Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (12): 2614-2622.doi: 10.12307/2025.380
Previous Articles Next Articles
Relationship between hypertension and osteoporosis in different racial groups
Zhang Yibo1, Lu Jianqi2, Mao Meiling1, Chen Lidan1, Lu Wei1, Zhang Zheng1, Zhang Yunli1, Chen Jiayong1
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine Graduate School, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Cardiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, the Sub-center of the National Clinical Medical Research Center for Cardiovascular Diseases of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-04-09Accepted:2024-06-11Online:2025-04-28Published:2024-09-11 -
Contact:Lu Jianqi, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Cardiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, the Sub-center of the National Clinical Medical Research Center for Cardiovascular Diseases of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zhang Yibo, Master candidate, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine Graduate School, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (Regional Program), No. 82160887 (to LJQ); National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 81673891 (to LJQ); Operational Construction of Scientific Research Specialized Subject of National TCM Clinical Research Base, National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. JDZX2015146 (to LJQ); Guangxi Natural Science Foundation, Nos. 2021JJA140661 and 2021GXNSFBA196018 (both to LJQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Chen Lidan, Lu Wei, Zhang Zheng, Zhang Yunli, Chen Jiayong . Relationship between hypertension and osteoporosis in different racial groups[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2614-2622.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

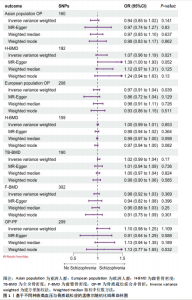
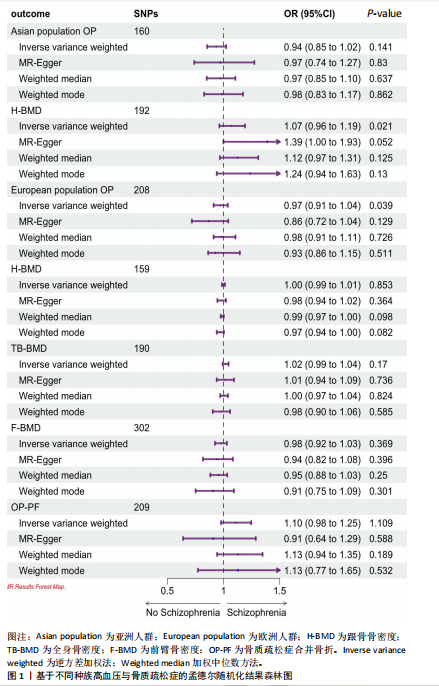
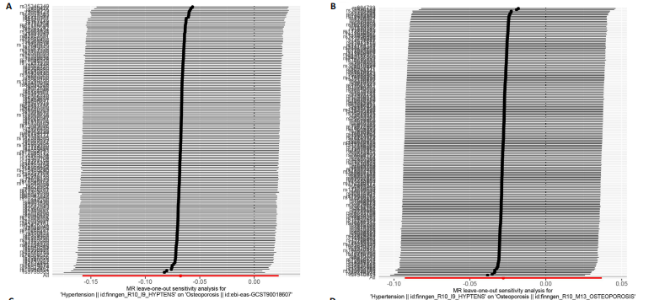
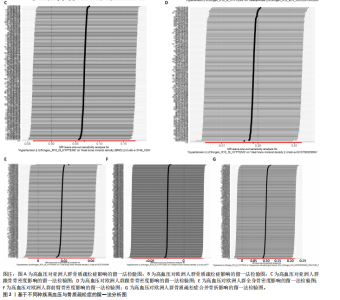
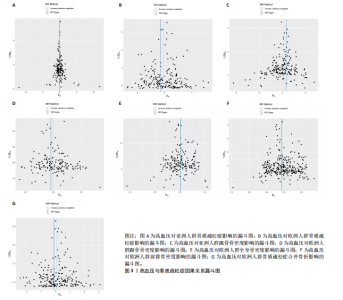
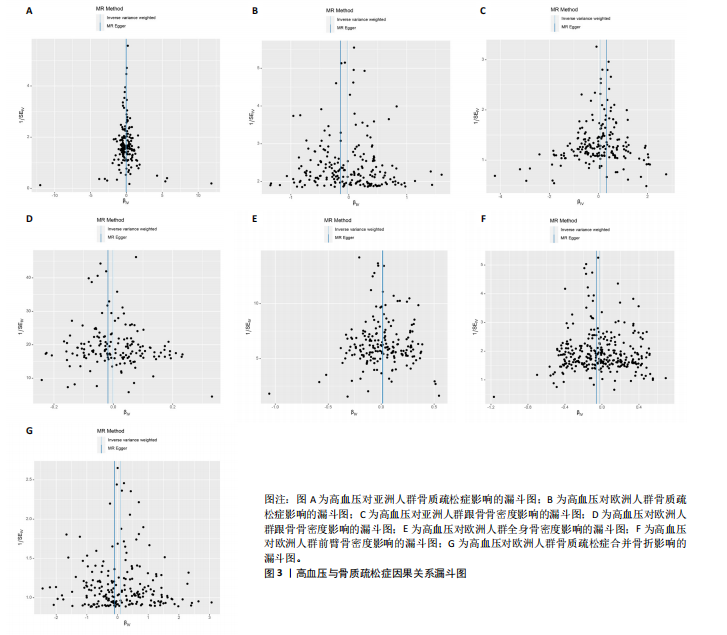
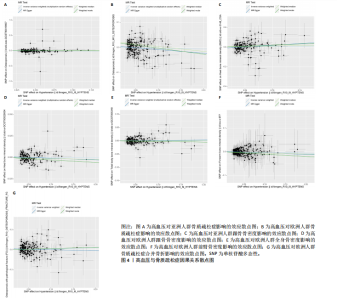
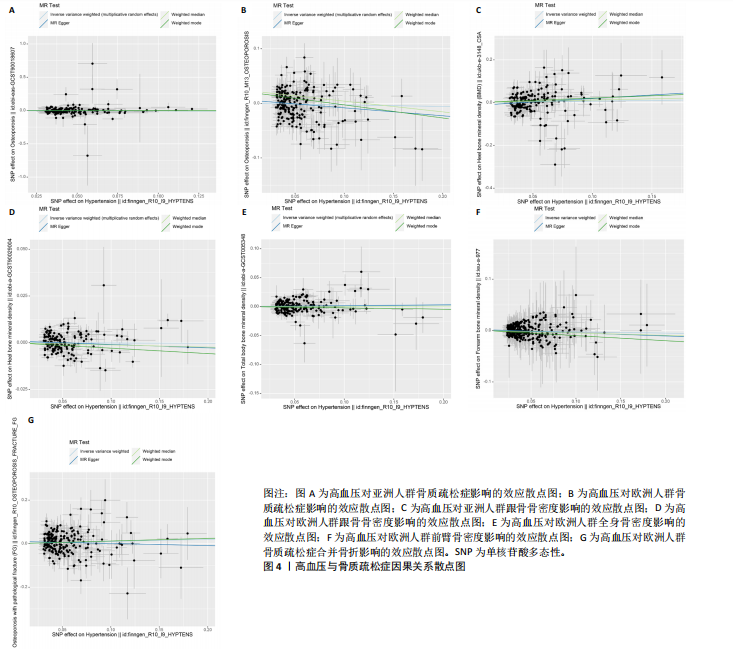
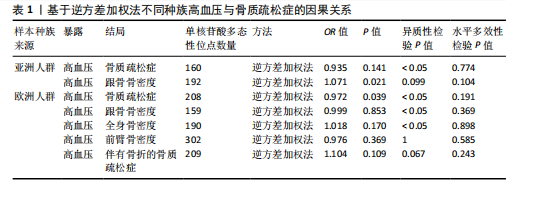
2.1 工具变量 根据上述标准选择与骨质疏松症和骨密度相关的工具单核苷酸多态性,研究从亚洲人群骨质疏松症、欧洲人群骨质疏松症、亚洲人群跟骨骨密度、欧洲人群跟骨骨密度、全身骨密度、前臂骨密度及骨质疏松症合并骨折的GWAS数据集中分别筛选出了160,208,192,159,190,302,209个单核苷酸多态性。 2.2 孟德尔随机化分析结果 孟德尔随机化逆方差加权法分析表明,高血压与亚洲人群跟骨骨密度(OR=1.071,95%CI:0.963-1.191,P=0.021,b=0.068)之间呈现正向因果效应;与欧洲人群骨质疏松症(OR=0.972,95%CI:0.911-1.038,P=0.039,b=-0.028)之间呈现负向因果效应。