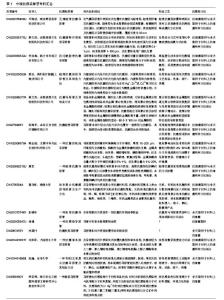
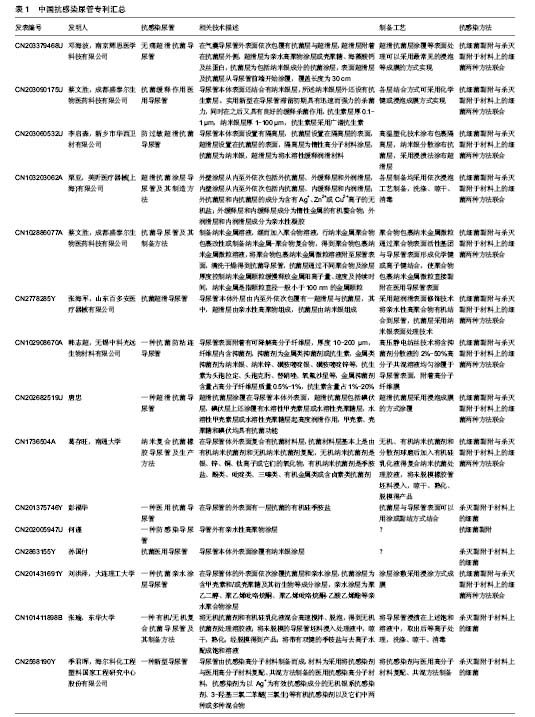
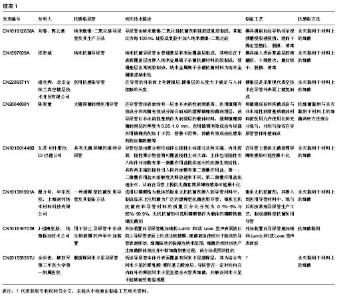
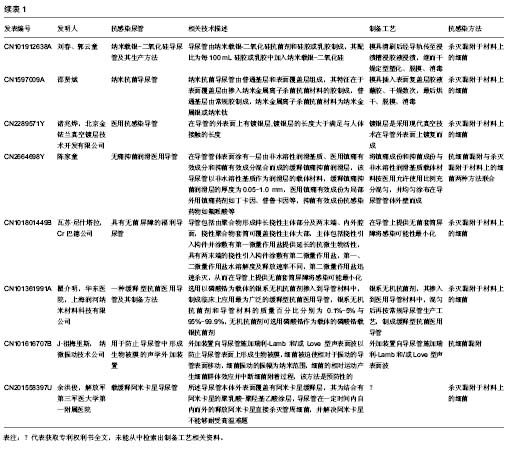
| [1] Nicolle L.Urinary catheter-associated infections.Infect Dis Clin North Am.2012; 26(1):13-27.
[2] Yang L,Liu Y,Wu H,et al.Combating biofilms. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol.2012;65(2): 146-157.
[3] Tambyah PA,Oon J.Catheter-associated urinary tract infection. Curr Opin Infect Dis.2012;25(4):365-370.
[4] Bruellhoff K,Fiedler J,Möller M,et al.Surface coating strategies to prevent biofilm formation on implant surfaces.Int J Artif Organs.2010;33(9):646-653.
[5] 陈红蕾,孙乐民,敬卿,等.SooPAT及百度、Google专利搜索引擎比较[J].高校图书馆工作,2011,31(3):46-48.
[6] Lebeaux D, Ghigo JM. Management of biofilm-associated infections: what can we expect from recent research on biofilm lifestyles? Med Sci (Paris).2012;28(8-9):727-739.
[7] Hatt JK, Rather PN.Role of bacterial biofilms in urinary tract infections.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol.2008;322:163-192.
[8] Chenoweth CE,Gould CV,Saint S.Diagnosis, management, and prevention of catheter-associated urinary tract infections. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2014;28(1):105-119.
[9] Pickard R,Lam T,MacLennan G,et al.Antimicrobial catheters for reduction of symptomatic urinary tract infection in adults requiring short-term catheterisation in hospital: a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet.2012;380(9857): 1927-1935.
