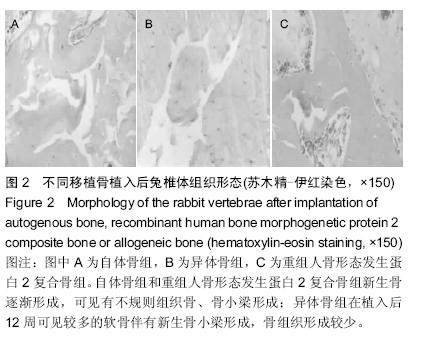
| [1] Wang Y, Ho CC, Bang E, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein 2 stimulates noncanonical SMAD2/3 signaling via the BMP type 1A receptor in gonadotrope-like cells: implications for FSH synthesis. Endocrinology. 2014;155(5):1970-1981.
[2] Murphy CM, Schindeler A, Gleeson JP, et al. A collagen-hydroxyapatite scaffold allows for binding and co-delivery of recombinant bone morphogenetic proteins and bisphosphonates. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(5):2250-2258.
[3] 韩玮,李煜明.密固达预防全髋关节置换植入后骨质疏松临床研究[J].现代仪器与医疗,2015,11(4):119-120.
[4] Roh JS, Yeung CA, Field JS, et al. Allogeneic morphogenetic protein vs. recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 in lumbar interbody fusion procedures: a radiographic and economic analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2013;8:49.
[5] 谭富强,刘渤,刘浠,等.骨形态发生蛋白-9对兔骨髓间充质干细胞诱导分化作用[J].中华实验外科杂志,2015,32(7):1527-1530.
[6] 余翔,夏远军,章莹,等.壳聚糖/硫酸葡聚糖/重组人骨形态发生蛋白-2微球诱导异位成骨的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2015, 17(7):616-623.
[7] 王根林,陈广东,朱雪松,等.丝素蛋白/双相磷酸钙/半水硫酸钙/重组人骨形态发生蛋白-2骨水泥的制备及修复椎体骨缺损的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2015,17(1):82-86.
[8] Lu J, Sun B, Huo R, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 antagonizes bone morphogenetic protein-4 induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and apoptosis. J Cell Physiol. 2014;229(10):1503-1510.
[9] 李军,王云,鲍小明,等.rhBMP-2体外诱导骨质疏松大鼠BMSCs成骨及VEGF表达的研究[J].中国骨伤,2015,4(5):446-449.
[10] 马立坤,邓江,叶鹏,等.携重组人骨形态发生蛋白2聚乳酸缓释微球的生物支架复合自体松质骨修复骨缺损[J].现代预防医学, 2015,42(5):882-885.
[11] Hyzy SL, Olivares-Navarrete R, Schwartz Z, et al. BMP2 induces osteoblast apoptosis in a maturation state and noggin-dependent manner. J Cell Biochem. 2012;113(10): 3236-3245.
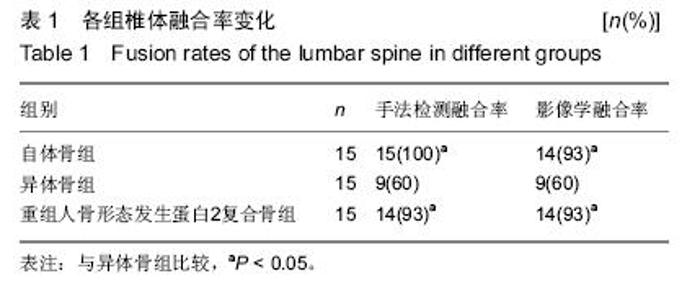
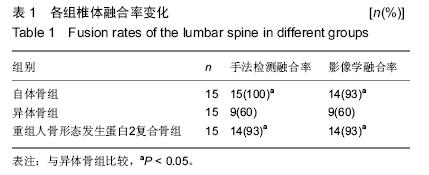
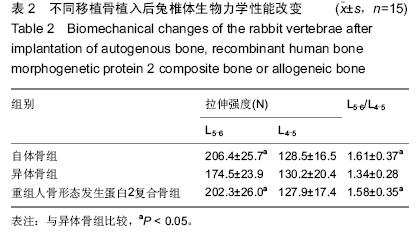
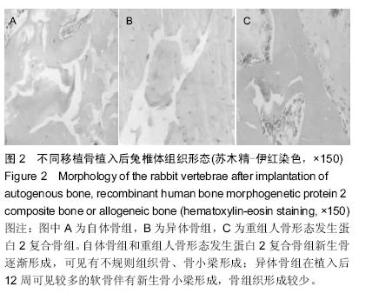
[12] 王展,张军,王登峰,等.重组人骨形态发生蛋白2复合骨在腰椎融合中的效果[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,3(25):3957-3961.