结果并未显示高血压与亚洲人群骨质疏松症、欧洲人群跟骨骨密度、全身骨密度、前臂骨密度及骨质疏松症合并骨折存在显著相关性(亚洲人群骨质疏松症:OR=0.935,95%CI=0.854-1.023,P=0.141,b=-0.068;欧洲人群跟骨骨密度:OR=0.999,95%CI=0.986-1.012,P=0.853,b=-0.001;欧洲人群全身骨密度:OR=1.018,95%CI=0.992-1.044,P=0.170,b=0.018;欧洲人群前臂骨密度:OR=0.976,95%CI=0.924-1.030,P=0.369,b=-0.025;欧洲人群骨质疏松症合并骨折:OR=1.104,95%CI=0.978-1.246,P=0.109,b=0.010)。通过Stsiger检测,暴露与结局之间无反向因果关系。孟德尔随机化分析结果见表1及图1。 2.3 敏感性分析 敏感性Cochran’s Q检验结果表明,亚洲人群骨质疏松症(P < 0.05)、跟骨骨密度(P=0.099)、欧洲人群骨质疏松症(P < 0.05)、跟骨骨密度(P < 0.05)、全身骨密度(P < 0.05)、前臂骨密度(P=1),骨质疏松症合并骨折(P=0.067)。亚洲人群骨质疏松症、欧洲人群骨质疏松症、跟骨骨密度、全身骨密度存在显著的异质性(P < 0.05);亚洲人群跟骨骨密度、欧洲人群前臂骨密度、骨质疏松症合并骨折均为P > 0.05,表明不存在显著异质性,见表1。 使用MR-Egger方法来确定单核苷酸多态性的潜在水平多效性。结果显示亚洲人群骨质疏松症(P=0.774)、跟骨骨密度(P=0.104)、欧洲人群骨质疏松症(P=0.191)、跟骨骨密度(P=0.369)、全身骨密度(P=0.898)、前臂骨密度(P=0.585),骨质疏松症合并骨折(P=0.243),结果显示其截距均为P > 0.05,没有发现水平多效性,所选工具变量具有可靠性,见表1。 留一法显示高血压与骨质疏松症之间的联系不由单一单核苷酸多态性所主导,敏感性分析结果显示在逐个剔除法中未见明显影响结果的单核苷酸多态性(图2)。漏斗图显示当某一单核苷酸多态性作为工具变量时,代表因果关系的效应点对称分布(图3),表示其可能受潜在偏倚影响的可能性较少。图4是估算的单核苷酸多态性对暴露和结局影响大小的散点图,散点图和漏斗图排除了潜在异常值和水平多效性的可能性。此外,MR-Steiger分析的结果证实了暴露与结局之间不存在反向因果关系。敏感性分析进一步排除了异质性和水平多效性的影响,证明了结果的稳健性。"
| [1] CHIN KY, NG BN, ROSTAM M, et al. A Mini Review on Osteoporosis: From Biology to Pharmacological Management of Bone Loss. J Clin Med. 2022;11(21):6434. [2] BLACK DM, ROSEN CJ. Clinical Practice. Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(3):254-262. [3] ZHU X, BAI W, ZHENG H. Twelve Years of GWAS Discoveries for Osteoporosis and Related Traits: Advances, Challenges and Applications. Bone Res. 2021;9(1):23. [4] SHI YK, YUAN KH, FU ZM, et al. The Relationship between Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Osteoporosis Based on Different Ethnic Groups: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2024;114(4):386-396. [5] O’SHEA PM, GRIFFIN TP, FITZGIBBON M. Hypertension: The Role of Biochemistry in The Diagnosis and Management. Clin Chim Acta. 2017;465:131-143. [6] YANG S, NGUYEN ND, CENTER JR, et al. Association between Hypertension and Fragility Fracture: A Longitudinal Study. Osteoporos Int. 2014;25(1):97-103. [7] HU Z,YANG K, HU Z, et al. Determining The Association between Hypertension and Bone Metabolism Markers in Osteoporotic Patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100(24):e26276. [8] AZEEZ TA. Osteoporosis and Cardiovascular Disease:A Review.Mol Biol Rep. 2023;50(2): 1753-1763. [9] YE Z, LU H, LIU P. Association between Essential Hypertension and Bone Mineral Density: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 2017;8(40):68916-68927. [10] PINAR-GUTIERREZ A, GARCIA-FONTANA C, GARCIA-FONTANA B, et al. Obesity and Bone Health: A Complex Relationship. