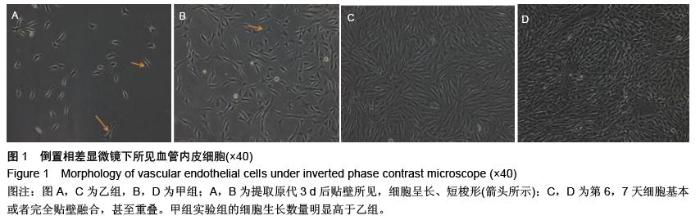
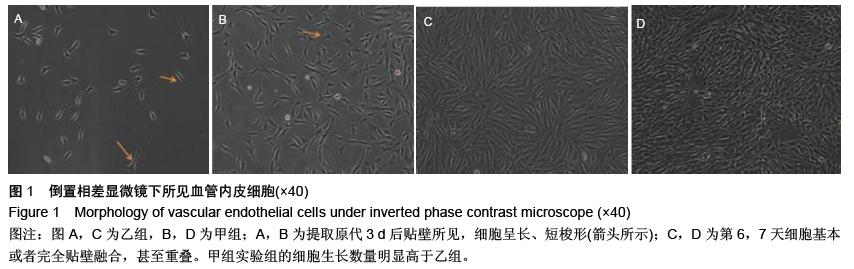
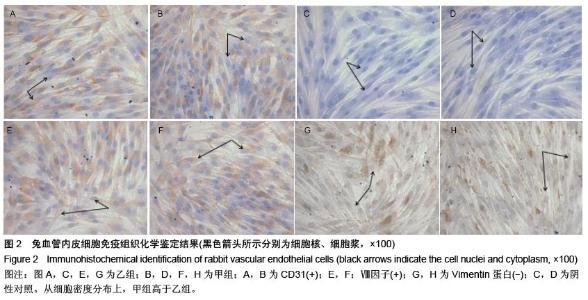
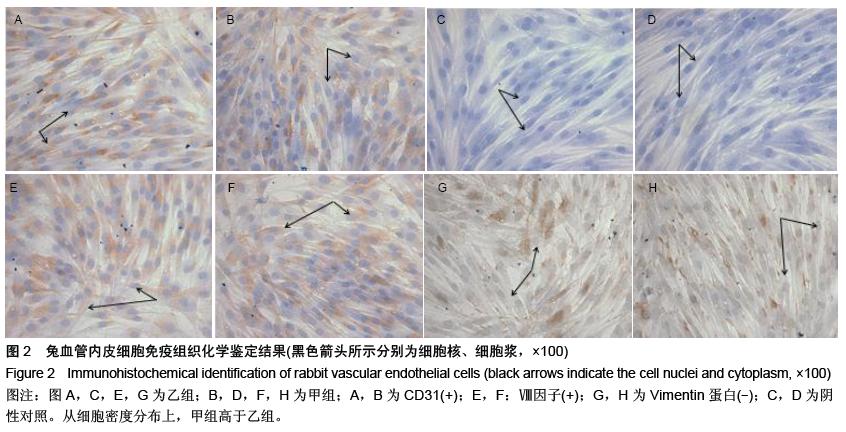
| [1] Yamada T,Ueda M,Egashira N,et al.Involvement of intracellular cAMP in epirubicin-induced vascular endothelial cell injury.J Pharmacol Sci. 2016;130(1): 33-37.
[2] Stone JR,Bruneval P,Angelini A,et al.Consensus statement on surgical pathology of the aorta from the Society for Cardiovascular Pathology and the Association for European Cardiovascular Pathology:I. Inflammatory diseases.Cardiovasc Pathol.2015;24(5):267-278.
[3] Ku?era J,Dvo?ánková B, Smetana K, et al.Fibroblasts isolated from the malignant melanoma influence phenotype of normal human keratinocytes.Journal of Applied Biomedicine.2015;13(3):195-198.
[4] Bielenberg DR, D'Amore PA. All Vessels Are Not Created Equal. Am J Pathol. 2013;182(4):1087-1091.
[5] Liu X, Tian J, Bai Q, et al. The effect and action mechanism of resveratrol on the vascular endothelial cell by high glucose treatment. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2016; 23(1):S16-21.
[6] Tang J, Meng Q, Cai Z, et al.Transplantation of VEGFl65-overexpressing vascular endothelial progenitor cells relieves endothelial injury after deep vein thrombectomy. Thrombosis Res.2016;137:41-45.
[7] Nakashima Y, Morimoto M, Toda K, et al. Inhibition of the proliferation and acceleration of migration of vascular endothelial cells by increased cysteine-rich motor neuron 1.Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2015;462(3):215-220.
