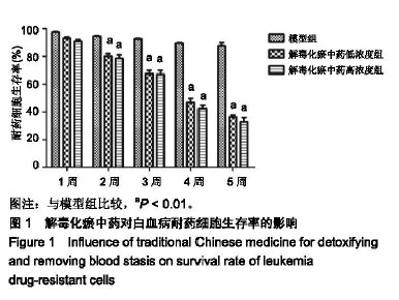
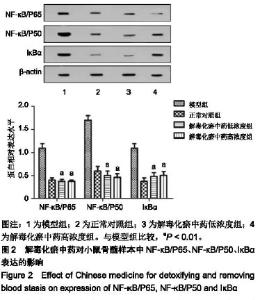
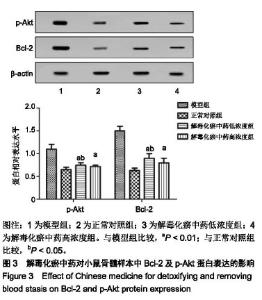
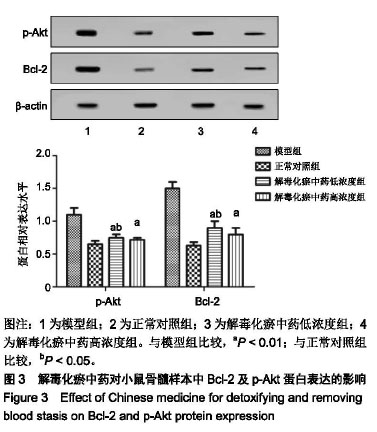
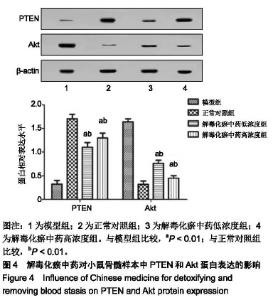
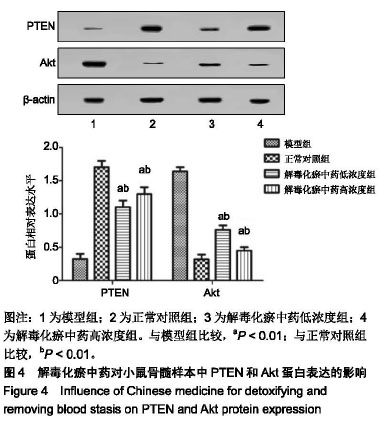
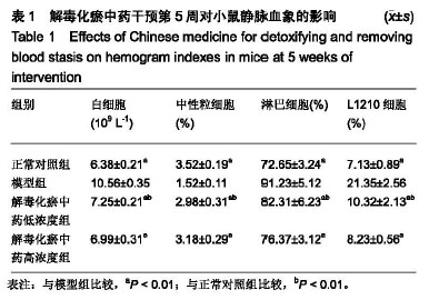
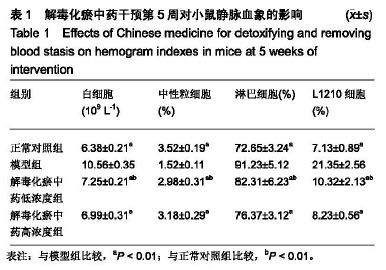
| [1]张晓辉.如何预防白血病[J]. 中华养生保健, 2016(8):66-67.[2]Kansagra A, Litzow M. Treatment of Young Adults with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2017; 12(3):187-196.[3]Chen XP, Li W, Xiao XF, et al. Phytochemical and pharmacological studies on Radix Angelica sinensis. Chin J Nat Med. 2013;11(6):577-587.[4]Ma H, Cheng L, Hao K, et al. Reversal effect of ST6GAL 1 on multidrug resistance in human leukemia by regulating the PI3K/Akt pathway and the expression of P-gp and MRP1. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e85113.[5]Sun Y, Peng R, Peng H, et al. miR-451 suppresses the NF-kappaB-mediated proinflammatory molecules expression through inhibiting LMP7 in diabetic nephropathy. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2016;433:75-86.[6]Sun BT, Zheng LH, Bao YL, et al. Reversal effect of Dioscin on multidrug resistance in human hepatoma HepG2/ adriamycin cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011;654(2):129-134.[7]Hien TT, Kim HG, Han EH, et al. Molecular mechanism of suppression of MDR1 by puerarin from Pueraria lobata via NF-kappaB pathway and cAMP-responsive element transcriptional activity-dependent up-regulation of AMP-activated protein kinase in breast cancer MCF-7/adr cells. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2010;54(7):918-928.[8]张献,冯欣.PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路抑制剂在宫颈癌治疗中的研究进展[J].现代药物与临床,2018,33(5):1278-1284.[9]吴宥熹,徐俊,刘立亚,等. PI3K-Akt-mTOR信号通路介导的细胞自噬在荭草苷抗小鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤中的作用研究[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2017,21(1):20-24.[10]赖芸,陈子珺.有毒中药抗白血病的作用及机制研究进展[J].中成药, 2016, 38(4):875-879.[11]杨小娜,郭建美,姚海英,等.中医药治疗白血病的研究进展[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2016, 25(10):1134-1137.