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(15):8303. [11] LAWLOR DA, HARBORD RM, STERNE JA, et al. Mendelian Randomization: Using Genes as Instruments for Making Causal Inferences in Epidemiology. Stat Med. 2008;27(8):1133-1163. [12] DAVEY SG, HEMANI G. Mendelian Randomization: Genetic Anchors for Causal Inference in Epidemiological Studies. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23(R1):R89-R98. [13] RICHARDS JB, RIVADENEIRA F, INOUYE M, et al. Bone Mineral Density, Osteoporosis, and Osteoporotic Fractures:A Genome-wide Association Study. Lancet. 2008; 371(9623):1505-1512. [14] ISHIGAKI K, AKIYAMA M, KANAI M, et al. Large-scale Genome-wide Association Study in A Japanese Population Identifies Novel Susceptibility Loci Across Different Diseases. Nat Genet. 2020;52(7):669-679. [15] CONROY MC, LACEY B, BESEVIC J, et al. UK Biobank: A Globally Important Resource for Cancer Research. Br J Cancer. 2023;128(4):519-527. [16] MEDINA-GOMEZ C, KEMP JP, TRAJANOSKA K, et al. Life-Course Genome-wide Association Study Meta-analysis of Total Body BMD and Assessment of Age-Specific Effects. Am J Hum Genet. 2018;102(1):88-102. [17] SEKULA P, DEl GMF, PATTARO C, et al. Mendelian Randomization as An Approach to Assess Causality Using Observational Data. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;27(11): 3253-3265. [18] SANDERSON E. Multivariable Mendelian Randomization and Mediation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2021;11(2). [19] YU X, CHENG X, LV L, et al. The Association between Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Autoimmune Diseases:A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024;11: 1331111. [20] HEMANI G, TILLING K, DAVEY SG. Orienting The Causal Relationship between Imprecisely Measured Traits Using GWAS Summary Data. PLoS Genet. 2017;13(11):e1007081. [21] VERBANCK M, CHEN CY, NEALE B, et al. Publisher Correction: Detection of Widespread Horizontal Pleiotropy in Causal Relationships Inferred from Mendelian Randomization between Complex Traits and Diseases. Nat Genet. 2018;50(8):1196. [22] RIZZOLI R. Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: Assessment and Management. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2018;32(5):739-757. [23] YILMAZ E, ÜNVER S. Investigation of The Relationship between Magnesium Level and Vitamin D, Bone Mineral Density, and Chronic Diseases in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis Magnes Res. 2023;36(2):40-48. [24] CATENA C, COLUSSI GL, BROSOLO G, et al. Salt, Aldosterone, and Parathyroid Hormone: What is The Relevance for Organ Damage?. Int J Endocrinol. 2017;2017: 4397028. [25] EVANS JM, WANG S, GREB C, et al. Body Size Predicts Cardiac and Vascular Resistance Effects on Men’s and Women’s Blood Pressure. Front Physiol. 