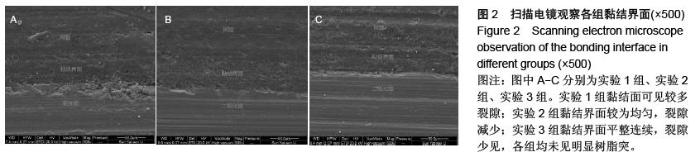
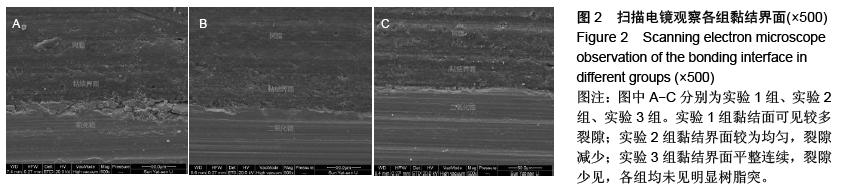
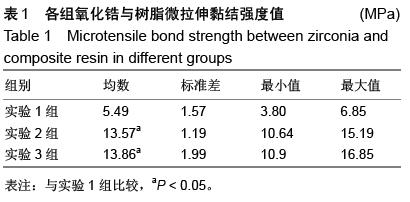
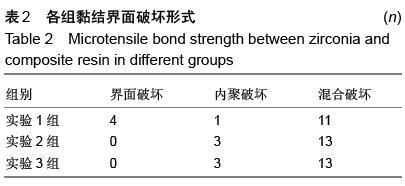
| [1] 杜桥,牛光良.氧化锆的表面粗化和改性[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2015,42(1):97-101.
[2] 赵克.浅谈——与氧化锆陶瓷修复体粘接强度相关的表面处理技术[J].口腔材料器械杂志, 2013,22(4):169-171.
[3] Casucci A,Osorio E,Osorio R,et al.Influence of different surface treatments on surface zirconia frameworks.J Dent.2009;37(11):891-897.
[4] de Souza G,Hennig D,Aggarwal A,et al.The use of MDP-based materials for bonding to zirconia.J Prosthet Dent.2014;112(4):895-902.
[5] 闫海鑫,吴琳,袁月,等.喷砂处理对氧化锆陶瓷基底与饰瓷结合强度的影响[J].口腔医学, 2011,31(2):96-98.
[6] 陈晨,谢海峰,宋鑫,等.氧化锆处理剂和自粘接树脂水门汀对氧化锆陶瓷粘接的效果评价[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2013,31(5):500-503.
[7] Inokoshi M,Kameyama A,De Munck J,et al.Durable bonding to mechanically and/or chemically pre-treated dental zirconia. J Dent.2013;41(2):170-179.
[8] 陈利民,王夏衡,王蔚,等.氧化物陶瓷与 3 种树脂水门汀初期粘接强度比较[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 2010,26(2): 153-156.
[9] 孟翔峰,陈渊华,俞青,等.不同类型粘接底涂剂对氧化锆陶瓷树脂粘接耐久性的影响[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2011, 27(4):474-477.
[10] 谢海峰,陈晨,王晓菲,等.氧化锆处理剂对氧化锆陶瓷短期粘结强度的影响[J].口腔医学, 2013,33(8):505-508.
[11] Kim MJ,Kim YK,Kim KH,et al.Shear bond strengths of various luting cements to zirconia ceramic: surface chemical aspects. J Dent.2011;39(11):795-803.
[12] Mosharraf R,Rismanchian M,Savabi O,et al.Influence of surface modification techniques on shear bond strength between different zirconia cores and veneering ceramics.J Adv Prosthodont. 2011;3(4): 221-228.
[13] Akin GE,Kaval ME,Turk T,et al.Surface Roughness and Bond Strength of Zirconia Posts to a Resin Cement After Various Surface Pretreatments. Photomedand Laser Surg.2015; 33(5):246-251.
[14] He M,Zhang Z,Zheng D,et al.Effect of sandblasting on surface roughness of zirconia-based ceramics and shear bond strength of veneering porcelain.Dent Mater J.2014;33(6):778-785.
