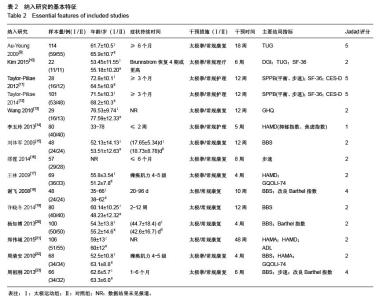
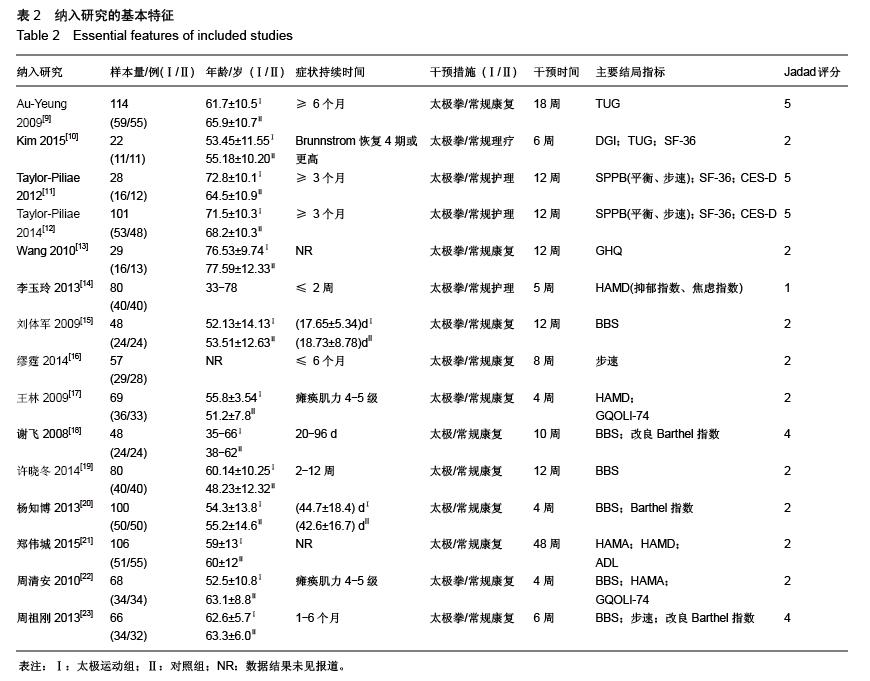
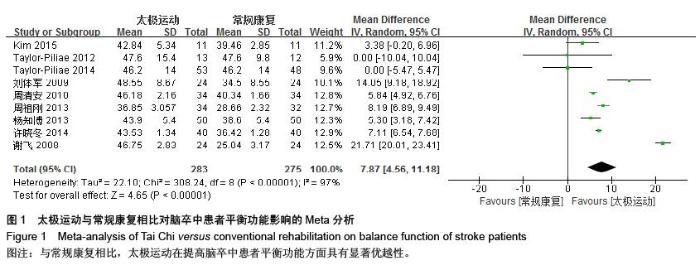
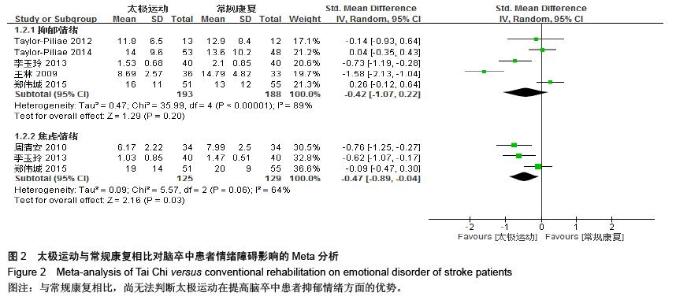
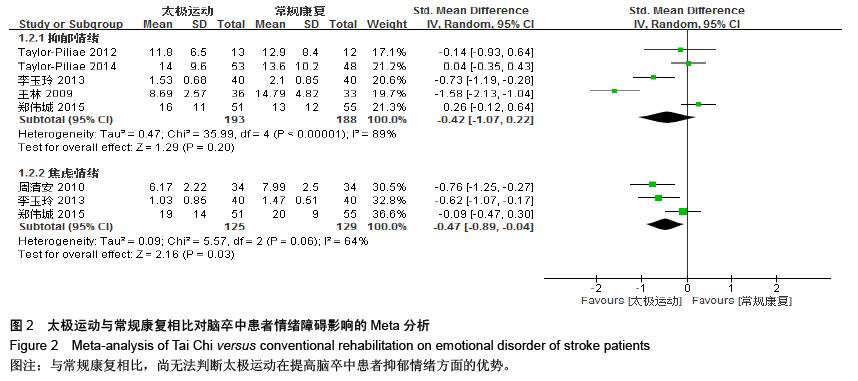
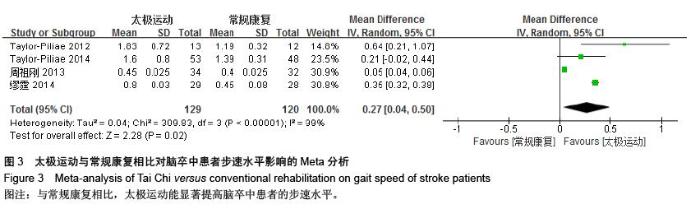
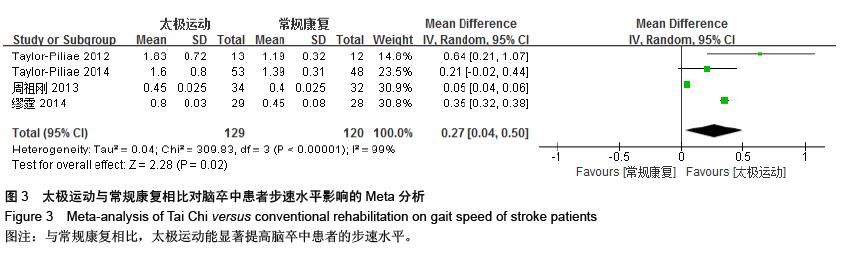
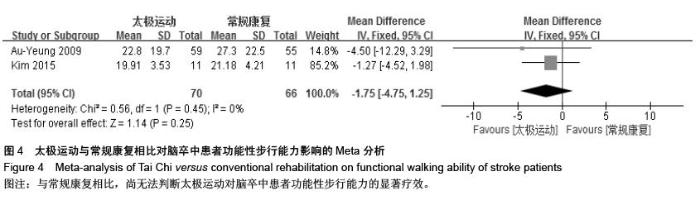
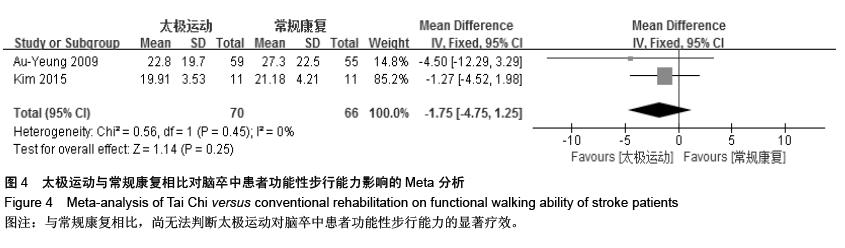
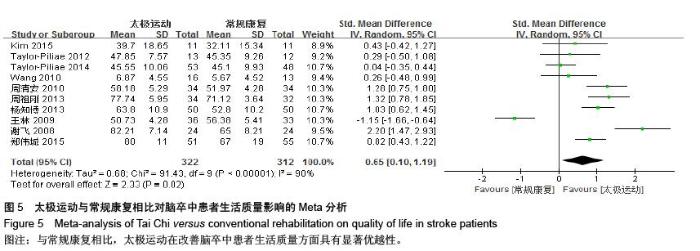
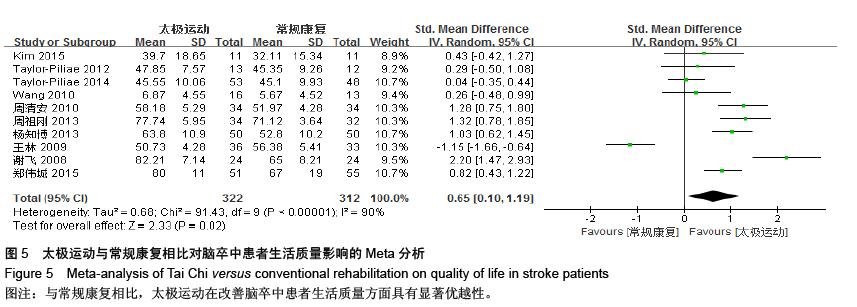
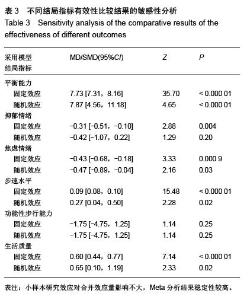
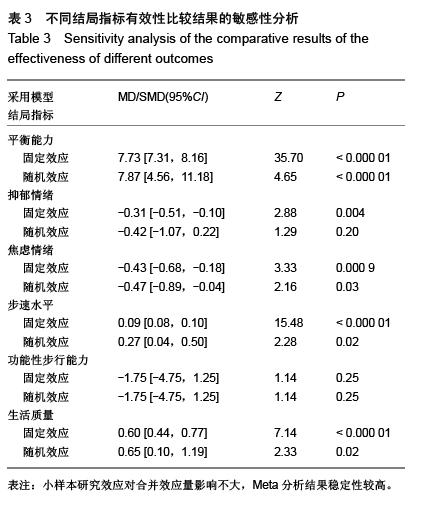
| [1] 王陇德.中国脑卒中防治报告(2015)[M].北京:中国协和医科大学出版社,2015. [2] Voukelatos A, Cumming RG, Lord SR, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of tai chi for the prevention of falls: the Central Sydney tai chi trial. J Am Geriatr Soc.2007;55:1185-1191. [3] 谢榆,魏刚,郭云柯,等. 太极治疗膝骨关节炎系统评价及meta分析[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2015,30:483-489. [4] Cheng TO. Tai Chi: the Chinese ancient wisdom of an ideal exercise for cardiac patients.Int J Cardiol.2007;117:293-295. [5] Li F, Harmer P, Fitzgerald K, et al. Tai Chi and Postural Stability in Patients with Parkinson's Disease. New England Journal of Medicine.2012;366:511-519. [6] Wang C, Schmid C H, Rones R, et al. A randomized trial of tai chi for fibromyalgia. N Engl J Med.2010;363:743-754. [7] 各类脑血管疾病诊断要点[J]. 