2017;8:561. [26] ASABA Y, ITO M, FUMOTO T, et al. Activation of Renin-angiotensin System Induces Osteoporosis Independently of Hypertension. J Bone Miner Res. 2009; 24(2):241-250. [27] ILIC K, OBRADOVIC N, VUJASINOVIC-STUPAR N. The Relationship Among Hypertension, Antihypertensive Medications, and Osteoporosis: A Narrative Review. Calcif Tissue Int. 2013;92(3):217-227. [28] CAUDARELLA R, VESCINI F, RIZZOLI E, et al. Salt Intake, Hypertension, and Osteoporosis. J Endocrinol Invest. 2009;32(4 Suppl):15-20. [29] AL-MAKKI A, DIPETTE D, WHELTON PK, et al. Hypertension Pharmacological Treatment in Adults: A World Health Organization Guideline Executive Summary.Hypertension. 2022;79(1):293-301. [30] PAPAIOANNOU G, MIRZAMOHAMMADI F, KOBAYASHI T. Ras Signaling Regulates Osteoprogenitor Cell Proliferation and Bone Formation. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(10):e2405. [31] CHAI H, GE J, LI L, et al. Hypertension is Associated with Osteoporosis: A Case-control Study in Chinese Postmenopausal Women. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021; 22(1):253. [32] CARBONE LD, VASAN S, PRENTICE RL, et al. The Renin-angiotensin Aldosterone System and Osteoporosis:Findings from The Women’s Health Initiative. Osteoporos Int. 2019;30(10):2039-2056. [33] WANG B, YANG J, FAN L, et al. Osteogenic Effects of Antihypertensive Drug Benidipine on Mouse MC3T3-E1 Cells in Vitro. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2021;22(5):410-420. [34] JAVED F, KHAN SA, AYERS EW, et al. Association of Hypertension and Bone Mineral Density in An Elderly African American Female Population. J Natl Med Assoc. 2012;104(3-4):172-178. [35] LI ZF, GUO ZF, CAO J, et al. Plasma Ghrelin and Obestatin Levels are Increased in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Peptides. 2010;31(2):297-300. [36] NOUH O, ABD E M, HASSOUNA AA. Association between Ghrelin Levels and BMD: A Cross Sectional Trial. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2012;28(7):570-572. [37] REJNMARK L, VESTERGAARD P, MOSEKILDE L. Treatment with Beta-blockers, ACE Inhibitors, and Calcium-channel Blockers is Associated with A Reduced Fracture Risk: A Nationwide Case-control Study. J Hypertens. 2006;24(3):581-589. [38] SOWERS MR, CLARK MK, JANNAUSCH ML, et al. Body Size, Estrogen Use and Thiazide Diuretic Use Affect 5-year Radial Bone Loss in Postmenopausal Women. Osteoporos Int. 1993;3(6):314-321. [39] AUNG K, HTAY T. Thiazide Diuretics and The Risk of Hip Fracture. