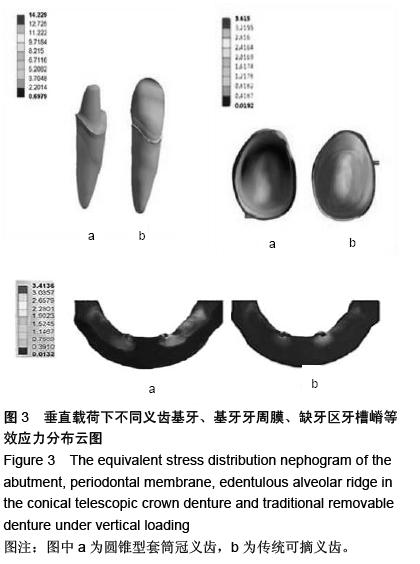
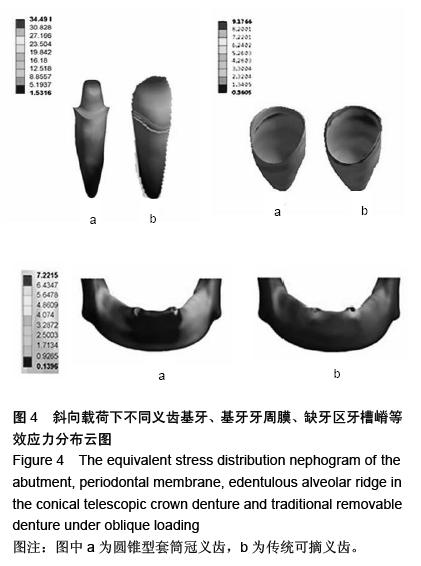
| [1] Lutz W,Sanderson W,Sche bov S.The coming acceleration of global population ageing.Nature. 2008;451(7179):716-719.
[2] Nations U,Division P.World population prospects:the 2000 revision.New York:United Nations,2003.
[3] 赵铱民.口腔修复学[M].7版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 2012:42.
[4] Nickenig HJ,Spiekermann H,Wichmann M,et al. Survival and complication rates of combined tooth-implant-supported fixed and removable partial dentures.Int J Prosthodont.2008;21(2):13l-137.
[5] Stancic I,Jelenkovic A.Retention of telescopic denture in elderly patients with maximum partially edentulous arch.Gerodontology.2008;25(3):162-167.
[6] Wostmann B,Balkenhol M,Weber A,et al.Long-term analysis of telescopic crown retained removable partial dentures:survival and need for maintenance.J Dent. 2007;35(12):939-945.
[7] 李彤,张强,张丽.不同合金套筒冠义齿对中重度牙周病伴牙列缺损修复效果的临床观察[J].医药前沿, 2011,16(15): 2514.
[8] 梁星,郭大伟.磁性附着体与冠外附着体的联合应用[J].中国实用口腔杂志,2009,2(8): 23-24.
[9] Jorge JH,Giampaolo ET,Vergani CE,et al.Clinical evaluation of abutment teeth of removable partial denture by means of the Periotest method.J Oral Rehabil.2007;34(3):222-227.
[10] Preshaw PM,Walls AW,Jakubovics NS,et al.Association of removable partial denture use with oral and systemic heath.J Dent.2011;39(11):711-719.
[11] Dittmer MP,Borchers L,Stiesch M,et al.Stresses and distortions within zirconia-fixed dental prostheses due to the veneering process.Acta Biomater. 2009;5(8): 3231-3239.
[12] Freitas-Junior AC,Rocha EP,Bonfance EA,et al.Biomechanical evaluation of internal and external hexagon platform switched implant-abutment connections:An in vitro laboratory and three-dimensional finite element analysis.Dent Mater. 2012;28(10):218-228.
[13] Aoda K,Shimamura I,Tahara Y,et al.Retainer design for unilateral extension base partial removable dental prosthesis by three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Prosthodont Res.2010;54(2):84-91.
[14] 王莉.圆锥型套筒冠义齿在临床中的应用[J].中国实用医药,2015,10(3):41-42.