中华神经科杂志,1996,29(6):379. [8] Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials.1996;17:1-12. [9] Au-Yeung SS, Hui-Chan CW, Tang JC. Short-form Tai Chi improves standing balance of people with chronic stroke. Neurorehabil Neural Repair.2009;23:515-522. [10] Kim H, Kim YL, Lee SM. Effects of therapeutic Tai Chi on balance, gait, and quality of life in chronic stroke patients. Int J Rehabil Res.2015;38:156-161. [11] Taylor-Piliae RE, Coull BM. Community-based Yang-style Tai Chi is safe and feasible in chronic stroke: a pilot study. Clin Rehabil.2012;26:121-131. [12] Taylor-Piliae RE, Hoke TM, Hepworth JT, et al. Effect of Tai Chi on physical function, fall rates and quality of life among older stroke survivors. Arch Phys Med Rehabil.2014;95:816-824. [13] Wang W, Sawada M, Noriyama Y, et al. Tai Chi exercise versus rehabilitation for the elderly with cerebral vascular disorder: a single-blinded randomized controlled trial. Psychogeriatrics.2010;10:160-166. [14] 李玉玲,胡杏娟,温馨.坐式太极运动在脑卒中后抑郁患者康复训练中的应用[J].齐鲁护理杂志,2013:19(23)4-6. [15] 刘体军,秦萍,陈杏枝.太极拳改善脑卒中患者平衡功能的疗效观察[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2009,31(11):781-782. [16] 缪霆,代新年,闫玮娟,等.太极拳训练对脑卒中偏瘫患者步态参数的影响[J].中国疗养医学,2014:987-988. [17] 王林,周清安,徐建银,等.太极拳对脑梗死后抑郁状态康复作用的观察[J].中国社区医师(医学专业),2012,14(18)222. [18] 谢飞. 太极康复法对脑卒中患者平衡障碍的康复研究[J]. 吉林大学,2008. [19] 许晓冬,白晶,张洪丽,等.太极桩功对中风后偏瘫平衡功能障碍患者的影响[J].河北中医,2014,36(8):1149-1150. [20] 杨知博,刘东,常悦松,等.太极平衡法治疗中风后偏瘫平衡障碍的临床研究[J].代医学,2013,19(24):5-7. [21] 郑伟城,张影红,江雪琴,等.