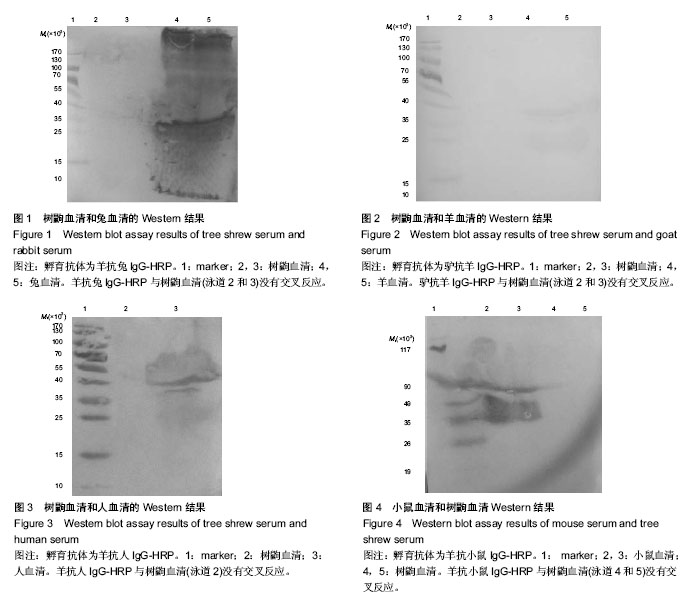
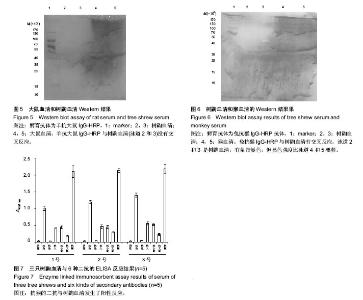
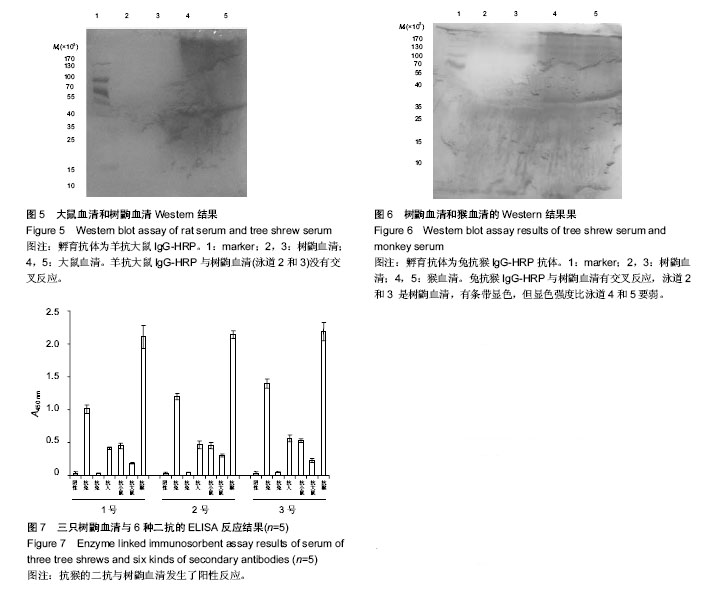
| [1] Imai M, Mineda T, Oikawa M. Some affinities and differences between the tree-shrews (Tupaia), insectivora and primates. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn. 1975; 51(6): 337-350.
[2] Cao J, Yang EB, Su JJ, et al.The tree shrews: adjuncts and alternatives to primates as models for biomedical research. J Med Primatol.2003; 32(3): 123-130.
[3] Palley LS, Schlossman SF, Letvin NL. Common tree shrews and primates share leukocyte membrane antigens. J Med Primatol.1984; 13(2): 67-71.
[4] Chen G, Wang W, Meng S, et al.CXC chemokine CXCL12 and its receptor CXCR4 in tree shrews (Tupaia belangeri): structure, expression and function. PLoS One. 2014; 9(5): e98231.
[5] Hofer HO. Lightmicroscopical investigations of the sublingua of Microcebus murinus (Cheirogaleidae, Lemuriformes) with remarks on the phylogenetic relations of the tree shrews (Scandentia) to primates. Z Morphol Anthropol. 1989; 78(1): 25-42.
[6] Murakami DM,Fuller CA. The retinohypothalamic projection and oxidative metabolism in the suprachiasmatic nucleus of primates and tree shrews. Brain Behav Evol.1990; 35(5): 302-312.
