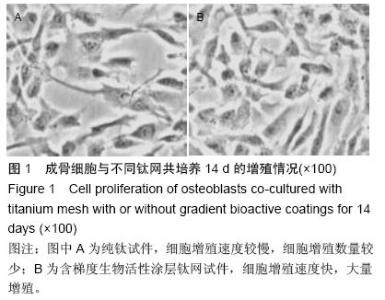
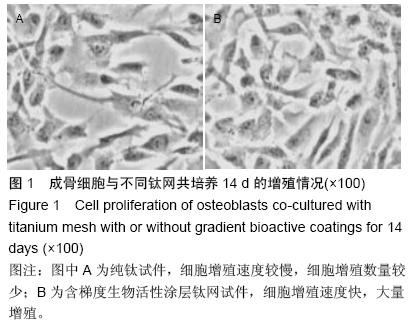
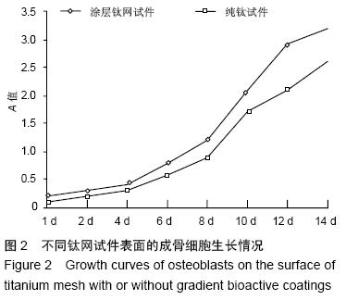
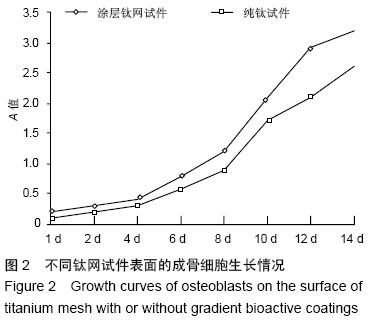
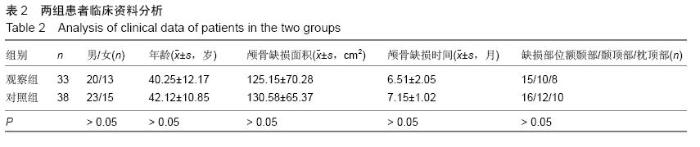
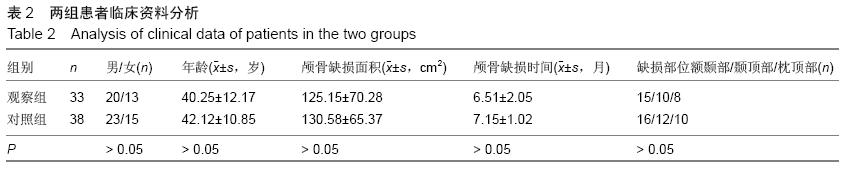
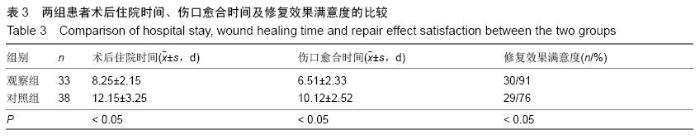
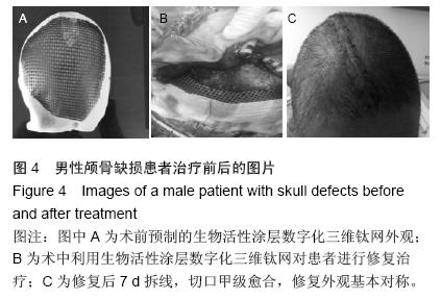
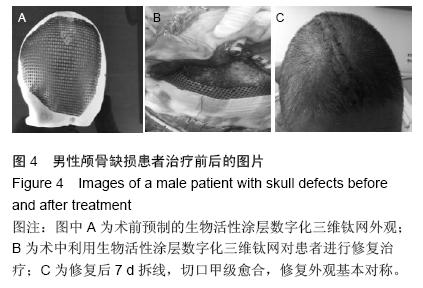
| [1] 叶迅,赵元立,朱琳,等.颅骨修补材料钛金属表面梯度生物活性涂层的生物相容性研究[J].北京医学, 2008,30(1): 8-12.[2] 叶迅,朱琳,唐光昕,等.纯钛表面梯度生物活性涂层材料生物相容性研究[J].中华神经外科疾病研究杂志, 2011, 10(6):543-547.[3] 龚雪.多孔纯钛表面纳米掺锶羟基磷灰石涂层构建及其生物学评价[D].浙江大学,2012.[4] 魏艳萍,王潇婕,马晓洁,等.Ti6Al4V活性及耐磨涂层对成骨细胞生物学行为影响[J].临床口腔医学杂志, 2006, 22(10):587-589.[5] 叶迅.复合氧化及水热沉淀法制备纯钛表面梯度生物活性涂层的生物相容性研究[D].首都医科大学,2005.[6] 尹大宇.钽涂层对生物医用钛合金抗腐蚀性能影响的实验研究[D].第四军医大学,2011.[7] 关泰红.梯度生物活性涂层材料激光快速成形制备技术及其理化性能初步研究[D].第四军医大学,2009.[8] 梁芳慧,王克光,周廉,等.多孔钛表面梯度磷灰石涂层的简单化学法制备[J].稀有金属材料与工程, 2003,32(11): 930-933.[9] Wieding J,Souffrant R,Mittelmeier W,et al.Finite element analysis on the biomechanical stability of open porous titanium scaffolds for large segmental bone defects under physiological load conditions.Med Eng Phys.2013;35(4):422-432.[10] 陈晓明,李世普,韩庆荣,等.在非水溶液体系中电泳沉积Ti6Al4V/BG/IIA梯度涂层[J].硅酸盐学报, 2001,29(6): 565-568.[11] 朱琳,公衍道,赵南明,等.前成骨细胞MC3T3-E1在梯度TiO2涂层修饰钛上的增殖与分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(44):8830-8834. [12] Schipper J,Ridder GJ,Spetzger U,et al.Individual prefabricated titanium implants and titanium mesh in skull base reconstructive surgery.A report of cases.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol.2004;261(5):282-290.[13] 郑敏,樊丁,李秀坤,等.激光熔覆钛基生物陶瓷涂层的制备及其界面研究[J].稀有金属材料与工程, 2009,38(11): 2004-2007.[14] 徐益,秦传江,赵柏森,等.钛基羟基磷灰石涂层的界面结构及梯度设计[J].表面技术,2005,34(1):58-61.[15] Goyenvalle E,Aguado E,Pilet P,et al.Biofunctionality of MBCP ceramic granules (TricOs) plus fibrin sealant (Tisseel) versus MBCP ceramic granules as a filler of large periprosthetic bone defects: an investigative ovine study.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010;21(6): 1949-1958. [16] 刘世敏,周宇.钛合金表面生物活性涂层的发展历程及趋势研究[J].材料工程,2009,(7):88-92.[17] 徐淑华,罗承萍,王迎军,等.羟基磷灰石生物活性梯度涂层材料的界面特点[J].中国有色金属学报, 2002,12(z1):163-167.[18] Miyamoto I,Funaki K,Yamauchi K,et al.Alveolar ridge reconstruction with titanium mesh and autogenous particulate bone graft: computed tomography-based evaluations of augmented bone quality and quantity.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2012;14(2):304-311.[19] 贺刚.纳米羟基磷灰石/含氟磷灰石/TiO<,2>梯度涂层对钛种植体表面改性的研究[D].四川大学,2006.[20] Schlegel KA,Sindet-Pedersen S,Hoepffner HJ.Clinical and histological findings in guided bone regeneration (GBR) around titanium dental implants with autogeneous bone chips using a new resorbable membrane.J Biomed Mater Res. 2000;53(4):392-399.