[10] Johnson JR,Kuskowski MA,Wilt TJ.Systematic review: antimicrobial urinary catheters to prevent catheter-associated urinary tract infection in hospitalized patients.Ann Intern Med. 006;144(2):116-126.
[11] Pickard R,Lam T,Maclennan G,et al.Types of urethral catheter for reducing symptomatic urinary tract infections in hospitalised adults requiring short-term catheterisation: multicentre randomised controlled trial and economic evaluation of antimicrobial- and antiseptic-impregnated urethral catheters (the CATHETER trial).Health Technol Assess.2012;16(47):1-197.
[12] Meddings J,Rogers MA,Krein SL,et al.Reducing unnecessary urinary catheter use and other strategies to prevent catheter-associated urinary tract infection: an integrative review.BMJ Qual Saf.2014;23(4):277-289.
[13] Siddiq DM,Darouiche RO.New strategies to prevent catheter- associated urinary tract infections.Nat Rev Urol.2012; 9(6): 305-314.
[14] Ramanathan R, Duane TM.Urinary tract infections in surgical patients.Surg Clin North Am.2014;94(6):1351-1368.
[15] Romanò CL,Toscano M,Romanò D,et al.Antibiofilm agents and implant-related infections in orthopaedics: where are we?J Chemother.2013;25(2):67-80.
[16] 本刊中文部.本期专题:防止细菌生物膜生成的抗菌生物材料[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(47): 8755,8756, 8776.
[17] 施光峰.临床留置导管相关感染的诊治进展[J].中华实用内科杂志, 2007,27(1):68-70.
[18] Tambyah PA,Oon J.Catheter-associated urinary tract infection.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2012;25(4):365-370.
[19] Krachler AM,Orth K.Targeting the bacteria-host interface: strategies in anti-adhesion therapy.Virulence.2013;4(4): 284-294.
[20] Otto M.Physical stress and bacterial colonization.FEMS Microbiol Rev.2014;38(6):1250-1270.
[21] Rodrigues LR.Inhibition of bacterial adhesion on medical devices. Adv Exp Med Biol.2011;715:351-367.
[22] Imazatoa S,Ebia N,Takahashia Y,et al.Antibacterial activity of bactericide-immobilized filler for resin-based restoratives. Biomaterials.2003; 24(20): 3605-3609.
[23] Regev-Shoshani G,Ko M,Miller C,et al. Slow release of nitric oxide from charged catheters and its effect on biofilm formation by Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54(1):273-279.
[24] 车小强,张松营,陈云平,等.多种抗菌剂抗菌性及混合加入复合树脂的抗菌性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(16):3002-3009.
[25] Yi H,Kazuro F,Ryotaro H,et al.Generating elastic, biodegradable polyurethane/poly( lactide-co- glycolide) fibrous sheets with controlled antibiotic release via two-stream electrospinning. Biomaterials.2008;9(4): 1200-1207.
[26] Di Luca M,Maccari G,Nifosì R.Treatment of microbial biofilms in the post antibiotic era: prophylactic and therapeutic use of antimicrobial peptides and their design by bioinformatics tools. Pathog Dis.2014;70(3):257-270.
[27] 张文辉,金小海.药物涂层支架涂层的工艺[J].国际生物医学工程杂志,2006,29(1): 42-44.
[28] Norowski PA Jr,Bumgardner JD.Biomaterial and antibiotic strategies for peri-implantitis: a review.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2009;88(2):530-543.
[29] Bruellhoff K,Fiedler J,Möller M,et al.Surface coating strategies to prevent biofilm formation on implant surfaces.Int J Artif Organs.2010;33(9):646-653.
[30] Dong J, Zhang S, Ma J,et al.Preparation, characterization, and in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of a novel anti-tuberculosis reconstruction implant.PLoS One.2014;9(4): e94937.
[31] Stickler DJ.Clinical complications of urinary catheters caused by crystalline biofilms: something needs to be done.J Intern Med.2014;276(2):120-129.
[32] Feneley RC,Kunin CM,Stickler DJ.An indwelling urinary catheter for the 21st century.BJU Int.2012;109(12):1746-1749. |