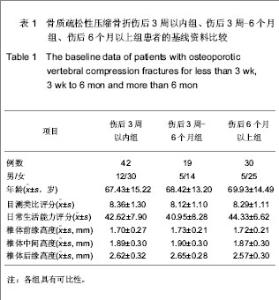
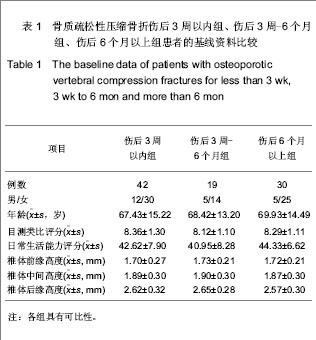
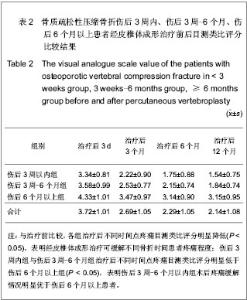
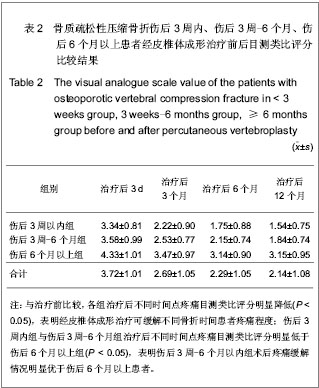
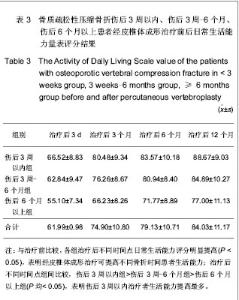
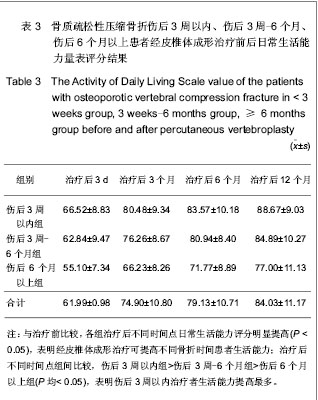
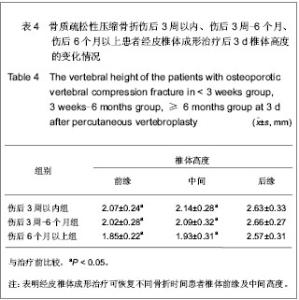
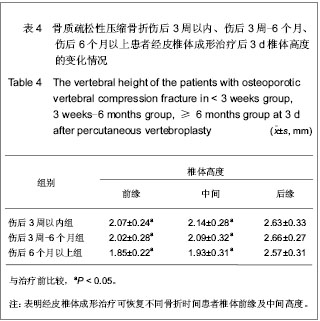
| [1] Thillainadesan J,Schlaphoff G,Gibson KA,et al.Long-term outcomes of vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fractures. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol.2010;54(4):307-314.[2] Ross PD.Osteoporosis Frequency, Consequences,and Risk Factor. Arch Interned.1996;156(13):1399-1411.[3] Zhonghuayixuehui Guzhi Shusong he Gukuangyan Jibing Fenhui.Zhonghua Guzhi Shusong he Gukuangyan Jibing Zazhi. 2011;4(1):2-17.中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2011,4(1):2-17.[4] Rousing R,Hansen KL,Andersen MO,et al.Twelve-months follow-up in forty-nine patients with acute/semiacute osteoporotic vertebral fractures treatedconservatively or with percutaneous vertebroplasty:aclinical randomized study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2010;35 (5):478-482.[5] Heini PF.Vertebroplasty: an update: value of percutaneous cement augmentation after randomized, placebo-controlled trials.Orthopade.2010;39(7):658-664.[6] Becker S,Pfeiffer KP,Ogon M. Comparison of inpatient treatment costs after balloon kyphoplasty and non-surgical treatment of vertebral body compression fractures.Eur Spine J.2011; 20(8): 1259-1264. [7] Anselmetti GC,Muto M,Guglielmi G,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty.Radiol Clin North(Am). 2010; 48(3):641-649.[8] Buchbinder R,Osborne RH,Ebeling PR,et al.A randomized trial of vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic vertebral fractures.N Engl J Med. 2009;361:557-568. [9] Flors L,Lonjedo E,Leiva-Salinas C,et al.Vesselplasty: a new technical approach to treat symptomatic vertebral compression fractures.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;193: 218-226.[10] Rousing R,Andersen MO,Jespersen SM,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty compared to conservative treatment in patients with painful acute or subacute osteoporotic vertebral fractures: three-months follow-up in a clinical randomized study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2009;34:1349-1354. [11] Kaufmann TJ,Jensen ME,Schweickert PA,et al.Age of fracture and clinical outcomes of percutaneous vertebroplasty.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.2001;2(10): 1860-1863.[12] Brown DB,Glaiberman CB,Gilula LA,et al.Correlation between preprocedural MRI findings and clinical outcomes in the treatment of chronic symptomatic vertebral compression fractures with percutaneous vertebroplasty. AJR Am J Roentgeno.2005;184(6): 1951-1955.[13] Zhonghua Yixuehui.Beijing:Renmin Weisheng Chubanshe. 2006.中华医学会.临床诊疗指南-骨质疏松症和骨矿盐疾病分册[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2006.