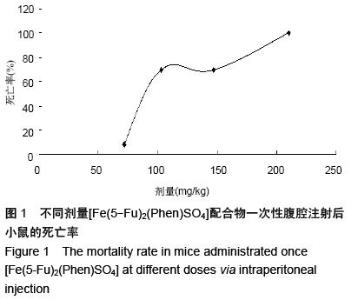
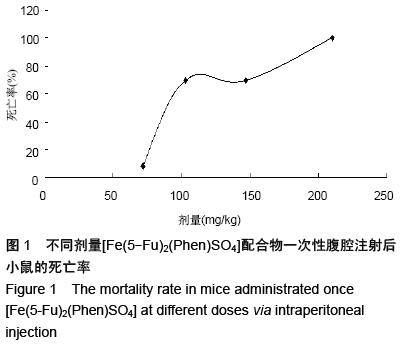
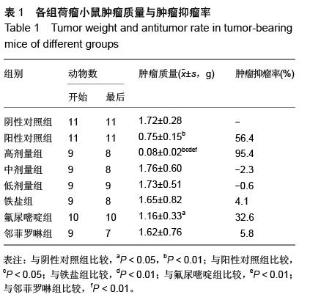
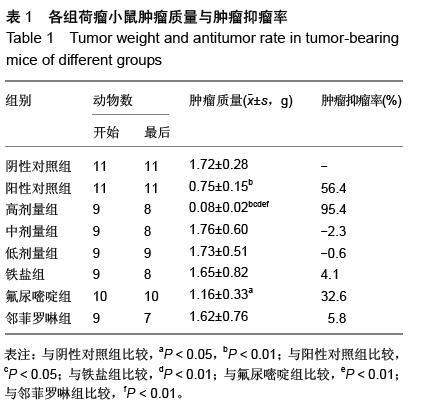
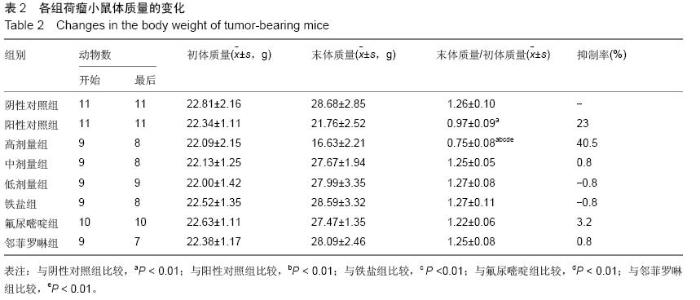
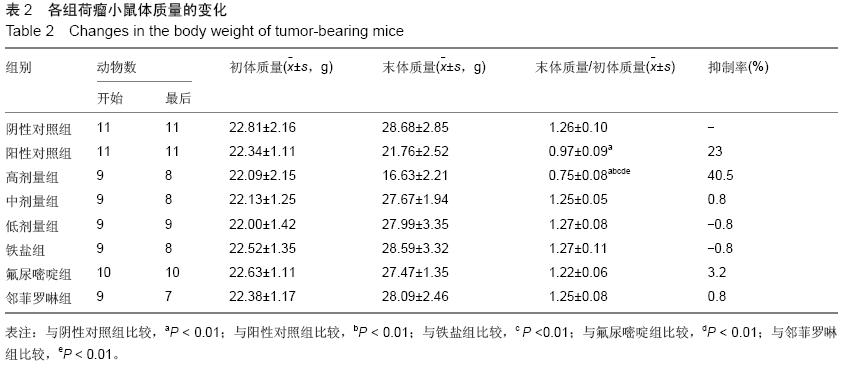
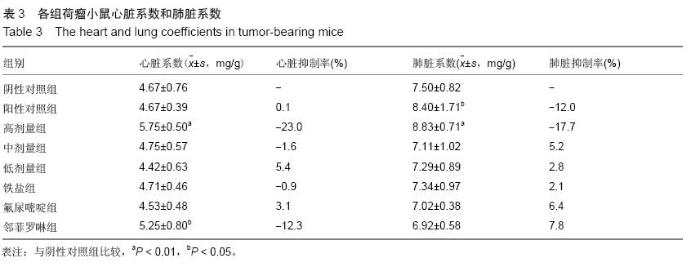
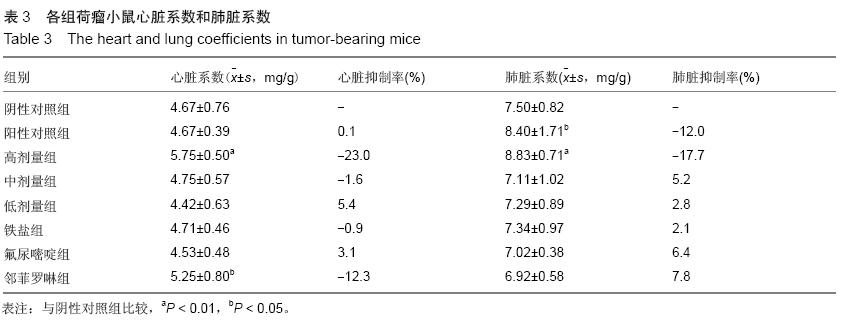
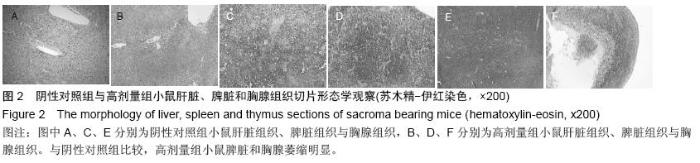
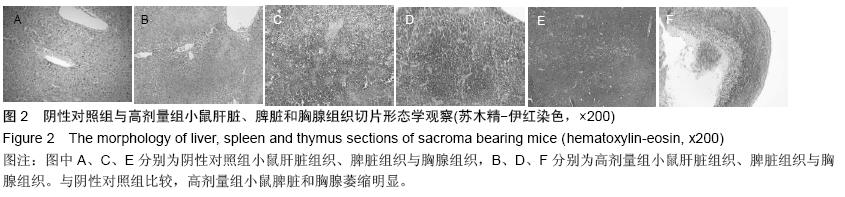
| [1] Rosenberg B, VanCamp L, Trosko JE, et al. Platinum compounds: a new class of potent antitumour agents. Nature.1969;222:385-386.[2] Frezza M, Hindo S, Chen D, et al. Novel Metals and Metal Complexes as Platforms for Cancer Therapy. Curr Pharm Des. 2010;16(16):1813-1825.[3] Jungwirth U, Kowol CR, Keppler BK, et al. Anticancer Activity of Metal Complexes: Involvement of Redox Processes. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;15(4): 1085-1127.[4] 李燕红,吴娟,徐宁志,等.新型抗肿瘤药物研究进展[J].武警医学,2011,10(22):901-903.[5] Daniel KG, Chen D, Orlu S, et al. Clioquinol and pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate complex with copper to form proteasome inhibitors and apoptosis inducers in human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. 2005; 7:R897-908. [6] Muhammad N, Guo Z. Metal-based anticancer chemotherapeutic agents. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2014;19C:144-153. [7] 祝兴勇,尤启冬,张文萍,等.铂(Ⅱ)类抗肿瘤药物[J].化学进展,2008,9(20):1324-1332.[8] Mazzaferro S,Bouchemal K,Ponchel G.Oral delivery of anticancer drugs II: the prodrug strategy.Drug Discov Today.2013;18(1-2):93-98.[9] Prachayasittikul V, Pingaew R, Nantasenamat C, et al. Investigation of aromatase inhibitory activity of metal complexes of 8-hydroxyquinoline and uracil derivatives. Drug Des DevTher. 2014;8:1089-1096.[10] Fatfat M, Merhi RA, Rahal O, et al. Copper chelation selectively kills colon cancer cells through redox cycling and generation of reactive oxygen species. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:527.[11] 蔡放,江仁望.天然产物的金属铜配合物研究进展[J].亚太传统医药,2011,7(6):163-168.[12] 牟永平,吴刚,周立社,等.抗肿瘤金属配合药物及其药理作用的研究进展[J].中国药理学通报, 2007,23(11): 1409-1413.[13] 黎七雄,汪晖,肖清秋,等.半数致死量(LD50)Bliss法的评价及计算[J].数理医药学杂志,1995,8(4):318-320.[14] 姜晓东,阎政礼,周桂凤.R程序在Bliss法计算半数致死量中的运用[J].