[21] Winkler PA,Stummer W,Linke R,et al.The influcnce of cranioplasty on postural blood flow regulation,cercbrovas-cular reserve capacity,and cerebral glucose metabolism.J Neurosurg.2000;93(1):53-61.[22] Sakamoto S,Eguchi K,Kiura Y,et al.CT perfusion iIIlaging in the syndrome of the sinking skin flap before and after cranioplasty.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2006; 108(6):583-585.[23] Kuo JR,Wang CC,Chio CC,et al.Neurological improvement after cranioplasty-analysis by transcranial Doppler uitrasonography.J Clin Neurosci. 2004;11(5):486-489.[24] 王守臣,张玉芳,赵爱军,等.颅骨修补术56例颅内血流动力学分析[J].中国误诊学杂志,2008,8(24):5967-5968.[25] Yoshida K ,Furuse M,Izawa A,et al.Dynamics of cerebral blood flow and metabolism in patients with cranioplasty evaluated by 133Xe CT and 31P magnetic resortKllce spectroscopy.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1996;61:166-171.[26] 徐启文.钛表面HA生物活性梯度涂层的仿生制备研究[D].华南理工大学,2004.[27] 何陨,牛蓓.钛基/涂层型羟基磷灰石功能梯度生物材料研究进展[J].成都大学学报(自然科学版), 2013,32(3): 289-291, 302.[28] 倪永金.钛表面电泳沉积羟基磷灰石及其复合涂层的研究[D].厦门大学,2007.[29] 郑敏.钛合金表面激光熔覆制备生物陶瓷涂层及其生物活性研究[D].兰州理工大学,2008. [30] Sándor GK,Tuovinen VJ,Wolff J,et al.Adipose stem cell tissue-engineered construct used to treat large anterior mandibular defect: A case report and review of the clinical application of good manufacturing practice-level adipose stem cells for bone regeneration. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;71(5):938-950.[31] 梁景文,章翔,王西玲.钛颅骨修补材料对患者机体免疫功能的影响[J].第四军医大学学报,2002,23(23):2120. [32] 汤立,杨秋荣,吴称平.传统钛网修补颅骨与三维塑形钛网修补颅骨临床疗效对比[J].医学临床研究, 2014,31(2): 313-315.[33] Weng D,Poehling S,Pippig S,et al.The effects of recombinant human growth/differentiation factor-5 (rhGDF-5) on bone regeneration around titanium dental implants in barrier membrane-protected defects: a pilot study in the mandible of beagle dogs.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2009;24(1):31-37.[34] 高家诚,王勇,张亚平,等.液相沉积制备梯度生物活性涂层的研究[C].//第四届中国功能材料及其应用学术会议论文集,2001:1283-1284,1290.[35] 熊信柏,邹春莉,冯岩鹏,等.钛合金表面高频感应热梯度新方法制备生物活性钙磷涂层探索[J].稀有金属材料与工程, 2007,36(7):1249-1252.[36] Urban IA,Lozada JL,Jovanovic SA,et al.Vertical ridge augmentation with titanium-reinforced, dense-PTFE membranes and a combination of particulated autogenous bone and anorganic bovine bone-derived mineral: a prospective case series in 19 patients.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2014;29(1):185-193.[37] Murakami N,Saito N,Horiuchi H,et al.Repair of segmental defects in rabbit humeri with titanium fiber mesh cylinders containing recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2) and a synthetic polymer.J Biomed Mater Res. 2002;62(2):169-174.[38] 王静,田雪粉,任志峰,等.钛表面种籽层水热沉积制备羟基磷灰石生物涂层[C].//第十四届全国生物材料大会论文集, 2013:265-269.[39] 宁成云,王迎军,陈晓峰,等.梯度结构羟基磷灰石生物活性涂层的性能[J].材料研究学报,2006,20(1):69-72.[40] 郑扣松.HA生物活性梯度涂层的制备和性能研究[D].华中科技大学,2006 |