[13] Hammond E, Lang J, Maeda Y, et al. The Wnt Effector Transcription Factor 7-Like 2 Positively Regulates Oligodendrocyte Differentiation in a Manner Independent of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. J Neurosci. 2015;35(12):5007-5022.
[14] Chuang JH, Tung LC, Lin Y. Neural differentiation from embryonic stem cells in vitro: An overview of the signaling pathways. World J Stem Cells. 2015;7(2):437-447.
[15] Zhan Q,Song R,Zeng Q,et al. Activation of TLR3 Induces Osteogenic Responses in Human Aortic Valve Interstitial Cells through the NF-β and ERK1/2 Pathways. Int J Biol Sci. 2015;11(4):482-493.
[16] Chiovaro F, Chiquet-Ehrismann R, Chiquet M. Transcriptional regulation of tenascin genes. Cell Adh Migr. 2015;9(1-2): 34-47.
[17] Thorey F, Wenert K, Wwizbauer A, et al. Coating of titanium implants with copolymer supports bone regeneration: a comparative in vivo study in rabbits. J Appl Biomater Biomech. 2011;9(1):26-33.
[18] Zhang PX, Jiang XR, Wang L, et al. Dorsal root ganglion neurons promote proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(1):119-123.
[19] Fu R, Gao S, Peng F, et al. Relationship between abnormal osteoblasts and cellular immunity in multiple myeloma. Cancer Cell Int. 2014;14:62.
[20] Ramasubramanian A, Jeeawoody S, Yang F. Gene delivery of osteoinductive signals to a human fetal osteoblast cell line induces cell death in a dose-dependent manner. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2015;5(2):160-167.
[21] Gao Q, Tong W, Luria JS, et al. Effects of bone morphogenetic protein-2 on proliferation and angiogenesis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;39(3):266-271.
[22] Seeherman HJ, Li XJ, Bouxsein ML. et al. rhBMP-2 induces transient bone resorption followed by bone formation in a nonhuman primate core-defect model. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(2):411-426.
[23] Fukumoto R, Burns TM, Kiang JG. Ciprofloxacin enhances stress erythropoiesis in spleen and increases survival after whole-body irradiation combined with skin-wound trauma. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e90448.
[24] Liu DD, Ge K, Jin Y, et al. Terbium promotes adhesion and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells via activation of the Smad-dependent TGF-β/BMP signaling pathway. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2014;19(6):879-891.
[25] Kim JG, Kim HJ, Kim SE, et al. Enhancement of tendon-bone healing with the use of bone morphogenetic protein-2 inserted into the suture anchor hole in a rabbit patellar tendon model. Cytotherapy. 2014;16(6):857-867.
[26] García EV, Valdecantos PA,Barrera D, et al. Bone morphogenetic proteins in the bovine oviduct: differential expression of BMP-5 in the isthmus during the estrous cycle. Theriogenology. 2014;81(8):1032-1041.
[27] Song Y, Ju Y, Morita Y, et al. Surface functionalization of nanoporous alumina with bone morphogenetic protein 2 for inducing osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;37:120-126.
[28] Hu JJ, Liu YW, He MY, et al. Proteomic analysis on effectors involved in BMP-2-induced osteogenic differentiation of beagle bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Proteome Sci. 2014;12(1):13.
[29] Zhou Y, Wang JY, Feng H, et al. Overexpression of c1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein-3 promotes phosphate-induced vascular smooth muscle cell calcification both in vivo and in vitro. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014; 34(5):1002-1010.
[30] Pourtaheri S, Emami A, Hwang K, et al. Cervical corpectomy with ultra-low-dose rhBMP-2 in high-risk patients: 5-year outcomes. Orthopedics. 2013;36(12):931-935. |