[8] Liu S, Yuan Q, Li X, et al.Role of vascular peroxidase 1 in senescence of endothelial cells in diabetes rats. Int J Cardiol.2015;197:182-191.
[9] Tian X, Li Y. Endothelial Cell Senescence and Age-Related Vascular Diseases. J Genet Genomics. 2014;41(9):485-495.
[10] 李琼,王佐林.血管内皮祖细胞在构建组织工程骨中的研究进展[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2013,23(6):471-475.
[11] 余希杰,杨志明,解慧琪,等.血管内皮细胞对体外培养成骨细胞生物学特性的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2001,18 (4): 355-356.
[12] Zhao Y,Tan YZ,Zhou LF,et al.Morphological observation and in vitro angiogenesis assay of endothelial cells isolated from human cerebral cavernous malformations. Stroke.2007;38(4):1313-1319.
[13] 刘新晖,张锡庆,王晓东,等.兔肾微血管内皮细胞的体外培养及鉴定方法[J].苏州大学学报:医学版,2003,23(6): 658-661.
[14] Dimaio TA, Wentz BL, Lagunoff M. Isolation and characterization of circulating lymphatic endothelial colony forming cells.Exp Cell Res.2016:340(1): 159-169.
[15] Le GY, Essackjee HC, Ballard HJ. Intracellular adenosine formation and release by freshly-isolated vascular endothelial cells from rat skeletal muscle: effects of hypoxia and/or acidosis.Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2014; 450(1):93-98.
[16] Shoda T, Futamura K, Orihara K, et al.Recent advances in understanding the roles of vascular endothelial cells in allergic inflammation.Allergol Int.2016;65(1):21-29.
[17] Hayakawa K,Seo JH,Pham LD,et al.Cerebral endothelial derived vascular endothelial growth factor promotes the migration but not the proliferation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells in vitro. Neuroscience Letters.2012;513(1):42-46.
[18] Ataollahi F, Pingguan-Murphy B, Moradi A, et al. New method for the isolation of endothelial cells from large vessels. Cytotherapy.2014;16(8):1145-1152.
[19] Kobayashi M, Inoue K, Warabi E, et al.A simple method of isolating mouse aortic endothelial cells.J Atheroscler Thromb.2005;12(3):138-142.
[20] Kajimoto K,Hossen MN, Hida K,et al.Isolation and culture of microvascular endothelial cells from murine inguinal and epididymal adipose tissues. J Immunol Methods. 2010;357(1-2):43-50.
[21] Andre P, Michel M, Schott C,et al. Characterization of cultured rat aortic endothelial cells. J Physiol Paris. 1992;86(4):177-184.
[22] Diaz-Santana A,Shan M,Stroock AD. Endothelial cell dynamics during anastomosis in vitro.Integr Biol (Camb).2015;7(4):454-466.
[23] Sadanandam A,Rosenbaugh EG, Singh S, et al.Semaphorin 5A promotes angiogenesis by increasing endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and decreasing apoptosis. Microvasc.2010;79(1):1-9.
[24] Lu J, Rao MP, Macdonald NC, et al.Improved endothelial cell adhesion and proliferation on patterned titanium surfaces with rationally designed, micrometer to nanometer features.Acta Biomaterialia.2008;4(1): 192-201.
[25] Novosel EC, Kleinhans C, Kluger PJ. Vascularization is the key challenge in tissue engineering. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2011;63(4-5):300-311.
[26] Eller-Borges R,Batista WL,Da Costa PE,et al.Ras, Rac1, and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) signaling in nitric oxide induced endothelial cell migration. Nitric Oxide.2015;47:40-51.
[27] Liu MM, Flanagan TC, Lu CC, et al. Culture and characterisation of canine mitral valve interstitial and endothelial cells.Vet J.2015;204(1):32-39.
[28] 肖荣冬,翁国星.兔血管内皮细胞的培养及生物学特性[J].福建医科大学学报,2006,40(5):452-455.
[29] Tseng S, Chang M, Hsu M,et al.Arecoline inhibits endothelial cell growth and migration and the attachment to mononuclear cells.Journal of Dental Sciences.2014;9(3):258-264.
[30] Stach K, Zaddach F, Nguyen XD, et al. Effects of nicotinic acid on endothelial cells and platelets. Cardiovasc Pathol.2012;21(2):89-95.
[31] Marelli-Berg FM,Peek E,Lidington EA, et al.Isolation of endothelial cells from murine tissue.J Immunol Methods.2000;244(1-2):205-215.
[32] 秦苏萍,李慧,李小翠,等. CIA大鼠滑膜成纤维细胞的原代培养及鉴定[J].免疫学杂志,2014,30(12):1096-1099. |