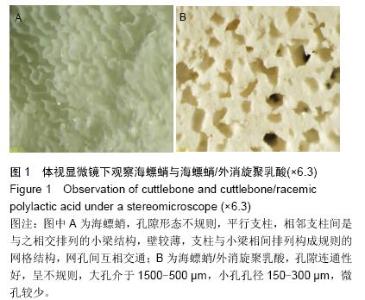
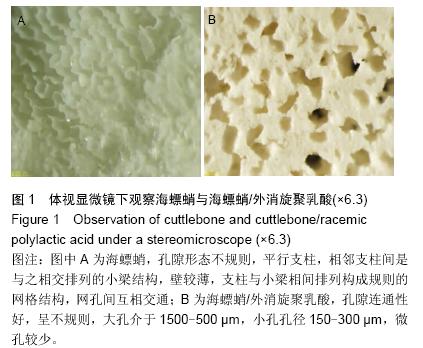
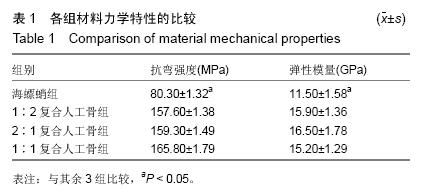
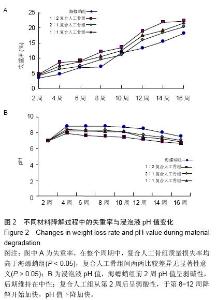
| [1] 肖建德.现代骨移植学[M].北京:科学出版社,2006.
[2] 汤勇智,陈建庭,赵成毅,等.纳米珍珠层粉的降解实验及其复合人工骨的生物相容性研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2009, 17 (2): 131-134.
[3] 刘金标.可塑形重组人工骨的研制及体内外相关实验研究[D].第一军医大学,2001:68.
[4] 李兰,吴启南.海螵蛸的化学成分研究[J].现代中药研究与实践, 2009,23(2):52-54.
[5] Wu CW,Chi CF,He GY,et al.Determination of 8 trace elements in mantle muscle and cuttlebone of Sepiella maindroni by ICP-MS using microwave digestion for sample preparation. Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi.2009;29(12):3395-3398.
[6] 高云,董福慧,郑军.海螵蛸对骨愈合相关基因表达的影响[J].中医正骨,2004,16(7):1-3.
[7] 刘艺,顾国奎,刘克泉,等.海螵蛸接骨动物实验的组织学研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,1995,3(5):6-8.
[8] García-Enriquez S, Guadarrama HE, Reyes-González I,et al.Mechanical performance and in vivo tests of an acrylic bone cement filled with bioactive sepia officinalis cuttlebone. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2010;21(1):113-125.
[9] 刘建全,王大平,黄江鸿,等.聚L-乳酸/纳米羟基磷灰石复合人工骨材料的制备及研究[J].深圳中西医结合杂志, 2014, 24 (4): 11-14.
[10] 袁野,靳安民,舒小秋,等.外消旋聚乳酸及其复合材料的生物相容性特征[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(1):64-65.
[11] 闵少雄,靳安民,朱立新,等.三维支架材料外消旋聚乳酸复合藻酸钙的生物相容性观察[J].中国临床康复,2003,7(23):3153-3155.
[12] Davy DT.Biomechanical issues in bone transplantation. Orthop Clin North Am.1999; 30(4):553-563.
[13] Cadman J,Chang CC,Chen J,et al.Bioinspired lightweight cellular materials--understanding effects of natural variation on mechanical properties. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013;33(6):3146-3152.
[14] Milovac D,Gallego Ferrer G,Ivankovic M,et al.PCL-coated hydroxyapatite scaffold derived from cuttlefish bone: morphology, mechanical properties and bioactivity.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2014;34:437-445.
[15] Goldberg VM.Selection of bone grafts for revision total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2000;(381):68-76.
[16] Ramasamy P,Subhapradha N,Shanmugam V,et al.Extraction, characterization and antioxidant property of chitosan from cuttlebone Sepia kobiensis (Hoyle 1885). Int J Biol Macromol. 2014;64:202-212.
[17] Vairamani S,Subhapradha N,Ramasamy P,et al. Physicochemical characteristics and antioxidant efficacy of chitosan from the internal shell of spineless cuttlefish Sepiella inermis.Prep Biochem Biotechnol.2013;43(7):696-716.
[18] Lee KM,Shim H,Lee GS,et al.Chitin from the Extract of Cuttlebone Induces Acute Inflammation and Enha,nces MMP1 Expression.Biomol Ther (Seoul).2013;21(3):246-250.
[19] 张亮.不同比例β-TCP/PDLLA骨替代材料及其复合rhBMP-2人工骨的实验研究[D].第一军医大学,2001:58.
[20] 王玮. RhBMP-2壳聚糖纳米微球及复合人工骨的制备和成骨活性研究[D].南方医科大学,2011:105.
[21] Giannoudis PV,Tzioupis C.Clinical applications of BMP-7: the UK perspective.Injury.2005;36 Suppl 3:S47-50.
[22] 沈霖,杨家玉,杨艳萍,等.海螵蛸/骨形态发生蛋白质复合材料的研制及其诱导成骨实验研究[J].中国中医骨伤科,1993,1(4):1-4.
[23] 蓝天,李彪,龚跃昆,等.骨髓间充质干细胞复合可注射型geneX及转化生长因子β2的成骨诱导效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(28):4435-4438.
[24] 刘军.生物活性玻璃复合VEGF修复兔桡骨骨缺损的实验研究[D].泰山医学院,2011:62.
[25] Yi HC,Tang LH,Zhang XP.[Experimental study on bone defect treated by combined autologous bone marrow transplantation, cuttlebone, and sodium hyaluronate]. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi.2011;31(8):1122-1126.
[26] Petite H,Viateau V,Bensaid W,et al.Tissue-engineered bone regeneration. Nat Biotechnol.2000; 18(9): 959-963.
[27] Tao K,Mao T,Chen F,et al.The preparation of a new hydroxyapatite and the study on its cytocompatibility.Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi.2006;23(4):887-890.
[28] 许善锦,张法浩,方国永,等.乌贼骨中矿物相转化研究[J].科学通报,1997,42(2):199-202.
[29] Hongmin L,Wei Z,Xingrong Y,et al.Osteoinductive nanohydroxyapatite bone substitute prepared via in situ hydrothermal transformation of cuttlefish bone.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2015;103(4):816-824.
[30] Hung YW, Ko WS,Liu WH,et al.Local review of treatment of hand enchondroma (artificial bone substitute versus autologous bone graft) in a tertiary referral centre: 13 years' experience.Hong Kong Med J.2015;21(3):217-223. |