实用预防医学,2011,18(3):431-432.[15] Cui BK, Liu S, Li SH, et al. Effect of Tea Polyphenol on Oxidative Injury in S180 Cells Induced Hepatocarcinoma Mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13:5571-5583.[16] 冯浩丽,高建平.党参多糖体内抗肿瘤活性研究及急性毒性实验[J].山西中医, 2012,28(8):49-50.[17] 朱坤杰,宋娟,沈云虹,等.库拉索芦荟多糖和木立芦荟多糖体内抗肿瘤作用[J].中成药, 2010,11(32):1978-1980. [18] Aikemu A, Umar A, Yusup A, et al. Immunomodulatory and antitumour effects of abnormal Savda Munziq on S180 tumour-bearing mice. BMC Complem Altern M. 2012;12:157.[19] 孙燕,王俊平,苏龙,等.黄连解毒汤对小鼠S180移植性肿瘤的抑制作用[J].东北农业大学学报,2013,44(9):63-67.[20] 赵凤丽,袁野,孙婷婷,等.人参皂苷结构修饰物HRG的体内抗肿瘤活性研究[J].中国药学杂志, 2012,20(47):1625-1629.[21] Zhang Y, Xiao Y, Wang P, et al. Compositions and Anti-Tumor Activity of Pyropolyporus fomentarius Petroleum Ether Fraction In Vitro and In Vivo. PLoS One.2014;9(10): e109599. [22] 覃华,张琰,韩艳,等.穿心莲内酯对S180小鼠体内抗肿瘤作用的研究[J].科学技术与工程, 2010,10(28):6971-6874.[23] 周轶平,陈元晓,周云,等.铜、铁、锌-氟尿嘧啶配合物合成及其对肿瘤细胞增殖的抑制[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(39):6309-6315.[24] 沈建忠.动物毒理学[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2002.[25] 李寿祺.动物毒理学原理与方法[M].成都:四川大学出版社,2003.[26] Yuan HM, Song JM, Li XG, et al. Enhanced immunostimulatory and antitumor activity of different derivatives of k–carrageenan oligosaccharides from Kappaphycus striatum. J Appl Phycol. 2011;23:59-65.[27] Alexander M, Steffen J. Development and function of dendritic cell subsets.Immunity. 2014;40(5):642-656.[28] Liu RM, Zhang XJ, Liang GY, et al. Antitumor and antimetastatic activities of chloroform extract of medicinal mushroom Cordyceps taii in mouse models. BMC Complem Altern M. 2015;15:216.[29] Liu RM, Zhang XJ, Liang GY, et al. Erratum to: 'Antitumor and antimetastatic activities of chloroform extract of medicinal mushroom Cordyceps taii in mouse models'.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015; 15:284.[30] Schneider T, Ehrig K, Liewert I, et al. Interference with the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis as potential antitumor strategy: superiority of a sulfated galactofucan from the brown alga Saccharina latissima and fucoidan over heparins. Glycobiology. 