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;(10):D5185. [40] BOKRANTZ T, SCHIOLER L, BOSTROM KB, et al. Antihypertensive Drug Classes and The Risk of Hip Fracture: Results from The Swedish Primary Care Cardiovascular Database. J Hypertens. 2020;38(1):167-175. [41] OTT SM, LACROIX AZ, SCHOLES D, et al. Effects of Three Years of Low-dose Thiazides on Mineral Metabolism in Healthy Elderly Persons. Osteoporos Int. 2008;19(9):1315-1322. [42] DESBIENS LC, KHELIFI N, WANG YP, et al. Thiazide Diuretics and Fracture Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. JBMR Plus. 2022; 6(11):e10683. [43] CRUZ DN. The Renal Tubular Na-Cl Co-transporter (NCCT): A Potential Genetic Link between Blood Pressure and Bone Density? Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2001;16(4):691-694. [44] IWAI M, KANNO H, INABA S, et al. Nifedipine, A Calcium-channel Blocker, Attenuated Glucose Intolerance and White Adipose Tissue Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetic KK-A(y) Mice. Am J Hypertens. 2011;24(2):169-174. [45] SRIKANTHAN P, CRANDALL CJ, MILLER-MARTINEZ D, et al. Insulin Resistance and Bone Strength: Findings from The Study of Midlife in The United States. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(4):796-803. [46] TIAN Z, MIYATA K, TABATA M, et al. Nifedipine Increases Energy Expenditure by Increasing PGC-1α Expression in Skeletal Muscle. Hypertens Res. 2011;34(11):1221-1227. [47] DOYLE L, CASHMAN KD. The DASH Diet May Have Beneficial Effects on Bone Health. Nutr Rev. 2004;62(5):215-220. [48] ALTAWILI AA, ALTAWILI M, ALWADAI AM, et al. An Exploration of Dietary Strategies for Hypertension Management: A Narrative Review. Cureus. 2023;15(12):e50130. [49] DOYLE L, CASHMAN KD. The Effect of Nutrient Profiles of The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) Diets on Blood Pressure and Bone Metabolism and Composition in Normotensive and Hypertensive Rats. Br J Nutr. 2003;89(5): 713-724. [50] LIN PH, GINTY F, APPEL LJ, et al. The DASH Diet and Sodium Reduction Improve Markers of Bone Turnover and Calcium Metabolism in Adults. J Nutr. 2003;133(10): 3130-3136. [51] MOVASSAGH EZ, VATANPARAST H. Current Evidence on The Association of Dietary Patterns and Bone Health: A Scoping Review. Adv Nutr. 2017;8(1):1-16. [52] ZHOU XJ, LU K, LIU ZH, et al. U-shaped Relationship Found between Fibrinogen-to-albumin Ratio and Systemic Inflammation Response Index in Osteoporotic Fracture Patients. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):11299. |
