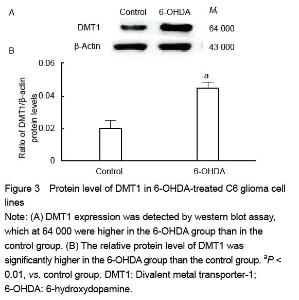
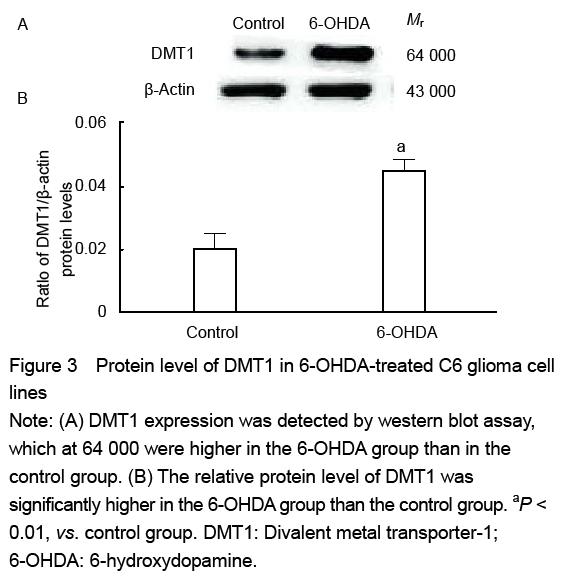
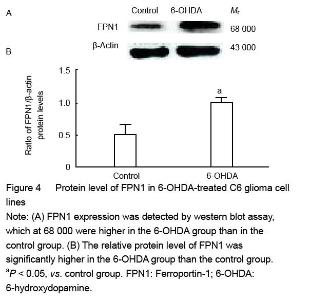
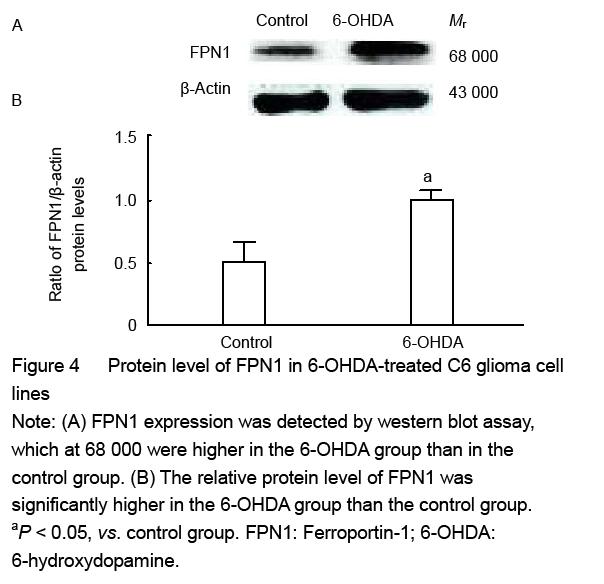
| [1] Haddad D, Nakamura K. Understanding the susceptibility of dopamine neurons to mitochondrial stressors in Parkinson’s disease. FEBS Lett. 2015; 589(24 Pt A):3702-3713.
[2] Zeineddine R, Yerbury JJ. The role of macropinocytosis in the propagation of protein aggregation associated with neurodegenerative diseases. Front Physiol. 2015;6:277.
[3] Goldman JG, Aggarwal NT, Schroeder CD. Mild cognitive impairment: an update in Parkinson's disease and lessons learned from Alzheimer's disease. Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2015;5(5):425-443.
[4] Youdim MB, Stephenson G, Ben Shachar D. Ironing iron out in Parkinson's disease and other neurodegenerative diseases with iron chelators: a lesson from 6-hydroxydopamine and iron chelators, desferal and VK-28. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004; 1012:306-325.
[5] Devos D, Moreau C, Devedjian JC, et al. Targeting chelatable iron as a therapeutic modality in Parkinson’s disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014;21(2):195-210.
[6] Singh N, Haldar S, Tripathi AK, et al. Iron in neurodegenerative disorders of protein misfolding: a case of prion disorders and Parkinson’s disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014;21(3):471-484.
[7] Weinreb O, Mandel S, Youdim MB, et al. Targeting dysregulation of brain iron homeostasis in Parkinson’s disease by iron chelators. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013; 62:52-64.
[8] Martin WR, Wieler M, Gee M. Midbrain iron content in early Parkinson disease: a potential biomarker of disease status. Neurology. 2008;70(16 Pt 2):1411-1417.
[9] Wieler M, Gee M, Martin WR. Longitudinal midbrain changes in early Parkinson’s disease: iron content estimated from R2*/MRI. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2015; 21(3):179-183.
[10] Qian ZM, Shen X. Brain iron transport and neurodegeneration. Trends Mol Med. 2001;7(3): 103-108.
[11] Gunshin H, Mackenzie B, Berger UV, et al. Cloning and characterization of a mammalian proton-coupled metal-ion transporter. Nature. 1997;388(6641):482-488.
[12] Garrick MD, Dolan KG, Horbinski C, et al. DMT1: a mammalian transporter for multiple metals. Biometals. 2003;16(1):41-54.
[13] Ke Y, Qian ZM. Divalent metal transporter-1: a newly discovered important ferroportin. Shengwu Huaxue yu Shengwu Wuli Jinzhan. 2002;29(2):184-188.