2015;25(8):812-824. [31] Abu N, Mohamed NE, Yeap SK, et al. In vivo antitumor and antimetastatic effects of flavokawain B in 4T1 breast cancer cell-challenged mice. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015;9:1401-1417. [32] Bastian A,Thorpe JE, Disch BC, et al. A small molecule with anticancer and antimetastatic activities induces rapid mitochondrial-associated necrosis in breast cancer. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.2015;353(2):392-404. [33] Schmieder R, Hoffmann J, Becker M, et al. Regorafenib (BAY 73-4506): antitumor and antimetastatic activities in preclinical models of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2014;135(6): 1487-9146.[34] Shin Y, Kim GD, Jeon JE, et al. Antimetastatic effect of halichondramide, a trisoxazole macrolide from the marine sponge Chondrosia corticata, on human prostate cancer cells via modulation of epithelial-to- mesenchymal transition. Mar Drugs. 2013;11(7):2472- 2485. [35] Gangjee A, Namjoshi OA, Yu J, et al. N2-Trimethylacetyl substituted and unsubstituted-N4- phenylsubstituted-6- (2-pyridin-2-ylethyl)-7H-pyrrolo [2,3-d]pyrimidine-2,4-diamines: design, cellular receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitory activities and in vivo evaluation as antiangiogenic, antimetastatic and antitumor agents. Bioorg Med Chem. 2013;21(5): 1312-1323. [36] Sun T, Chen QY, Wu LJ, et al. Antitumor and antimetastatic activities of grape skin polyphenols in a murine model of breast cancer. Food Chem Toxicol. 2012;50(10):3462-3467.[37] Alam A, Blanc I, Gueguen-Dorbes G, et al. SAR131675, a potent and selective VEGFR-3-TK inhibitor with antilymphangiogenic, antitumoral, and antimetastatic activities. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11(8):1637-1649. [38] Zhou L, Du L, Chen X, et al. The antitumor and antimetastatic effects of N-trimethyl chitosan-encapsulated camptothecin on ovarian cancer with minimal side effects. Oncol Rep. 2010; 24(4): 941-948.[39] Zhu H, Liu XW, Cai TY, et al. Celastrol acts as a potent antimetastatic agent targeting beta1 integrin and inhibiting cell-extracellular matrix adhesion, in part via the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010;334(2):489-499. |