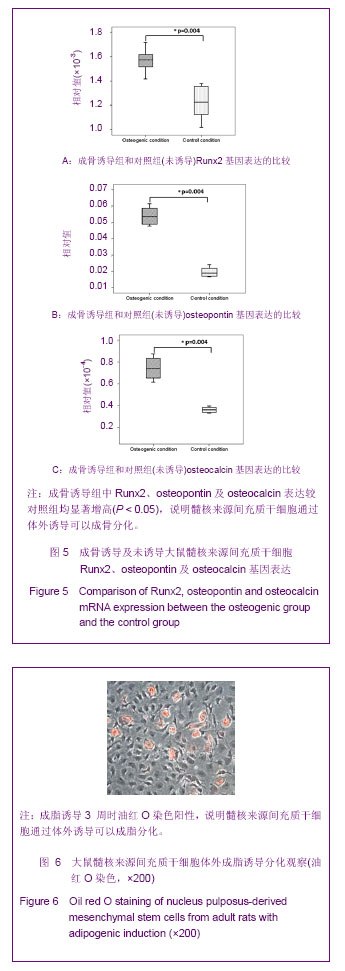
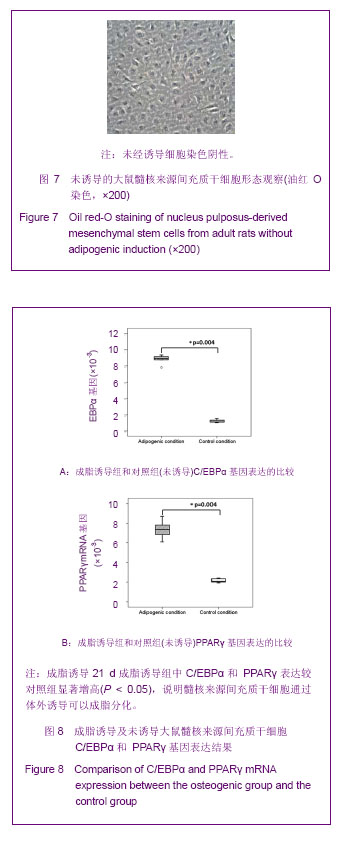
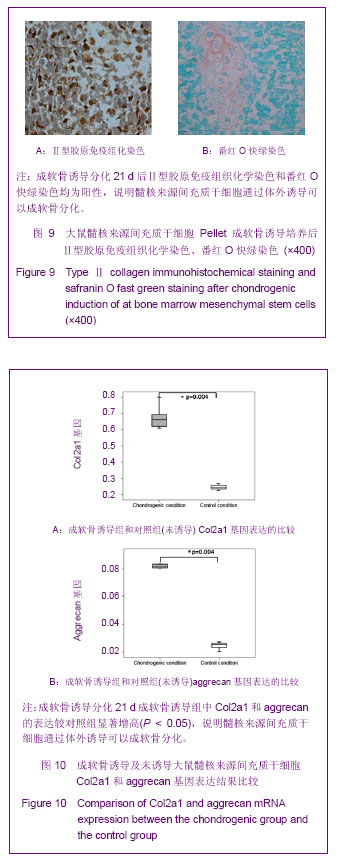
| [1] Manek NJ, MacGregor AJ. Epidemiology of back disorders: prevalence, risk factors, and prognosis.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2005;17:134-140.[2] Juniper M, Le TK, Mladsi D. The epidemiology, economic burden, and pharmacological treatment of chronic low back pain in France, Germany, Italy, Spain and the UK: a literature-based review. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2009;10: 2581-92.[3] Adams MA, Roughley PJ.What is intervertebral disc degeneration, and what causes it? Spine.2006;31:2151-2161.[4] Singh K,Masuda K,An HS.Animal models for human disc degeneration.Spine J.2005;5:267S-279S.[5] Hadjipavlou AG, Tzermiadianos MN, Bogduk N, et al.The pathophysiology of disc degeneration: a critical review. 2008; 90(10):1261-1270.[6] 王善正,王宸,芮云峰.椎间盘退变的生物学治疗:从基础研究到临床应用[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2012,6(17):58-61.[7] Freemont AJ.The cellular pathobiology of the degenerate intervertebral disc and discogenic back pain. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009;48(1):5-10.[8] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People's Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006-09-30.[9] Choi KS, Cohn MJ, Harfe BD. Identification of Nucleus Pulposus Precursor Cells and Notochordal Remnants in the Mouse: Implications for Disk Degeneration and Chordoma Formation. Dev Dyn. 2008;237(12):3953-3958[10] Hunter CJ, Matyas JR, Duncan NA.The notochordal cell in the nucleus pulposus: a review in the context of tissue engineering. Tissue Eng.2003;9(4):667-677.[11] Maldonado BA, Oegema TR Jr.Initial characterization of the metabolism of intervertebral disc cells encapsulated in microspheres.J Orthop Res.1992;10(5):677-690.[12] Weiler C, Nerlich AG, Schaaf R, et al.Immunohistochemical identification of notochordal markers in cells in the aging human lumbar intervertebral disc.Eur Spine J. 2010;19(10): 1761-1770.[13] Li L, Clevers H. Coexistence of quiescent and active adult stem cells in mammals. Science.2010;327(5965):542-545. [14] Lim JY,Loiselle AE,Lee JS,et al.Optimizing the osteogenic potential of adult stem cells for skeletal regeneration.J Orthop Res.2011;29(11): 1627-1633.[15] Ni M, Rui YF, Tan Q,et al.Engineered scaffold-free tendon tissue produced by tendon-derived stem cells.Biomaterials. 2013;34(8):2024-2037.[16] Lee WY,Lui PP,Rui YF.Hypoxia-mediated efficient expansion of human tendon-derived stem cells in vitro.Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(5-6):484-498.[17] Rui YF, Lui PP, Wong YM,et al.Altered fate of tendon-derived stem cells isolated from a failed tendon-healing animal model of tendinopathy.Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(7):1076-1085. [18] 王善正,王宸,芮云峰.自体激活富血小板血浆干预兔骨髓间充质干细胞体外成软骨分化的研究[J].中国组织工程研究,2013, 17(1):1-8.[19] Yang D,Sun S,Wang Z,et al.Stromal cell-derived factor-1 receptor CXCR4-overexpressing bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells accelerate wound healing by migrating into skin injury areas.Cell Reprogram. 2013; 15(3):206-215.[20] Song K,Wang Z,Li W,et al.In Vitro Culture,Determination,and Directed Differentiation of Adult Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Towards Cardiomyocyte-Like Cells Induced by Angiotensin II.Appl Biochem Biotechnol.2013;170(2):459-470.[21] Pazdro R, Harrison DE.Murine adipose tissue-derived stromal cell apoptosis and susceptibility to oxidative stress in vitro are regulated by genetic background.PLoS One.2013;8(4): e61235.[22] Rui YF, Lui PP, Li G,et al.Isolation and characterization of multipotent rat tendon-derived stem cells.Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(5):1549-1558. [23] Zhang J, Wang JH.Platelet-rich plasma releasate promotes differentiation of tendon stem cells into active tenocytes.Am J Sports Med.2010,38(12):2477-2486. [24] 胡新锋,王宸,芮云峰.自体富血小板血浆干预兔早期椎间盘退变的初步研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26(8):977-983. |