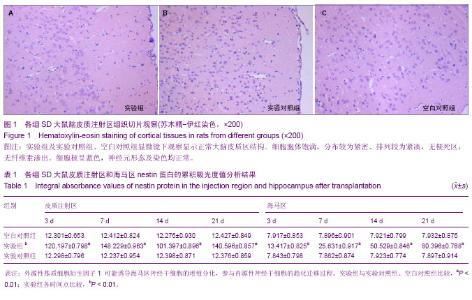
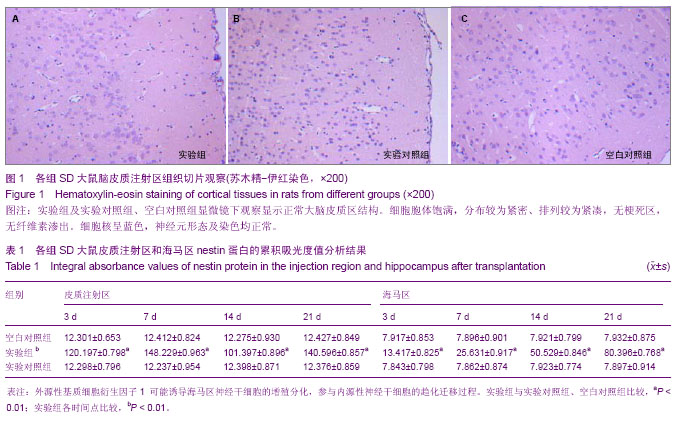
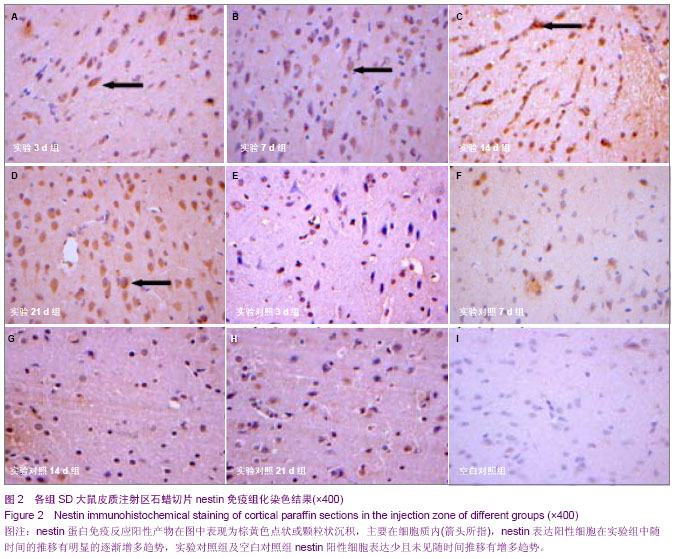
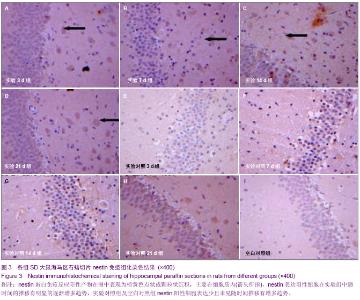
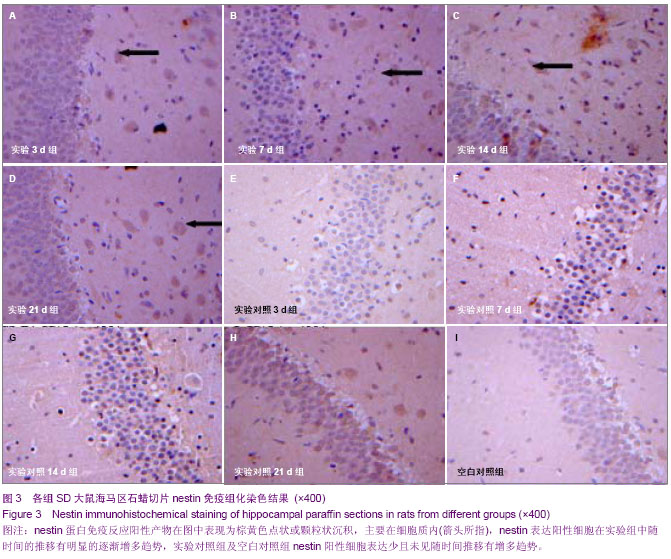
| [1] Reynolds BA, Tetzlaff W, Weiss S.A multipotent EGF-responsive striatal embryonic progenitor cell produces neurons and astrocytes.J Neurosci. 1992;12(11):4565-4574.