[7] Diogo R.The head and neck muscles of the Philippine colugo (Dermoptera: Cynocephalus volans), with a comparison to tree-shrews, primates, and other mammals. J Morphol.2009; 270(1): 14-51.
[8] Lin J, Chen G, Gu L, et al. Phylogenetic affinity of tree shrews to Glires is attributed to fast evolution rate. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2014; 71: 193-200.
[9] Nair J, Topka M, Khani A, et al.Tree shrews (Tupaia belangeri) exhibit novelty preference in the novel location memory task with 24-h retention periods. Front Psychol. 2014; 5: 303.
[10] Ni RJ, Shu YM, Wang J,et al. Distribution of vasopressin, oxytocin and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the hypothalamus and extrahypothalamic regions of tree shrews. Neuroscience. 2014; 265: 124-136.
[11] Fan Y, Yu DD,Yao YG. Positively selected genes of the Chinese tree shrew (Tupaia belangeri chinensis) locomotion system. Dongwuxue Yanjiu. 2014; 35(3): 240-248.
[12] He L, Frost MR, Siegwart JT Jr, et al. Gene expression signatures in tree shrew choroid in response to three myopiagenic conditions. Vision Res. 2014; 102: 52-63.
[13] Garraghty PE, Florence SL, Tenhula WN, et al. Parallel thalamic activation of the first and second somatosensory areas in prosimian primates and tree shrews. J Comp Neurol. 1991; 311(2): 289-299.
[14] Muller S, Stanyon R, O'Brien PC, et al. Defining the ancestral karyotype of all primates by multidirectional chromosome painting between tree shrews, lemurs and humans. Chromosoma. 1999; 108(6): 393-400.
[15] He L, Frost MR, Siegwart JT Jr, et al. Gene expression signatures in tree shrew choroid during lens-induced myopia and recovery. Exp Eye Res. 2014; 123: 56-71.
[16] Ruan P, Yang C, Su J, et al. [Expressions and significance of TLR2 and TLR4 in Kupffer cells of tree shrews chronically infected with hepatitis B virus]. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014; 30(7): 686-690.
[17] Pan XH, Yang XY, Yao X, et al. Bone-marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation to treat diabetic nephropathy in tree shrews. Cell Biochem Funct. 2014; 32(5): 453-463.
[18] McCollum LA and Roberts RC. Ultrastructural localization of tyrosine hydroxylase in tree shrew nucleus accumbens core and shell. Neuroscience. 2014; 271: 23-34.
[19] Ni RJ, Shu YM, Luo PH, et al. Immunohistochemical mapping of neuropeptide Y in the tree shrew brain. J Comp Neurol. 2014 Oct 17. doi: 10.1002/cne.23696. [Epub ahead of print]
[20] Schmelting B, Corbach-Sohle S, Kohlhause S, et al. Agomelatine in the tree shrew model of depression: effects on stress-induced nocturnal hyperthermia and hormonal status. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol.2014; 24(3): 437-447.
[21] Shen F, Duan Y, Jin S, et al. Varied behavioral responses induced by morphine in the tree shrew: a possible model for human opiate addiction. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014; 8: 333.
[22] Veit J, Bhattacharyya A, Kretz R, et al. On the relation between receptive field structure and stimulus selectivity in the tree shrew primary visual cortex. Cereb Cortex. 2014; 24(10): 2761-2771.
[23] Yu D, Xu L, Liu XH, et al. Diverse interleukin-7 mRNA transcripts in Chinese tree shrew (Tupaia belangeri chinensis). PLoS One. 2014; 9(6): e99859.
[24] Zhan L, Ding H, Lin S, et al. Experimental Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in the Chinese tree shrew. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2014; 360(1): 23-32.
[25] Zhao F, Guo X, Wang Y, et al. Drug target mining and analysis of the Chinese tree shrew for pharmacological testing.PLoS One.2014; 9(8): e104191.
[26] Zheng Y, Wang Q, Yun C, et al. Identification of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase sequence and expression profiles in tree shrew (Tupaia belangeri). PLoS One.2014; 9(6): e98552.
[27] Zhu Y, Duan Z, Mo G, et al. A novel 26RFa peptide containing both analgesic and anti-inflammatory functions from Chinese tree shrew. Biochimie. 2014; 102: 112-116. |