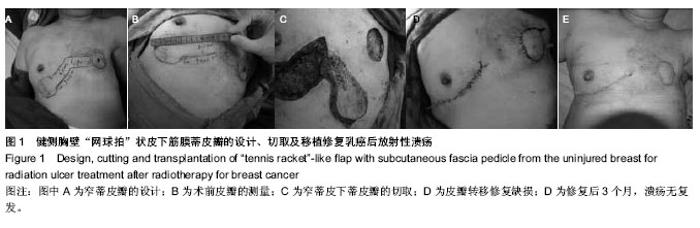
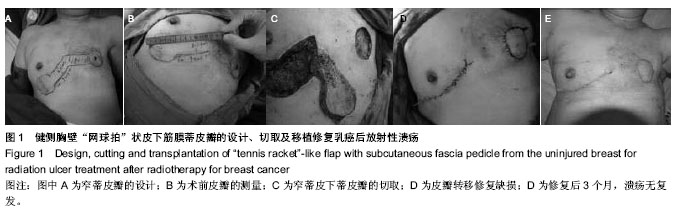
| [1] 李小静,宁金龙,张林,等.应用对侧胸三角岛状皮瓣即期修复胸壁乳腺癌术后再发病灶[J].中华显微外科杂志,2004,27(3): 221-222.
[2] 梁杰,都新光,李建赤.应用肌皮瓣修复前胸壁放射性溃疡[J].中华显微外科杂志,2007,30(2): 141-143.
[3] 杨兴华,黄晓元,龙剖虹.乳腺癌根治术后放射性溃疡的皮瓣修复[J].中华外科杂志,2006,44(7): 471-472.
[4] 林志潮,伍硕允,叶敏.应用肌皮瓣修复乳腺癌术后胸壁放射性溃疡创面[J].中华显微外科杂志,2012,35(4):317-318.
[5] 陈忠勇,叶祥柏,王锡华,等.乳腺癌术后放射性溃疡的皮瓣修复[J].中华医学美学美容杂志,2012,18(4):311-312.
[6] Goessler UR, Bugert P, Kassner S, et al.In vitro analysis of radiation-induced dermal wounds.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010;142(6):845-850.
[7] Jadhav SS, Sharma N, Meeks CJ,et al.Effects of combined radiation and burn injury on the renin-angiotensin system. Wound Repair Regen. 2013; 21(1):131-140.
[8] Palmer JH, Taylor GI.The vascular territories of the anterior chest wall.Br J Plast Surg. 1986;39(3):287-299.
[9] Barberini F, Brunone F.A "conservative" method of thoracic wall dissection: a proposal for teaching human anatomy.Ital J Anat Embryol. 2008; 113(3):187-195.
[10] Cariou JL.1984-1994: ten years of skin flaps. Improvements and conceptual developments. Development of vascular concepts, classification and clinical concepts].Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 1995; 40(5):447-525.
[11] 宋慧锋,柴家科,柳春明,等.胸部多源血供皮瓣在颌颈部组织缺损或畸形修复中的应用[J].中华烧伤外科杂志,2009,25(1):15-17.
[12] 阳富春,赵劲民,杨志,等.带蒂侧胸壁筋膜皮瓣修复肩前锁骨区皮肤软组织巨大缺[J].中华显微外科杂志,2008,31(1):58-60.
[13] 余道江,赵天兰,徐又佳,等.应用耳后窄蒂皮下蒂皮瓣修复耳廓内软组织缺损[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26(6):721-723.
[14] 余道江,赵天兰,徐又佳,等.负压封闭引流技术在狭长窄蒂皮瓣中的应用[J].中华整形外科杂志,2013,29(1):62-64.
[15] Zhao TL, Tang Y, Yu DJ,et al.The application of narrow pedicle flaps in repairing facial defects.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011;64(7):970-972.
[16] Kim JT, Ng SW, Kim YH.Application of various compositions of thoracodorsal perforator flap for craniofacial contour deformities.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2011; 64(7): 902-910.
[17] Hölzle F, Hohlweg-Majert B, Kesting MR, et al.Reverse flow facial artery as recipient vessel for perforator flaps. Microsurgery. 2009; 29(6):437-442.