[2] Lie DC, Song H, Colamarino SA,et al.Neurogenesis in the adult brain: new strategies for central nervous system diseases.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2004;44:399-421.
[3] Donovan MH, Yazdani U, Norris RD,et al.Decreased adult hippocampal neurogenesis in the PDAPP mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.J Comp Neurol. 2006;495(1):70-83.
[4] Palmer TD, Takahashi J, Gage FH.The adult rat hippocampus contains primordial neural stem cells.Mol Cell Neurosci. 1997; 8(6):389-404.
[5] Lee HJ, Kim KS, Park IH,et al.Human neural stem cells over-expressing VEGF provide neuroprotection, angiogenesis and functional recovery in mouse stroke model. PLoS One. 2007;2(1):e156.
[6] 陈二涛,潘栋超,冯东福,等.基质细胞衍生因子-1诱导神经干细胞靶向性迁移的实验研究[J].中华神经医学杂志,2010,9(6): 561-565.
[7] 王崇谦,丁鹏,牟临杰,等. 颅脑损伤后内源性神经干细胞增殖与迁移中的基质细胞衍生因子1[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(6): 998-1002.
[8] 科技部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006.
[9] Janowski M.Functional diversity of SDF-1 splicing variants. Cell Adh Migr. 2009;3(3):243-249.
[10] van der Meulen AA, Biber K, Lukovac S,et al.The role of CXC chemokine ligand (CXCL)12-CXC chemokine receptor (CXCR)4 signalling in the migration of neural stem cells towards a brain tumour.Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2009; 35(6):579-591.
[11] Kokovay E, Goderie S, Wang Y,et al.Adult SVZ lineage cells home to and leave the vascular niche via differential responses to SDF1/CXCR4 signaling.Cell Stem Cell. 2010; 7(2):163-173.
[12] Chen J, Chemaly E, Liang L,et al.Effects of CXCR4 gene transfer on cardiac function after ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Pathol. 2010;176(4):1705-1715.
[13] Dotan I, Werner L, Vigodman S,et al.CXCL12 is a constitutive and inflammatory chemokine in the intestinal immune system. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2010;16(4):583-592.
[14] Chong BF, Mohan C.Targeting the CXCR4/CXCL12 axis in systemic lupus erythematosus.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2009; 13(10):1147-1153.
[15] Imai H, Sunaga N, Shimizu Y,et al.Clinicopathological and therapeutic significance of CXCL12 expression in lung cancer.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2010 ;23(1):153-164.
[16] Liang X, Su YP, Kong PY,et al.Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells expressing SDF-1 promote hematopoietic stem cell function of human mobilised peripheral blood CD34+ cells in vivo and in vitro.Int J Radiat Biol. 2010;86(3):230-237.
[17] Yu J, Li M, Qu Z,et al.SDF-1/CXCR4-mediated migration of transplanted bone marrow stromal cells toward areas of heart myocardial infarction through activation of PI3K/Akt.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2010;55(5):496-505.
[18] Stumm R, Höllt V.CXC chemokine receptor 4 regulates neuronal migration and axonal pathfinding in the developing nervous system: implications for neuronal regeneration in the adult brain.J Mol Endocrinol. 2007;38(3):377-382.
[19] Almazán G, Vela JM, Molina-Holgado E,et al.Re-evaluation of nestin as a marker of oligodendrocyte lineage cells.Microsc Res Tech. 2001;52(6):753-765.
[20] Ruehm SG, Zimny K, Debatin JF. Direct contrast-enhanced 3D MR venography. Eur Radiol. 2001;11(1):102-112.
[21] Shen L, Gao Y, Qian J,et al.The role of SDF-1α/Rac pathway in the regulation of endothelial progenitor cell polarity; homing and expression of Rac1, Rac2 during endothelial repair.Mol Cell Biochem. 2012;365(1-2):1-7.
[22] 侯传举,齐岩梅,张端珍,等.基质细胞衍生因子1α培养心肌细胞和成纤维细胞的增殖与迁移[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(7): 1220-1227.
[23] 王丽君,刘素芳,韩雪飞,等. 基质细胞衍生因子对海马神经细胞迁移的影响[J]. 中风与神经疾病杂志,2011,28(4):300-302.
[24] Yoo SW, Kim SS, Lee SY,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells promote proliferation of endogenous neural stem cells and survival of newborn cells in a rat stroke model.Exp Mol Med. 2008;40(4):387-397.
[25] Imitola J, Raddassi K, Park KI,et al.Directed migration of neural stem cells to sites of CNS injury by the stromal cell-derived factor 1alpha/CXC chemokine receptor 4 pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(52): 18117-18122. |