[14] Kloc W,Libionka W,Pierzak O,et al.The effectiveness of percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of different aetiology Vertebral Body Fractures. Stud Health Technol Inform.2012;176: 372-374. [15] Heo DH,Cho YJ.Segmental artery injury following percutaneous vertebroplasty using extrapedicular approach.J Korean Neurosurg Soc.2011;49(2):131-133. [16] Blattert TR,Katscher S,Josten C.Percutaneous techniques in the thoracic and lumbar spine.Unfallchirurg. 2011;114(1): 17-25.[17] Kim YJ,Lee JW,Kim KJ,et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for intravertebral cleft: analysis of therapeutic effects and outcome predictors.Skeletal Radiol. 2010;39(8):757-766.[18] Liebschner NA,Rosenberg WS,Keaveny TM.Effects of bone cement volume and distribution on vertebral stiffness after vertebroplasty.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2001;26(14): 1547-1554.[19] Tohmeh AG,Mathis JM,Fenton DC,et al.Biomechanical efficacy of unipedicular versus bipedicular vertebroplasty for the management of osteoporotic compression fractures.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1999;24(17):1772-1776.[20] Higgins KB,Harten RD,Langrana NA,et al.Biomechanical effects of unipedicular vertebroplasty on intact vertebrae. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2003;28(14):1540-1548. [21] Hoh BL,Rabinov JD,Pryor JC,et al. Balloon kyphoplasty for vertebral compression fracture using a unilateral balloon tamp via a uni-pedicular approach: technical note.Pain Physician. 2004;7(1):111-114.[22] Kin AK, Jensen ME, Dion JE, et al.Unilateral transpedicular percutaneous vertebroplasty:initial experience.Radiology. 2002; 222:737-741.[23] Wang HK,Lu K,Liang CL.Comparing clinical outcomes following percutaneous vertebroplasty with conservative therapy for acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Pain Med.2010;11(11):1659-1665. [24] Anselmetti GC,Manca A,Hirsch J,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty in osteoporotic patients: an institutional experience of 1,634 patients with long-term follow-up.J Vasc Interv Radiol.2011;22(12):1714-1720.[25] Rad AE,Kallmes DF.Correlation between preoperative pain duration and percutaneous vertebroplasty outcome.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011;32(10):1842-1845.[26] Hiwatashi A,Moritani T,Numaguchi Y,et al.Increase in vertebral body height after vertebroplasty.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.2003;24(2):185-189.[27] Teng MM,Wei CJ,Wei LC,et al. Kyphosis correction and height restoration effects of percutaneous vertebroplasty. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.2003;24(9):1893-1900.[28] Braunstein V,Sprecher CM,Gisep A,et al.Long-term reaction to bone cement in osteoporotic bone: new bone formation in vertebral bodies after vertebroplasty. J Anat.2008;212: 697-701.[29] Tanigawa N,Kariya S,Komemushi A,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fractures: long-term evaluation of the technical and clinical outcomes.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;196(6):1415-1418. [30] Nieuwenhuijse MJ,Van Erkel AR,Dijkstra PD.Cement leakage in percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: identification of risk factors. Spine J. 2011;11(9):839-848. |