[14] Yu X, Du T, Song N, et al. Decreased iron levels in the temporal cortex in postmortem human brains with Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2013;80(5):492-495.
[15] Kano O, Ikeda K, Iwasaki Y, et al. Decreased iron levels in the temporal cortex in postmortem human brains with Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2013; 81(13):1181-1182.
[16] Jiang H, Song N, Xu H, et al. Up-regulation of divalent metal transporter 1 in 6-hydroxydopamine intoxication is IRE/IRP dependent. Cell Res. 2010;20(3):345-356.
[17] Li W, Jiang H, Song N, et al. Oxidative stress partially contributes to iron-induced α-synuclein aggregation in SK-N-SH cells. Neurotox Res. 2011;19(3):435-442.
[18] Sangchot P, Sharma S, Chetsawang B, et al. Deferoxamine attenuates iron-induced oxidative stress and prevents mitochondrial aggregation and alpha-synuclein translocation in SK-N-SH cells in culture. Dev Neurosci. 2002; 24(2-3):143-153.
[19] Taniguchi R, Kato HE, Font J, et al. Outward- and inward-facing structures of a putative bacterial transition-metal transporter with homology to ferroportin. Nat Commun. 2015;6:8545.
[20] Li J, Qian ZM, Chang YZ, et al. Recent progress in the studies of ferroportin 1. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2004;35(4):349-351.
[21] Wang J, Jiang H, Xie JX.Ferroportin1 and hephaestin are involved in the nigral iron accumulation of 6-OHDA-lesioned rats. Eur J Neurosci. 2007;25(9): 2766-2772.
[22] Knyihár-Csillik E, Chadaide Z, Mihály A, et al. Effect of 6-hydroxydopamine treatment on kynurenine aminotransferase-I (KAT-I) immunoreactivity of neurons and glial cells in the rat substantia nigra. Acta Neuropathol. 2006;112(2):127-137.
[23] Wang J, Song N, Jiang H, et al. Pro-inflammatory cytokines modulate iron regulatory protein 1 expression and iron transportation through reactive oxygen/nitrogen species production in ventral mesencephalic neurons. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1832(5):618-625.
[24] Zhang HY, Wang ND, Song N, et al. 6-Hydroxydopamine promotes iron traffic in primary cultured astrocytes. Biometals. 2013;26(5):705-714.
[25] Bushong EA, Martone ME, Ellisman MH.Maturation of astrocyte morphology and the establishment of astrocyte domains during postnatal hippocampal development. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2004;22(2):73-86.
[26] Saavedra A, Baltazar G, Santos P, et al. Selective injury to dopaminergic neurons up-regulates GDNF in substantia nigra postnatal cell cultures: role of neuron-glia crosstalk. Neurobiol Dis. 2006;23(3):533-542.
[27] Mena MA, García de Yébenes J. Glial cells as players in parkinsonism: the “good”, the “bad”, and the “mysterious” glia. Neuroscientist. 2008;14(6):544-560.
[28] Halassa MM, Fellin T, Takano H, et al. Synaptic islands defined by the territory of a single astrocyte. J Neurosci. 2007;27(24):6473-6477.
[29] Kimelberg HK. Functions of mature mammalian astrocytes: a current view.Neuroscientist. 2010;16(1): 79-106.
[30] Zeinstra E, Wilczak N, Chesik D, et al. Simvastatin inhibits interferon-gamma-induced MHC class II up-regulation in cultured astrocytes. J Neuroinflammation. 2006;3:16.
[31] Abboud S, Haile DJ.A novel mammalian iron-regulated protein involved in intracellular iron metabolism.J Biol Chem. 2000;275(26):19906-19912.
[32] Jakel RJ, Kern JT, Johnson DA, et al. Induction of the protective antioxidant response element pathway by 6-hydroxydopamine in vivo and in vitro. Toxicol Sci. 2005;87(1):176-186.
[33] [33] Mladenka P, Sim?nek T, Hübl M, et al. The role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in cellular iron metabolism. Free Radic Res. 2006;40(3):263-272.
[34] Zhao R, WAng GQ. The effect of deferiprone on excess free iron accumulation, free radicals and functional outcome in intracerebral hemorrhage rats. Zhongfeng yu Shenjing Jibing Zazhi. 2015;32(4):344-346.
[35] Wang J, Song N, Xu HM, et al. The Role of Iron and Alpha-synuclein Interacting in Parkinson’s Disease. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2015;46(3):180-184.
[36] Junxia X, Hong J, Wenfang C, et al. Dopamine release rather than content in the caudate putamen is associated with behavioral changes in the iron rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol. 2003;182(2):483-489.
[37] Youdim MB. What have we learnt from CDNA microarray gene expression studies about the role of iron in MPTP induced neurodegeneration and Parkinson’s disease? J Neural Transm Suppl. 2003; (65):73-88.
[38] Salazar J, Mena N, Hunot S, et al. Divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1) contributes to neurodegeneration in animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(47):18578-18583.
[39] Zhang S, Wang J, Song N, et al. Up-regulation of divalent metal transporter 1 is involved in 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP(+))-induced apoptosis in MES23.5 cells. Neurobiol Aging. 2009; 30(9):1466-1476.
|