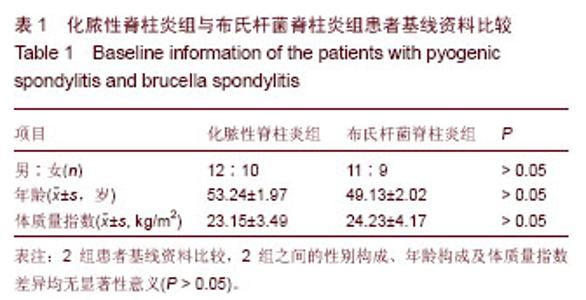
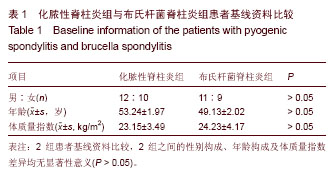
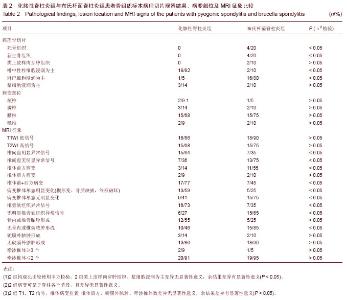
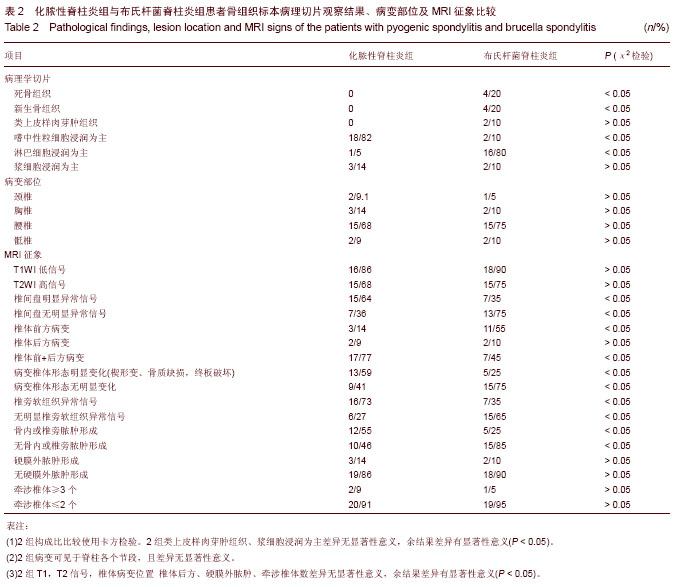
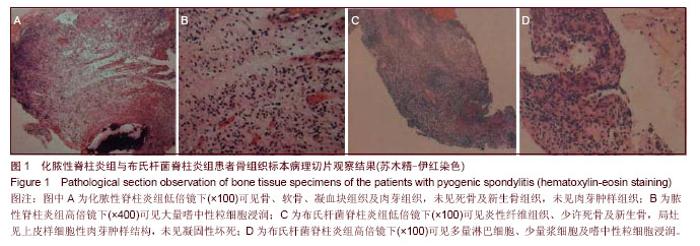
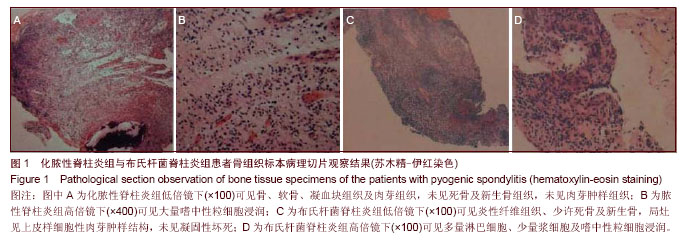
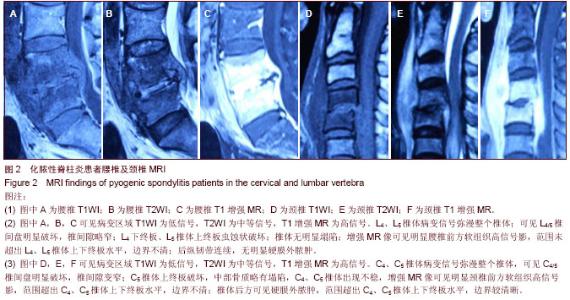
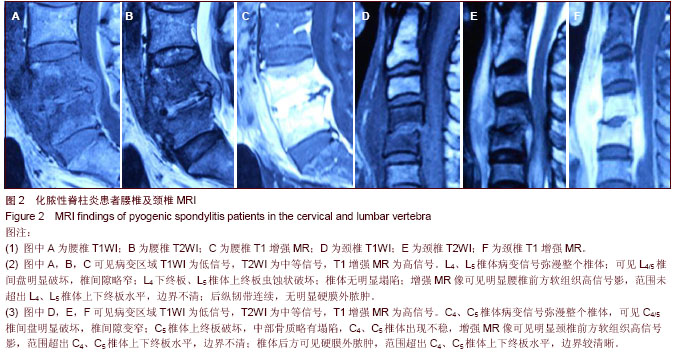
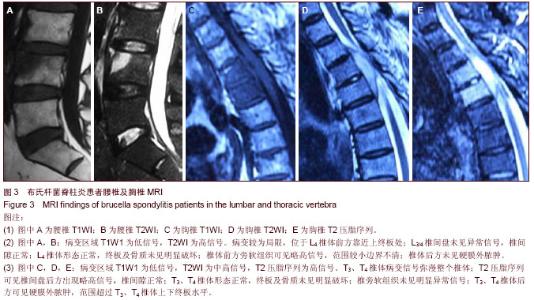
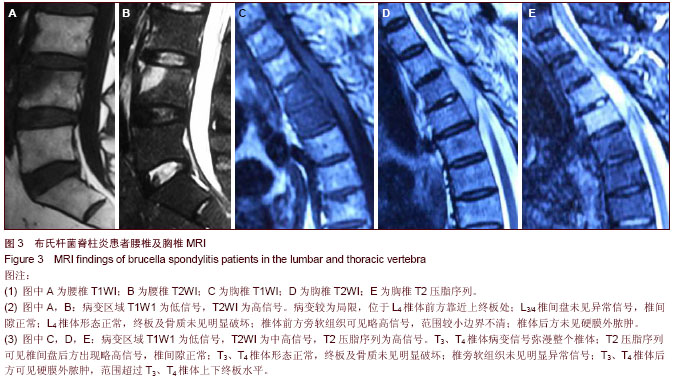
| [1] Cheung WY, Luk KD. Pyogenic spondylitis. Int Orthop. 2012; 36(2):397-404.[2] Sapico FL, Montgomerie JZ. Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis: report of nine cases and review of the literature. Rev Infect Dis. 1979;1(5):754-776.[3] Colmenero JD, Orjuela DL, Garcia-Portales R, et al. Clinical course and prognosis of Brucella spondylitis. Infection. 1992; 20(1):38-42.[4] 王大力,张士义.急性期布氏菌病治疗研究进展[J].中国地方病防治杂志,2001,16(2): 94-95.[5] Solera J, Lozano E, Martínez-Alfaro E, et al. Brucellar spondylitis: review of 35 cases and literature survey. Clin Infect Dise. 1999;29(6): 1440-1449.[6] 蔺长明,刘向辉. 通过饮食感染布氏杆菌病的分析报告[J]. 中国人兽共患病杂志,2001,17(2):58-59.[7] Bettini N, Girardo M, Dema E, et al. Evaluation of conservative treatment of non specific spondylodiscitis. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(1):143-150.[8] Compere EL, Garrison M. Correlation of pathologic and roentgenologic findings in tuberculosis and pyogenic infections of the vertebrae: The fate of the intervertebral disk. Ann Surg. 1936;104(6):1038-1067.[9] Currie S, Galea-Soler S, Barron D, et al. MRI characteristics of tuberculous spondylitis. Clin Radiol. 2011;66(8): 778-787.[10] Bettini N, Girardo M, Dema E, et al. Evaluation of conservative treatment of non specific spondylodiscitis. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(1):143-150.[11] 李玉林,唐建武.病理学[M]. 6版. 北京:人民卫生出版社, 2006.[12] 钟志军,陈泽良,黄克和,等.布氏杆菌病致病因子及防治研究进展[J].畜牧与兽医,2008,40(12): 96-101.