Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (12): 2605-2613.doi: 10.12307/2025.376
Previous Articles Next Articles
Causal relationship between peripheral blood cells and osteoporosis
Liu Kedi1, Chen Yongxi2, Qin Haibiao2, Guo Shenghui1, Qin Zhongshe1, Meng Juewei1, Cui Shanlin1, Fan Junhong1
- 1Graduate School of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530003, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530003, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-03-22Accepted:2024-06-13Online:2025-04-28Published:2024-09-11 -
Contact:Chen Yongxi, Master supervisor, Associate chief physician, Graduate School of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530003, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Liu Kedi, Master candidate, Graduate School of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530003, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Guangxi Traditional Chinese Medicine Appropriate Technology Development and Promotion Project, No. GZSY-23-28 (to CYX); Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine Research Project, No. 2022MS043 (to CYX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Kedi, Chen Yongxi, Qin Haibiao, Guo Shenghui, Qin Zhongshe, Meng Juewei, Cui Shanlin, Fan Junhong. Causal relationship between peripheral blood cells and osteoporosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2605-2613.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
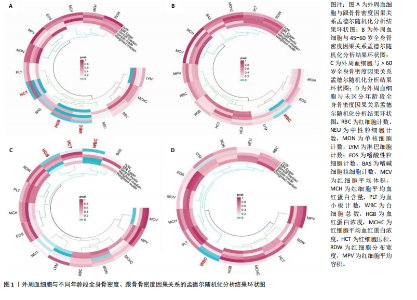
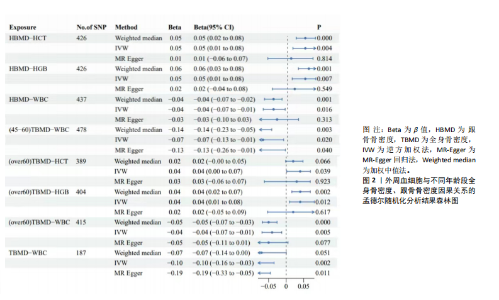
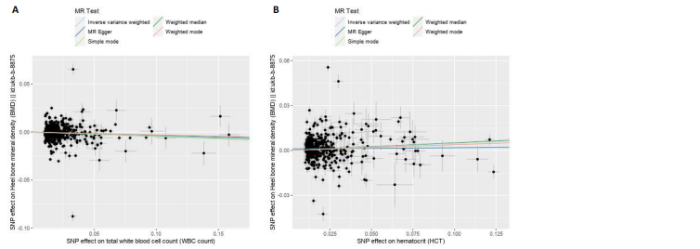
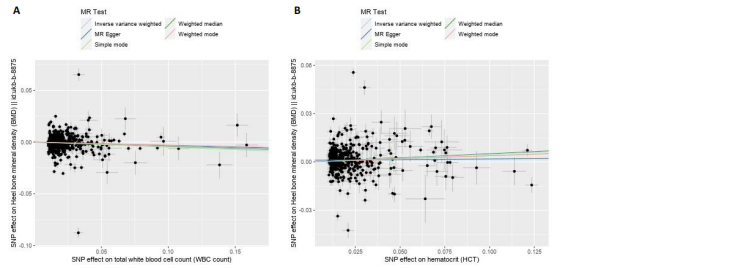
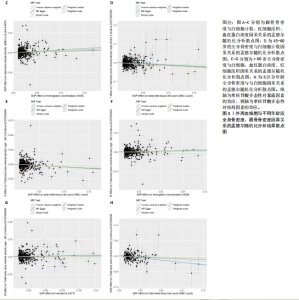
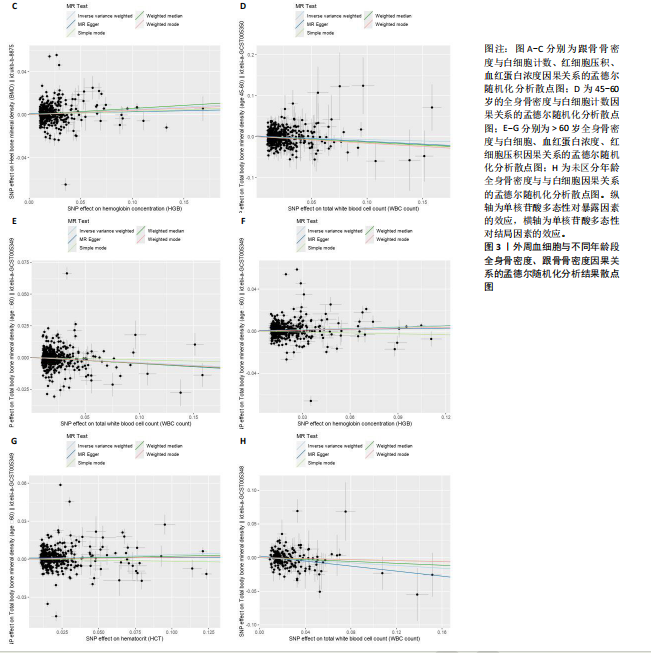
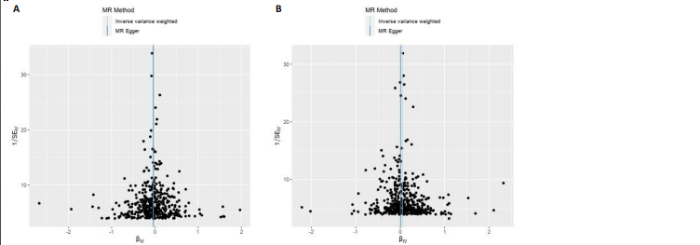
