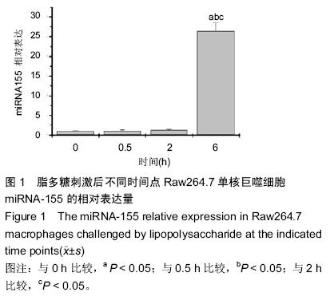
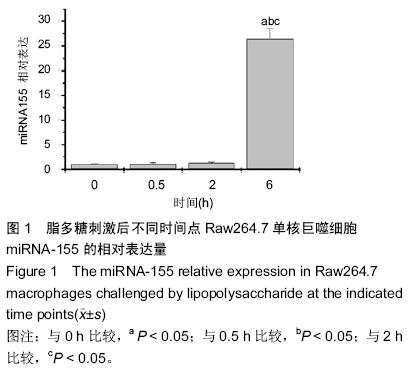
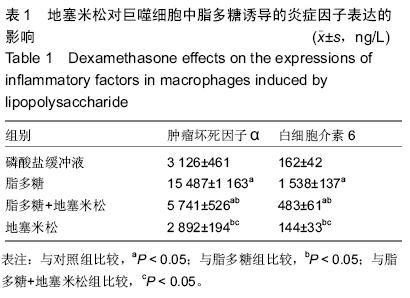
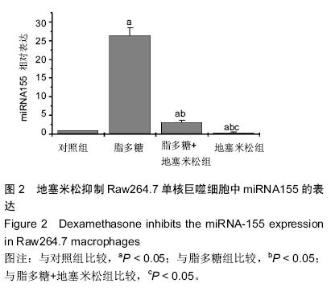
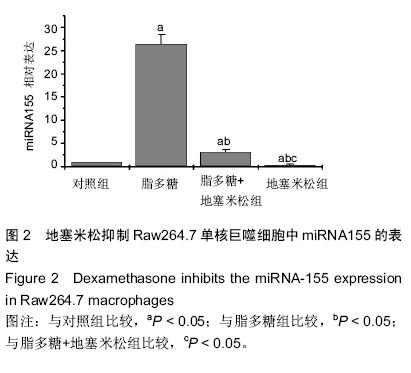
| [1] Hesse M, Arenz C. MicroRNA maturation and human disease. Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1095:11-25.[2] Moreno-Moya JM, Vilella F, Simon C. MicroRNA: key gene expression regulators. Fertil Steril. 2014;101(6): 1516-1523.[3] Elton TS, Selemon H, Elton SM, et al. Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013;532(1):1-12. [4] Gaieski DF, Edwards JM, Kallan MJ, et al. Benchmarking the incidence and mortality of severe sepsis in the United States. Crit Care Med. 2013;41(5): 1167-1174.[5] Jardin F, Figeac M. MicroRNAs in lymphoma, from diagnosis to targeted therapy. Curr Opin Oncol.2013; 25(5):480-486.[6] Roth C, Kasimir-Bauer S, Pantel K, et al. Screening for circulating nucleic acids and caspase activity in the peripheral blood as potential diagnostic tools in lung cancer. Mol Oncol. 2011;5(3):281-291.[7] Zoller M. Pancreatic cancer diagnosis by free and exosomal miRNA.World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2013;4(4):74-90.[8] Mattiske S, Suetani RJ, Neilsen PM, et al. The oncogenic role of miR-155 in breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2012;21(8):1236-1243.[9] Nikiforova MN, Tseng GC, Steward D, et al. MicroRNA expression profiling of thyroid tumors: biological significance and diagnostic utility.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93(5):1600-1608.[10] Lao G, Liu P, Wu Q, et al. Mir-155 promotes cervical cancer cell proliferation through suppression of its target gene LKB1. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(12): 11933-11938.[11] Faraoni I, Antonetti FR, Cardone J, et al. miR-155 gene: a typical multifunctional microRNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1792(6): 497-505.[12] Seddiki N, Brezar V, Ruffin N, et al. Role of miR-155 in the regulation of lymphocyte immune function and disease. Immunology. 2014;142(1):32-38.[13] Vigorito E, Perks KL, Abreu-Goodger C, et al. microRNA-155 regulates the generation of immunoglobulin class-switched plasma cells.Immunity. 2007;27(6):847-859.[14] 梁艳冰,王中华,唐皓,等.微小RNA-155在小鼠骨髓来源M1和M2巨噬细胞中表达的差异[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(10):1866-1870.[15] Tili E, Michaille JJ, Cimino A, et al. Modulation of miR-155 and miR-125b levels following lipopolysaccharide/TNF-alpha stimulation and their possible roles in regulating the response to endotoxin shock.J Immunol. 2007;179(8):5082-5089.[16] Martinez-Nunez RT, Louafi F, Sanchez-Elsner T. The interleukin 13 (IL-13) pathway in human macrophages is modulated by microRNA-155 via direct targeting of interleukin 13 receptor alpha1 (IL13Ralpha1). J Biol Chem. 2011;286(3):1786-1794. [17] McCoy CE, Sheedy FJ, Qualls JE, et al. IL-10 inhibits miR-155 induction by toll-like receptors. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(27):20492-20498.[18] O'Connell RM, Taganov KD, Boldin MP, et al. MicroRNA-155 is induced during the macrophage inflammatory response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(5):1604-1609.[19] Yin Q, Wang X, McBride J, et al. B-cell receptor activation induces BIC/miR-155 expression through a conserved AP-1 element.J Biol Chem. 2008;283(5): 2654-2662.[20] Lippai D, Bala S, Csak T, et al. Chronic alcohol-induced microRNA-155 contributes to neuroinflammation in a TLR4-dependent manner in mice. PLoS One. 2013;8(8): e70945.[21] Yin Q, McBride J, Fewell C, et al. MicroRNA-155 is an Epstein-Barr virus-induced gene that modulates Epstein-Barr virus-regulated gene expression pathways. J Virol. 2008;82(11):5295-5306.[22] Wang J, Wu M, Wen J, et al. MicroRNA-155 induction by Mycobacterium bovis BCG enhances ROS production through targeting SHIP1. Mol Immunol. 2014; 62(1):29-36.[23] Costinean S, Sandhu SK, Pedersen IM,et al.Src homology 2 domain-containing inositol-5-phosphatase and CCAAT enhancer-binding protein beta are targeted by miR-155 in B cells of Emicro-MiR-155 transgenic mice. Blood.2009;114(7):1374-1382.[24] Rao R, Rieder SA, Nagarkatti P, et al. Staphylococcal enterotoxin B-induced microRNA-155 targets SOCS1 to promote acute inflammatory lung injury. Infect Immun. 2014;82(7):2971-2979.[25] Urbanska J, Karewicz A, Nowakowska M. Polymeric delivery systems for dexamethasone. Life Sci. 2014; 96(1-2):1-6.[26] Ray A, Prefontaine KE. Physical association and functional antagonism between the p65 subunit of transcription factor NF-kappa B and the glucocorticoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.1994;91(2):752-756.[27] Haake SM, Dinh CT, Chen S, et al. Dexamethasone protects auditory hair cells against TNFalpha-initiated apoptosis via activation of PI3K/Akt and NFkappaB signaling. Hear Res. 2009;255(1-2):22-32.[28] Shah S, King EM, Chandrasekhar A, et al. Roles for the mitogen-activated protein kinase MAPK) phosphatase, DUSP1, in feedback control of inflammatory gene expression and repression by dexamethasone.J Biol Chem. 2014;289(19): 13667-13679. |