持续太极运动对缺血性脑卒中患者康复疗效前瞻性随机、对照试验[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2015,13(3):304-307. [22] 周清安,徐建银,胡爱平,等. 太极拳对脑梗死患者康复的影响[J]. 中国实用神经疾病杂志,2010,13(22):20-22. [23] 周祖刚. 强化太极步态训练对脑卒中偏瘫患者步态参数及步行能力的影响[J]. 成都中医药大学,2013. [24] Ostwald S K, Davis S, Hersch G, et al. Evidence-based educational guidelines for stroke survivors after discharge home. J Neurosci Nurs.2008;40:173-179, 191. [25] 张通.中国脑卒中康复治疗指南(2011完全版) [J].中国康复理论与实践,2012:301-318. [26] Dean C M, Rissel C, Sharkey M, et al. Exercise intervention to prevent falls and enhance mobility in community dwellers after stroke: a protocol for a randomised controlled trial. BMC Neurol.2009;9:38. [27] Yavuzer G, Eser F, Karakus D, et al. The effects of balance training on gait late after stroke: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil.2006;20:960-969. [28] Li F, Harmer P, Stock R, et al. Implementing an evidence-based fall prevention program in an outpatient clinical setting. J Am Geriatr Soc.2013;61:2142-2149. [29] 燕铁斌.“起立-行走”计时测试简介-功能性步行能力快速定量评定法[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2000,6(3):115-116. [30] 丛林,姜海涛,闵连秋.卒中后患者生活质量的性别差异[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志,2011,8(8):424-428. [31] 郭新峰. 中风病临床疗效评价指标体系的初步研究[D]. 广州中医药大学,2001. [32] 刘宏斌.老年痴呆患者生活质量及其影响因素[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2012,32(6):1237-1238. [33] 张骏,何廷尉,罗德儒,等. SF-36评价中风患者生命质量的信度和效度[J]. 中国行为医学科学,2001,10(5):416-419. |