[18] 伍丽君,赵天兰,余道江,等.缺氧缺血型狭长窄蒂皮瓣成活过程中SDF-1表达的实验研究[J].中华整形外科杂志,2012, 28(1):52-55.
[19] 赵天兰,余道江,谢晓明, 等.狭长窄蒂皮瓣在面额部皮肤癌治疗中的应用[J].中华整形外科杂志, 2012,28 ,28-31.
[20] 徐子寒,赵天兰,余道江,等.地拉罗司通过诱导上皮细胞间质化改变促进窄蒂皮瓣微血管生成的实验研究[J].中华整形外科杂志, 2012,28(5):352-355.
[21] 余道江,徐又佳,赵天兰,等.负压封闭引流技术波动法治疗硬皮病伴关节腔脓肿合并继发性骨髓炎一例[J].中华整形外科杂志, 2012,28(5):385-386.
[22] 余道江,赵天兰,徐又佳,等.负压封闭引流技术对淤血皮瓣微血管及微血栓的影响[J].中华医学美学美容杂志,2013,19(1):39-42.
[23] Lavery LA,La Fontaine J,Thakral G,et al.Randomized clinical trial to compare negative-pressure wound therapy approaches with low and high pressure, silicone-coated dressing, and polyurethane foam dressing.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014;133(3):722-726.
[24] Qu J,Yan R,Wang L,et al.Free dermatoplasty combined with vacuum sealing drainage for the treatment of large-area soft tissue defects accompanied by bone exposure in the lower leg.Exp Ther Med.2013;5(5):1375-1380.
[25] Ren GH,Li JW,Li RG,et al.Treatment of large circular soft tissue defect in lower extremities with a combination of bridge flaps and free skin graft covered by vacuum sealing drainage.Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2012;50(1):39-44.
[26] Chen Q,Liu DS,Hu W,et al.Treatment of high-pressure paint injection injuries of hand with debridement combined with vacuum sealing drainage technique.Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2011;24(10):851-853.
[27] Li RG, Yu B, Wang G,et al. Sequential therapy of vacuum sealing drainage and free-flap transplantation for children with extensive soft-tissue defects below the knee in the extremities. Injury.2012;43(6):822-828.
[28] 王文林,钟世镇,王武军,等.胸壁复合组织瓣用于心脏外科小切口的解剖学研究[J].中国局解手术学杂志, 2000,9(3):200-202.
[29] 梁大宁,罗少军,汤少明.第2-6肋间神经前皮支及其营养血管的解剖学研究[J].广东医学院学报, 2003,21(1):5-6.
[30] Gao JH, Hyakusoku H, Inoue S, et al.Usefulness of narrow pedicled intercostal cutaneous perforator flap for coverage of the burned hand.Burns. 1994;20(1):65-70.
[31] Hyakusoku H, Gao JH, Pennington DG, et al.The microvascular augmented subdermal vascular network (ma-SVN) flap: its variations and recent development in using intercostal perforators.Br J Plast Surg. 2002; 55(5):402-411.
[32] Barberini F, Brunone F.A "conservative" method of thoracic wall dissection: a proposal for teaching human anatomy.Ital J Anat Embryol. 2008; 113(3):187-195.
[33] Haidukewych GJ, Israel TA, Berry DJ.Reverse obliquity fractures of the intertrochanteric region of the femur.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83-A(5):643-650.
[34] Korkmaz MF, Erdem MN, Disli Z,et al.Outcomes of trochanteric femoral fractures treated with proximal femoral nail: an analysis of 100 consecutive cases.Clin Interv Aging. 2014;9:569-574.
[35] Park SY, Yang KH, Yoo JH,et al.The treatment of reverse obliquity intertrochanteric fractures with the intramedullary hip nail.J Trauma. 2008;65(4):852-857.
[36] Ahrengart L, Törnkvist H, Fornander P,et al.A randomized study of the compression hip screw and Gamma nail in 426 fractures.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(401):209-222.
[37] Parker MJ, Handoll HH.Gamma and other cephalocondylic intramedullary nails versus extramedullary implants for extracapsular hip fractures in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;(9):CD000093. |