[15] 陈少武,肖微,李智勇,等.种植体上部不同结构对下颌游离端义齿应力分布的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 2012, 28(3):294-297.
[16] 魏琦玲,李崴嵬.3种桩材料对于前磨牙应力分布影响的三维有限元分析[J].河北联合大学学报(医学版), 2013, 15(6): 773-774.
[17] Faverani LP,Barão VA,Ramalho-Ferreira G,et al.The influence of bone quality on the biomechanical behavior of full-arch implant-supported fixed prostheses.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;37:164-170.
[18] 董静,莫中军,潘韶霞,等.自凝树脂基托材料与下颌口腔黏膜滑动摩擦系数的实验研究[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2012,47(增刊):178-180.
[19] Muraki H,Wakabayashi N,Park I,et al.Finite element contact stress analysis of the RPD abutment tooth and periodontal ligament.J Dent.2004;32(8):659-665.
[20] 张杨,王超,张晓楠,等.动态载荷下不同骨质对天然牙-种植体联合修复应力分布的影响[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2015,33(3):286-290.
[21] 皮昕.口腔解剖生理学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2007: 293-294.
[22] Deck C,Nicolle S,Willinger R.Human Head FE Modelling:Improvement of Skull Geometry and Brain.Constitutive Laws[C].Proceeding of the 4th International Forum of Autanotive TrafficSafety (NFATS).Changsha,China:NFATS,2005:68-81.
[23] Yu Hs,Baik HS,Sung SJ,et al.Three-dimensional finite-element analysis of maxillary protraction with and without rapid palatal expansion.Eur J Orthod. 2007; 29(2):118-115.
[24] Palamara JE,Palamara D,Messer HH,et al.Tooth morphology and characteristics of non-carious cervical. J Dent.2006;34(3):185-194.
[25] 姚其卫,牟月照,王振林.下颌 Kennedy I 类可摘义齿有限元模型的建立[J].中国实用口腔杂志, 2010,3(7): 413-415.
[26] 贾如,王俊涛,逯宜,等.双重大连接体式与传统设计 R PD 支架及支持组织受力的三维有限元分析[J].中国美容医学,2013,22(2):279-282.
[27] Yeung AL,Lo E,Chow TW,et al.Oral health status of patients 5-6 years after placement of cobalt-chromium removable partial dentures.J Oral Rehabil. 2000; 27(3): 183-189.
[28] Dittmann B,Rammelsberg P.Survival of abutment teeth used for telescopic abutment retainers in removable partial dentures.Int J Prosthodont. 2008; 21(4):319-321.
[29] Goswami R,Mahajan P,Siwach A,et al.Telescopic over-denture:Perio- prostho concern for advanced periodontitis.Contemp Clin Dent.2013;4(3):402-405.
[30] 魏斌,陈洁,黄庆丰,等.套简冠与卡环固位型义齿修复末端游离缺失的应力分布比较[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2009,29(11):1288-1292.
[31] Lgarashi Y,Ogata A,Kuroiwa A,et al.Stress distribution and abutment tooth mobility of distal-extension removable partial dentures with different retainers an in vivo study.J Oral Rehabil.2009;26(2):111-116.
[32] Bernd W,Markus B,Andrea W,et al.Long-term analysis of Telescopic crown retained removable partial dentures: Survival and Need form aintenance.J Dent. 2007;35:939-945.
[33] 甘红,张修银,许晓岑,等.基牙及义齿支持形式对套筒冠义齿修复效果影响[J].口腔医学研究,2009,25(5):572-574.
[34] 李江峰,杜艳敏.套筒冠可摘义齿修复多数牙缺失体会[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2004,5(4):267-269.
[35] 杜凌晨.修复1000例56岁以上牙缺失病例的临床观察[J].中国医学工程,2010,18(4):125-126.
[36] 赵海红,王鹏,周军,等.孤立尖牙与单个种植体套筒冠覆盖义齿修复上颌牙列缺损1例[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2012, 30(6):659-661. |