[15] Fushiki R,Komine F,Blatz MB,et al.Shear bond strength between an indirect composite layering material and feldspathic porcelain-coated zirconia ceramics.Clin Oral Invest.2012;16(5):1401-1411.
[16] 胡道勇,钟恬,朱洪水.3种树脂表面处理技术对树脂核-玻璃离子水门汀粘接强度影响的实验研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2013,31(1):413.
[17] Nadabalung D,Powers J,Conelly M.Comparison of bond strengths of three denture base resins to treated Ni-Cr-Be alloy.J Prosthet Dent.1998;80:354-361.
[18] Hegde V,Katavkar R.A new dimension to conservative dentistry: Air abrasion.J Conserv Dent.2010;13:4-8.
[19] Kern M,Wegner S.Bonding to zirconia ceramic: adhesion methods and their durability.Dent Mater. 1998;14:64-71.
[20] Su N,Yue L,Liao Y,et al.The effect of various sandblasting conditions on surface changes of dental zirconia and shear bond strength between zirconia core and indirect composite resin.J Adv Prosthodont. 2015;7(3):214-223.
[21] 李磊丹,夏文薇.树脂微拉伸粘结强度测试法的影响因素[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志, 2011,21(10):604-606.
[22] 王瑜,龚玲,计艳,等.溶胶-凝胶法制备硅涂层提高牙科高强度陶瓷与复合树脂的粘接强度[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 2012,28(1):30-33.
[23] Palacios R,Johnson G,Phillips K,et al.Retention of zirconium oxide ceramic crowns with three types of cement.J Prosthet Dent.2006;96:104-114.
[24] Shahin R,Kern M.Effect of air-abrasion on the retention of zirconia ceramic crowns luted with different cements before and after artificial aging.Dent Mater.2010;26(9): 922-928.
[25] Wolfart M,Lehmann F,Wolfart S,et al.Durability of the resin bond strength to zirconia ceramic after using different surface conditioning methods.Dent Mater. 2007; 23(1):45-50.
[26] Piwowarczyk A,Lauer H,Sorensen JA.The shear bond strength between luting cements and zirconia ceramics after two pre-treatments.Oper Dent.2005;30(3):382.
[27] Ozcan M,Nijhuis H,Valandro L.Effect of various conditioning methods on the adhesion of dual cure resin cement with MDP functional monomer to zirconia after thermal aging. Dent Mater J.2008;27:99-104.
[28] May LG,Passos SP,Capelli DB,et al.Effect of silica coating combined to a MDP-based primer on the resin bond to Y-TZP ceramic.J Biomed Mater Res B.2010; 95(1):69-74.
[29] Seabra B,Arantes-Oliveira S,Portugal J.Influence of multimode universal adhesives and zirconia primer application techniques on zirconia repair.J Prosthet Dent. 2014;112(2):182-187.
[30] Amaral M,Belli R,Cesar PF,et al.The potential of novel primers and universal adhesives to bond to zirconia.J Dent. 2014;42(1):90-98.
[31] 谢海峰,陈晨,王晓菲,等.氧化锆处理剂对氧化锆陶瓷短期粘结强度的影响[J].口腔医学,2013,33(8):505-508.
[32] 白伟,林红,郑刚.一步法粘接剂对金属,陶瓷材料粘接性能的研究[J].北京大学学报:医学版,2014,46(2):336-338.
[33] Lindrgren J,Smeds J,Sjogren G.Effect of surface treatments and aging in water on bond strength to zirconia.Oper Dent. 2008;33:675-681.
[34] Tzanakakis E GC,Tzoutzas IG,Koidis PT.Is there a potential for durable adhesion to zirconia restorations? A systematic review.J Prosthet Dent.2015.
[35] Ozcan M,Nijhuis H,Valandro L.Effect of various conditioning methods on the adhesion of dual cure resin cement with MDP functional monomer to zirconia after thermal aging. Dent Mater J.2008;27:99-104.
[36] Kern M,Barloi A,Yang B.Surface conditioning influences zirconia ceramic bonding. J Dent Res. 2009;88(9):817-822.
[37] Piascik JR,Swift EJ,Thompson JY,et al.Surface modification for enhanced silanation of zirconia ceramics.Dent Mater. 2009;25(9):1116-1121. |