[12]宋艳秋,刘敏,李薇,等. K562/NOD-SCID小鼠白血病模型的建立[J].中国实验血液学杂志, 2007, 15(1):16-19.[13]周建军,乐秀芳.评价抗癌物质活性的改良MTT方法[J].中国医药工业杂志, 1993(10):455-457.[14]马武开,姚血明,唐芳,等.解毒化瘀药调控白血病HL60/adr细胞NF-κB-survivin通路研究[J].北京中医药大学学报, 2012,35(1): 25-28.[15]Chang HY, Pan KL, Ma FC, et al. The study on reversing mechanism of multidrug resistance of K562/A02 cell line by curcumin and erythromycin. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2006;27(4):254-258.[16]蒋卉男,刘卓刚,胡荣. Embelin逆转K562/D细胞对柔红霉素耐药与P-gp及MDR1 mRNA无关[J]. 中国实验血液学杂志, 2017, 25(5):1342-1349.[17]Li X, Wu C, Chen N, et al. PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and targeted therapy for glioblastoma. Oncotarget. 2016; 7(22):33440-33450.[18]Zhou ZQ, Li YL, Ao ZB, et al.Baicalin protects neonatal rat brains against hypoxic-ischemic injury by upregulating glutamate transporter 1 via the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B signaling pathway.Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(10):1625-1631.[19]Yan LX, Liu YH, Xiang JW, et al. PIK3R1 targeting by miR-21 suppresses tumor cell migration and invasion by reducing PI3K/AKT signaling and reversing EMT, and predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Int J Oncol. 2016;48(2):471-484.[20]严匡华,陈龙,严风梦.下调miR-21抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路对白血病细胞增殖凋亡的影响[J].中国免疫学杂志, 2018,34(3): 441-445.[21]白炎亮,张茵,于润红,等. PI3K/Akt传通路在急性白血病细胞中的表达及其意义[J]. 中国实用医刊, 2017, 44(19):75-79.[22]Canté-Barrett K, Spijkers-Hagelstein JA, Buijs-Gladdines JG, et al. MEK and PI3K-AKT inhibitors synergistically block activated IL7 receptor signaling in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 2016;30(9):1832-1843.[23]师丽晓,王建华,师晓东. PI3k/Akt/mTOR信号通路与儿童急性T淋巴细胞白血病[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2016,24(4): 1269-1274.[24]饶佳,卢玮,王芸芸,等. bcl-2基因过表达致急性髓系白血病对柔红霉素耐药机制的初步探讨[J].安徽医科大学学报, 2017, 52(3):369-372.[25]李攀登,王永红,肖芸,等. 氢醌对人白血病细胞凋亡及相关蛋白Bcl-2、Bax及Caspase-3表达的影响[J].现代预防医学, 2018, 45(5):878-882.[26]杨君义,徐飞.治疗慢性淋巴细胞白血病新药——BCL-2抑制剂venetoclax[J]. 中国新药与临床杂志, 2017,8(3):131-133. |