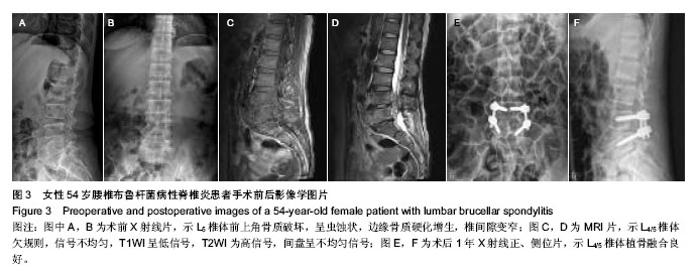
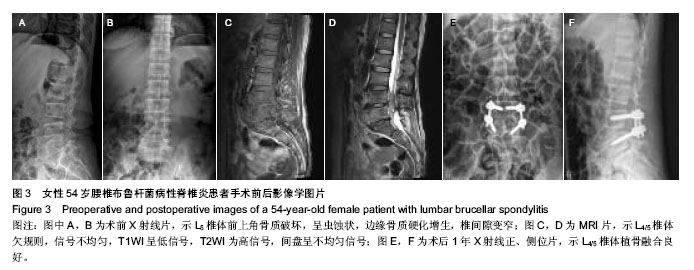
| [1] 章鹏,杨新明,孟宪勇.布鲁杆菌性脊柱炎的诊断和治疗进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(1):1029-1032.
[2] 米景川,塔娜,范蒙光,等.内蒙古人间布鲁杆菌病感染现状及病区划分[J].中国地方病防治杂志,2012,27(6):450-452.
[3] Solera J, Geijo P, Largo J, et al.A randomized, double-blind study to assess the optimal duration of doxycycline treatment for human brucellosis.Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39(12):1776-1782.
[4] Erdem H, Ulu-Kilic A, Kilic S,et al.Efficacy and tolerability of antibiotic combinations in neurobrucellosis: results of the Istanbul study.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012;56(3): 1523-1528.
[5] Gul HC, Erdem H, Bek S.Overview of neurobrucellosis: a pooled analysis of 187 cases.Int J Infect Dis. 2009;13(6): e339-343.
[6] Moraux A, Kermarrec E, Czarnecki E,et al.Spinal infections: typical and atypical imaging features.J Radiol. 2010;91(9 Pt 2):1049-1056.
[7] Solís García del Pozo J, Solera J. Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials in the treatment of human brucellosis. PLoS One. 2012; 7(2):e32090.
[8] Yilmaz MH, Mete B, Kantarci F, et al.Tuberculous, brucellar and pyogenic spondylitis: comparison of magnetic resonance imaging findings and assessment of its value.South Med J. 2007;100(6):613-614.
[9] 李勇.布氏杆菌脊柱炎误诊为脊柱结核16例分析[J].中国医药导报, 2009, 6(7):126-131.
[10] Lee IS, Lee JS, Kim SJ, et al. Fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography imaging in pyogenic and tuberculous spondylitis: preliminary study. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2009; 33(4):587-592.
[11] 买尔旦•买买提,田娟,盛伟斌,等.布鲁杆菌病性脊柱炎的诊断与手术治疗[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,32(4):323-330.
[12] 杨涛,吴兵.布氏杆菌病22例误诊分析[J]. 中国临床医生, 2005, 33(6):30-31.
[13] 杨新明,孟宪勇,张瑛,等.手术治疗胸腰椎布鲁杆菌性脊柱炎[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012,22(7):600-606.
[14] 张宇,祁全,沈洪涛,等.布鲁杆菌病脊柱炎的外科治疗[J].临床骨科杂志,2012,15(2):121-124.
[15] Tekkök IH, Berker M, Ozcan OE, et al.Brucellosis of the spine.Neurosurgery. 1993;33(5):838-844.
[16] Kaptan F, Gulduren HM, Sarsilmaz A,et al.Brucellar spondylodiscitis: comparison of patients with and without abscesses.Rheumatol Int. 2013;33(4):985-992.
[17] Ekici MA, Ozbek Z, Göko?lu A,et al.Surgical management of cervical spinal epidural abscess caused by Brucella melitensis : report of two cases and review of the literature.J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012:51(6):383-387.
[18] 杨新明,石蔚,杜雅坤,等.布氏杆菌性脊柱炎临床影像学表现及外科治疗[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(19):1463-1466.
[19] Solera J, Lozano E, Martínez-Alfaro E,et al.Brucellar spondylitis: review of 35 cases and literature survey.Clin Infect Dis.1999;29(6):1440-1449.
[20] Sanford JP. 抗微生物治疗指南[M]. 34版.上海: 第二军医大学出版社, 2004:48-51.
[21] Saltoglu N, Tasova Y, Inal AS, et al.Efficacy of rifampicin plus doxycycline versus rifampicin plus quinolone in the treatment of brucellosis.Saudi Med J. 2002;23(8):921-924.
[22] Ranjbar M, Keramat F, Mamani M, et al. Comparison between doxycycline-rifampin-amikacin and doxycycline-rifampin regimens in the treatment of brucellosis.Int J Infect Dis. 2007; 11(2):152-156.
[23] Alp E, Doganay M.Current therapeutic strategy in spinal brucellosis.Int J Infect Dis. 2008;12(6):573-577.
[24] Bouaziz MC, Bougamra I, Kaffel D,et al. Noncontiguous multifocal spondylitis: an exceptional presentation of spinal brucellosis.Tunis Med. 2010;88(4):280-284.
[25] Giannitsioti E, Papadopoulos A, Nikou P,et al.Long-term triple-antibiotic treatment against brucellar vertebral osteomyelitis.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2012;40(1):91-93.
[26] Kursun E,Turunc T,Demiroglu Y, et al. Evaluation of four hundred and forty seven brucellosis cases. Intern Med. 2013; 52:745-50.
[27] Buzgan T, Karahocagil MK, Irmak H, et al. Clinical manifestations and complications in 1028 cases of brucellosis: a retrospective evaluation and review of the literature.Int J Infect Dis. 2010; 14(6):e469-478. |