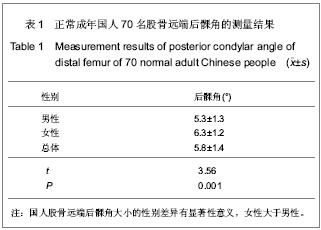
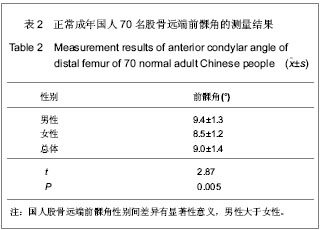
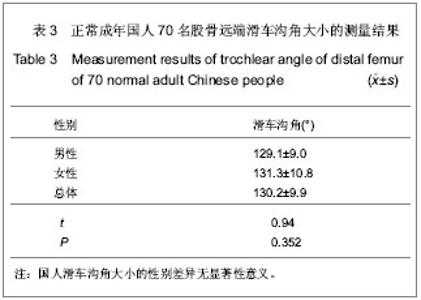
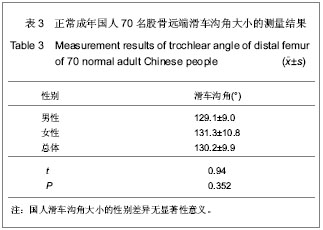
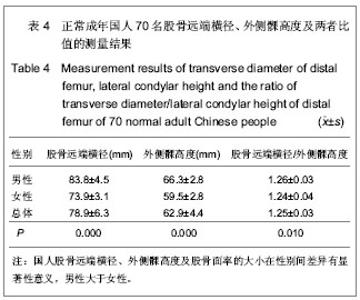
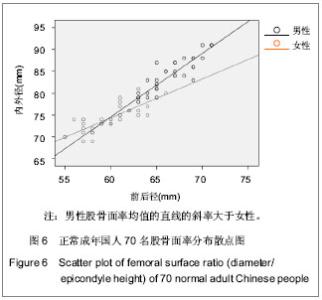
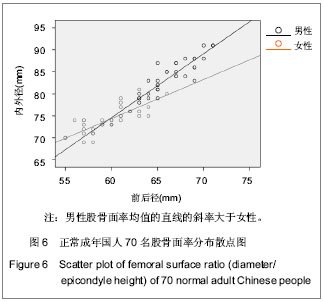
| [1] 吕厚山.膝关节置换的进展和现状[J].中华外科杂志,2004,42(1): 30-33.
[2] Keating EM, Meding JB, Faris PM,et al. Long-term followup of nonmodular total knee replacements. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(404):34-39.
[3] Buechel FF Sr. Long-term followup after mobile-bearing total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(404):40-50.
[4] Tosi LL, Boyan BD, Boskey AL. Does sex matter in musculoskeletal health? The influence of sex and gender on musculoskeletal health. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(7): 1631-1647.
[5] Akagi M, Matsusue Y, Mata T,et al. Effect of rotational alignment on patellar tracking in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;(366):155-163.
[6] Worland RL, Jessup DE, Vazquez-Vela Johnson G,et al. The effect of femoral component rotation and asymmetry in total knee replacements. Orthopedics. 2002;25(10):1045-1048.
[7] Berger RA, Rubash HE, Seel MJ,et al. Determining the rotational alignment of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty using the epicondylar axis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993;(286):40-47.
[8] Griffin FM, Insall JN, Scuderi GR.The posterior condylar angle in osteoarthritic knees. J Arthroplasty. 1998;13(7):812-815.
[9] Yip DK, Zhu YH, Chiu KY,et al. Distal rotational alignment of the Chinese femur and its relevance in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2004 ;19(5):613-619.
[10] Fulkerson JP,Hungerford DS.Biomechanics of the patellofemoral joint[A]//Disorders of the patellofemoral joint[M]. Baltimore:Williams & Wilkins,1990:25-41.
[11] Hofmann AA, Evanich JD, Ferguson RP,et al. Ten- to 14-year clinical followup of the cementless Natural Knee system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(388):85-94.
[12] Freeman MA, Todd RC, Bamert P, et al. ICLH arthroplasty of the knee: 1968--1977. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1978;60-B(3): 339-344.
[13] Insall IN. Revision of aseptic failed total knee arthroplasty[A]//W. Norman Scott. Insall & Scott Surgery of the Knee. New York:Churchill Livingston,1993:935-957.
[14] Chin KR, Dalury DF, Zurakowski D,et al. Intraoperative measurements of male and female distal femurs during primary total knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2002;15(4): 213-217.
[15] Hitt K, Shurman JR 2nd, Greene K,et al. Anthropometric measurements of the human knee: correlation to the sizing of current knee arthroplasty systems. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A Suppl 4:115-122.
[16] Lonner JH, Jasko JG, Thomas BS. Anthropomorphic differences between the distal femora of men and women. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(11):2724-2729.
[17] Tosi LL, Boyan BD, Boskey AL. Does sex matter in musculoskeletal health? The influence of sex and gender on musculoskeletal health. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(7): 1631-1647.
[18] Csintalan RP, Schulz MM, Woo J,et al. Gender differences in patellofemoral joint biomechanics. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(402):260-269.
[19] Kurtz S, Mowat F, Ong K,et al. Prevalence of primary and revision total hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 1990 through 2002. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(7): 1487-1497.
[20] Poilvache PL, Insall JN, Scuderi GR,et al. Rotational landmarks and sizing of the distal femur in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(331):35-46.
[21] Ritter MA, Harty LD, Davis KE,et al. Predicting range of motion after total knee arthroplasty. Clustering, log-linear regression, and regression tree analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A(7):1278-1285.
[22] Rand JA, Ilstrup DM. Survivorship analysis of total knee arthroplasty. Cumulative rates of survival of 9200 total knee arthroplasties.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991;73(3):397-409.
[23] Font-Rodriguez DE, Scuderi GR, Insall JN. Survivorship of cemented total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997;(345):79-86.
[24] Clarke HD, Hentz JG. Restoration of femoral anatomy in TKA with unisex and gender-specific components. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(11):2711-2716.
[25] 张建,董纪元,付忠田.人膝关节尺寸与5种人工膝关节假体尺寸的对照[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(4):635-638. |