[13] 杨新明,石蔚,杜雅坤,等.布氏杆菌性脊柱炎临床影像学及病理学表现[J].实用放射学杂志,2008,24(4): 522-525.[14] Colmenero JD, Jimenez-Mejias ME, Sanchez-Lora FJ, et al. Pyogenic, tuberculous, and brucellar vertebral osteomyelitis: a descriptive and comparative study of 219 cases. Ann Rheum Dis. 1997;56(12): 709-715.[15] Antunes JL. Infections of the spine. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1992;116(2-4):179-186.[16] Mete B, Kurt C, Yilmaz MH, et al. Vertebral osteomyelitis: eight years’ experience of 100 cases. Rheumatol Int. 2012; 32(11): 3591-3597.[17] Colmenero JD, Ruiz-Mesa JD, Plata A, et al. Clinical findings, therapeutic approach, and outcome of brucellar vertebral osteomyelitis. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46(3): 426-433.[18] Ariza J, Gudiol F, Valverde J, et al. Brucellar spondylitis: a detailed analysis based on current findings. Rev Infect Dis. 1985; 7(5): 656-664.[19] Glasgow MM. Brucellosis of the spine. Br J Surg. 1976;63(4): 283-288.[20] Solera J, Lozano E, Martínez-Alfaro E, et al. Brucellar spondylitis: review of 35 cases and literature survey. Clin Infect Dis. 1999;29(6):1440-1449.[21] Ledermann HP, Schweitzer ME, Morrison WB, et al. MR Imaging Findings in Spinal Infections: Rules or Myths. Radiology. 2003;228(2):506-514.[22] 周守国,王娟,赵晓梅,等.化脓性脊椎炎的MRI表现与分期(附50例报道)[J].影像诊断与介入放射学,2011,20(3):218-221.[23] Çelik AK, Aypak A, Aypak C. Comparative analysis of tuberculous and brucellar spondylodiscitis. Trop Doct. 2011; 41(3):172-174.[24] 吴伟,刘博,刘昭,等. MRI在布鲁氏脊柱炎与脊柱结核鉴别诊断中的价值[J]. 中国美容医学,2012,21(7):140-141.[25] Jung NY, Jee WH, Ha KY, et al. Discrimination of tuberculous spondylitis from pyogenic spondylitis on MRI. Am J Roentgenol. 2004;182(6): 1405-1410.[26] 杨新明,石蔚,杜雅坤,等.布氏杆菌性脊柱炎临床影像学表现及外科治疗[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007,19(19):1463-1466.[27] 杨景震,王成健,何凤丽,等.脊柱感染的MR研究(附11例报告)[J]. 中国医学影像技术,2002,15(5):488-489. |