parts.Drug Discov Today.2007;12(1-2):34-42.[6] Kitano HA robustness-based approach to systems- oritented drug design.Nat Rev Drug Discov.2007;6(3): 202-210.[7] Dvoracsko S,Stefanucci A,Novellino E,et al.The design of multitarget ligands for chronic and neuropathic pain.Future Med Chem.2015;7(18):2469-2483.[8] Zheng CS,Xu XJ,Ye HZ,et al.Computational approaches for exploring the potential synergy and polypharmacology of Duhuo Jisheng Decoction in the therapy of osteoarthritis.Mol Med Rep.2013;7(6): 1812-1818. [9] 徐晖,黄颖.中药治疗类风湿关节炎的研究进展[J].云南中医中药杂志,2015,36(1):88-90.[10] 徐筱杰.中药复方的计算机模拟研究[J].化学进展,1999, 11(2):202-204. [11] Xu XJ.New concepts and approaches for drug discovery based on Traditional Chinese medicine.Drug Discov Today Technol.2006;3(1):247-253.[12] Zheng CS,Xu XJ,Ye HZ,et al.Network pharmacology- based prediction of the multi-target capabilities of the compounds in Taohong Siwu decoction, and their application in osteoarthritis.Exp Ther Med.2013;6(1): 125-132.[13] 柯志鹏,张新庄,丁玥,等.利用网络药理学方法研究芪桂痛风片的药效物质基础与分子作用机制[J].中国中药杂志, 2015,40(14):2837-2842.[14] 郑春松,徐筱杰,叶蕻芝,等.青风藤治疗骨性关节炎药效物质基础多靶导向作用的计算机模拟研究[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2012,32(3):375-379.[15] 任海建,博强.雷公藤系列煎剂治疗类风湿性关节炎临床观察[J].中国现代药物应用,2007,1(4):33.[16] 汤淑彧,赵玉山,赵丽霞.雷公藤制剂治疗类风湿性关节炎有效性和安全性评价[J].山东医药, 2010,50(51):45-46.[17] 余递铧,何东初,张勇.雷公藤的毒性及减毒增效方法的研究进展[J].医学综述,2015,21(3):502-504.[18] 薛璟,贾晓斌,谭晓斌,等.雷公藤化学成分及其毒性研究进展[J].中华中医药杂志,2010,25(5):726-733.[19] 郑春松,徐筱杰,叶蕻芝,等.川芎活血化瘀和行气止痛作用的计算机模拟研究[J].中华中医药杂志, 2015,30(5):1432-1436.[20] Qin C,Zhang C,Zhu F,et al.Therapeutic target database update 2014:a resource for targeted therapeutics.Nucleic Acids Res.2014;42(Database issue):D1118-1123.[21] 黄钦,乔学斌,徐筱杰.中草药有效成分化合物的化学空间分析[J].计算机与应用化学,2007,24(1):41-44.[22] 罗兴燕,唐媚,邹强,等.蛋白激酶抑制剂在类风湿性关节炎的研究进展[J].成都医学院学报,2013,8(1):102-103.[23] Hao L,Zhu G,Lu Y,et al.Deficiency of cathepsin K prevents inflammation and bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis and periodontitis and reveals its shared osteoimmune role.FEBS Lett. 2015;589(12): 1331-1339.[24] Hong C,Shen C,Ding H,et al.An involvement of SR-B1 mediated p38 MAPK signaling pathway in serum amyloid A-induced angiogenesis inrheumatoid arthritis.Mol Immunol.2015;66(2):340-345.[25] 王苏丽,吕良敬.小分子“靶向”药物在类风湿关节炎中的研究进展[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2012,16(3):206-208.[26] 王玉树,史久华.类风湿性关节炎治疗靶点研究进展[J].国外医学:预防、诊断、治疗用生物制品分册, 2002, 25(5): 222-226.[27] 夏璇,黄清春,接力刚.类风湿关节炎“血瘀证”的研究进展[J].云南中医学院学报,2010,33(4):66-70.[28] Ruan KH,Wijaya C,Cervantes V,et al.Characterization of the prostaglandin H2 mimic: binding to the purified human thromboxane A2 receptor in solution.Arch Biochem Biophys.2008;477(2):396-403.[29] Deshpande M,Addess KJ,Bluhm WF,et al.The RCSB Protein Data Bank: a redesigned query system and relational database based on the mmCIF schema.Nucleic Acids Res.2005;(Database issue): D233-237. [30] Tang Y,Carbonetta D,Shetty S.Development of an integrated network visualisation and graph analysis tool for biological networks.Int J Comput Biol Drug Des.2012;5(2):152-163.[31] Lipinski CA,Lombardo F,Dominy BW,et al. Experimental and computational approaches to climate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings.Adv Drug Del Rev. 1997;23(1-3): 3-25.[32] 赵玲,胡耀华,柳润辉,等.中药治疗类风湿性关节炎及临床应用的研究进展[J].药学实践杂志,2011,29(6):416-419.[33] 杨文宇,万德光,杨鑫嵎.虚拟筛选辅助揭示中药药效物质基础的思路与初步实践[J].中草药, 2011,42(9): 1665-1672.[34] 赵晓莉,张新庄,狄留庆,等.中药复方制剂物质基础研究思路及方法探讨[J].世界科学技术—中医药现代化, 2009, 11(4):488-492.[35] 唐文富,万美华,黄熙.方剂组织药理学新假说[J].中草药, 2005,36(1):1-3.[36] 陈立武,郑春松,杜建.用分子对接法探讨清热消癥饮的抑瘤作用机制[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2007,12(3): 324-328.[37] Dobson CM.Chemical space and biology.Nature. 2004;432(16):824-828.[38] 陈亮,王鑫,冯心池,等.分子对接技术筛选石菖蒲中γ-氨基丁酸转氨酶抑制成分[J].沈阳药科大学学报, 2015, 32(3):204-207.[39] 龙伟,马世堂,刘培勋,等.基于CADD方法的黄连解毒汤抗炎药效物质基础多靶导向作用的研究[J].计算机与应用化学,2009,26(7):948-951.[40] 崔勇.雷公藤甲素治疗类风湿性关节炎作用机理的研究进展[J].泸州医学院学报,2006,29(3):263-265. |