| [1] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Chen Jiayong, Tang Meiling, Lu Jianqi, Pang Yan, Yang Shangbing, Mao Meiling, Luo Wenkuan, Lu Wei, Zhou Jiatan. Based on Mendelian randomization, the causal relationship between 1400 metabolites and sarcopenia and the correlation analysis of cardiovascular disease were investigated [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-11. |
| [3] | Zhou Jiajun, Ma Fei, Leng Yebo, Xu Shicai, He Baoqiang, Li Yang, Liao Yehui, Tang Qiang, Tang Chao, Wang Qing, Zhong Dejun. Assessing distribution characteristics and clinical significance of vertebral fractures in patients with osteoporosis based on whole spine MRI [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1883-1889. |
| [4] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [5] | Dong Tingting, Chen Tianxin, Li Yan, Zhang Sheng, Zhang Lei. Causal relationship between modifiable factors and joint sports injuries [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1953-1962. |
| [6] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [7] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [8] | Zhao Jiacheng, Ren Shiqi, Zhu Qin, Liu Jiajia, Zhu Xiang, Yang Yang. Bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers for primary osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1741-1750. |
| [9] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [10] | Li Yueyao, Zhang Min, Yang Jiaju. Cistanoside A mediates p38/MAPK pathway to inhibit osteoclast activity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1144-1151. |
| [11] | Zheng Lin, Jin Wenjun, Luo Shanshan, Huang Rui, Wang Jie, Cheng Yuting, An Zheqing, Xiong Yue, Gong Zipeng, Liao Jian. Eucommia ulmoides promotes alveolar bone formation in ovariectomized rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1159-1167. |
| [12] |
Huang Xiaobin, Ge Jirong, Li Shengqiang, Xie Lihua, Huang Jingwen, He Yanyan, Xue Lipeng.
Mechanisms of different yin nourishing and kidney tonifying methods on osteoclastysis pathway in ovariectomized rats #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1214-1219.
|
| [13] | Qian Kun, Li Ziqing, Sun Shui . Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the occurrence and development of common degenerative bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1285-1295. |
| [14] |
Zhao Wensheng, Li Xiaolin, Peng Changhua, Deng Jia, Sheng Hao, Chen Hongwei, Zhang Chaoju, He Chuan.
Gut microbiota and osteoporotic fractures #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1296-1304.
|
| [15] | Ma Haoyu, Qiao Hongchao, Hao Qianqian, Shi Dongbo. Causal effects of different exercise intensities on the risk of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1305-1311. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||