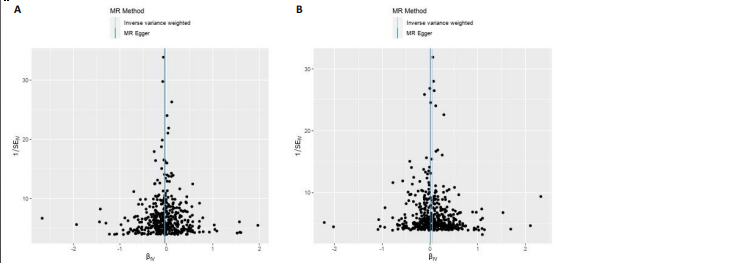
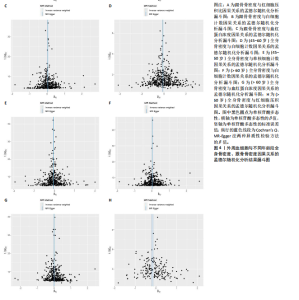
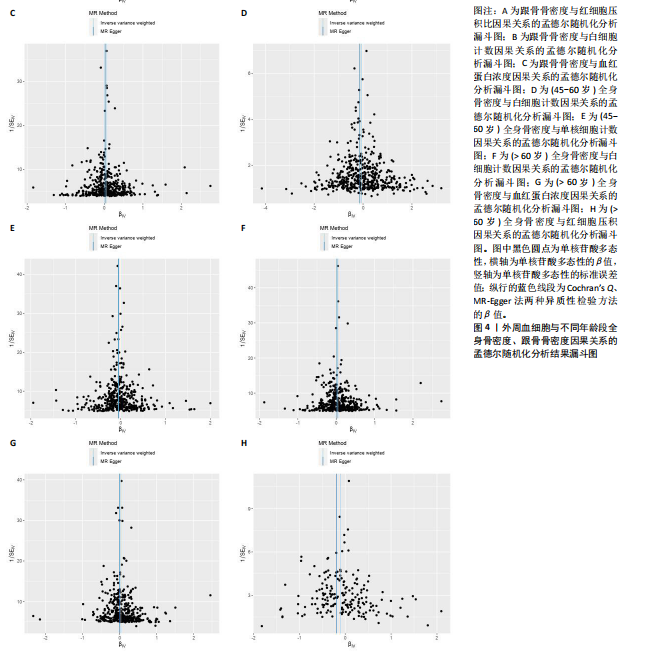
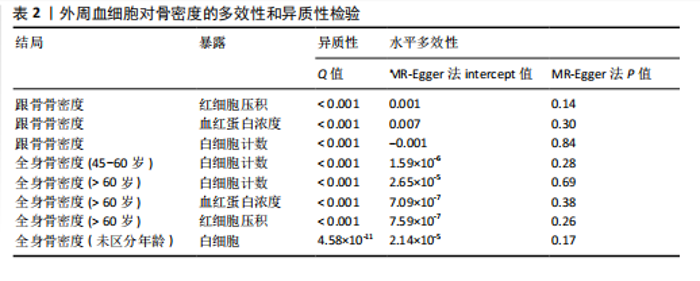
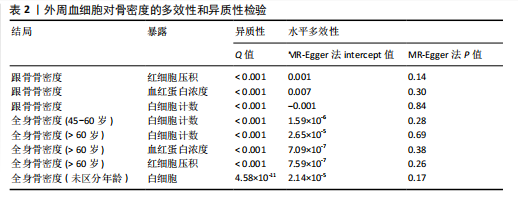
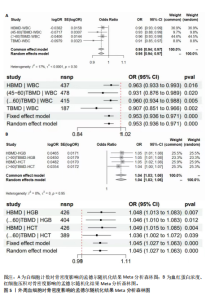
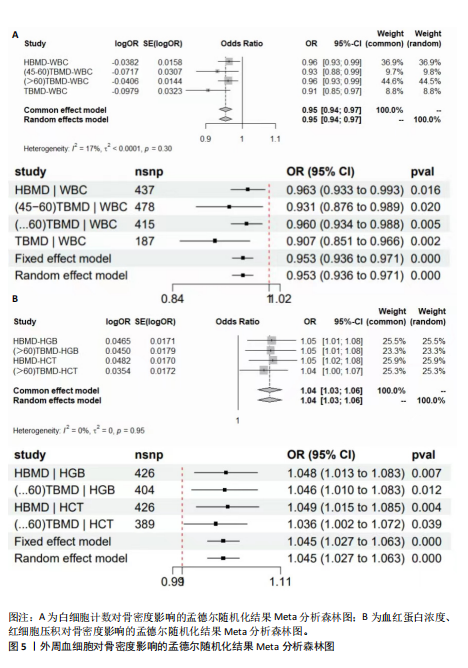
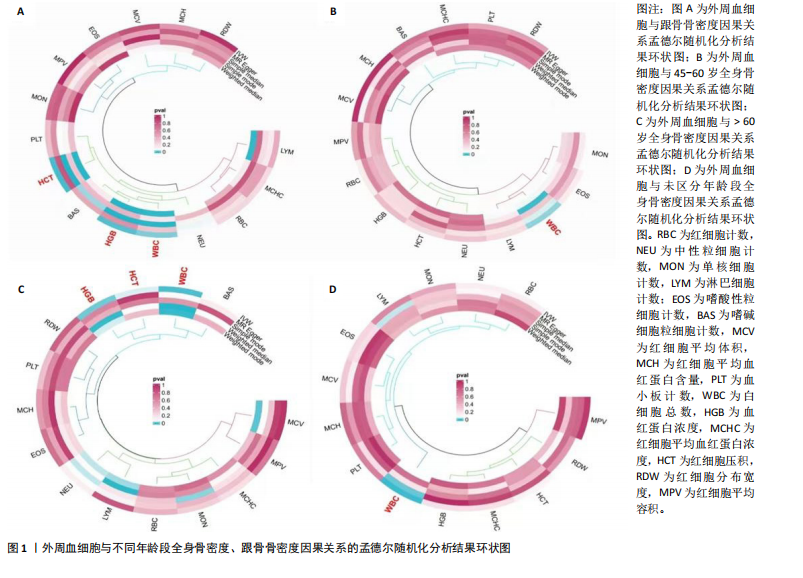
2.1 外周血细胞对骨密度影响的工具变量 在去除连锁不平衡的单核苷酸多态性后,查阅Phenoscanner数据库检索相关混杂因素(如肥胖、糖尿病、甲状腺功能障碍等)并剔除相关单核苷酸多态性,经 MR-PRESSO分析无离群值,最小F值为22,最大F值为 2 956,均符合F值> 10的要求,所有单核苷酸多态性均符合独立性假设和排他性假设。 2.2 孟德尔随机化分析结果 2.2.1 外周血细胞与不同年龄段全身骨密度及跟骨骨密度的因果关系 逆方差加权法分析结果表明:当不同年龄段骨密度作为结局时,白细胞计数与(45-60岁)全身骨密度呈负向因果关系(β=-0.07,95%CI:-0.13,-0.01,P=0.02),单核细胞计数与(45- 60岁)全身骨密度呈正向因果关系(β=0.05,95%CI:0.00,0.10,P=0.037);白细胞计数、嗜碱性粒细胞计数与(> 60岁)全身骨密度呈负向因果关系(β=-0.04,95%CI:-0.07,-0.01,P=0.005;β=-0.04,95%CI:-0.07,-0.00,P=0.038),血红蛋白浓度、红细胞压积与(> 60岁)全身骨密度呈正向因果关系(β=0.04,95%CI:0.01,0.08,P=0.012;β=0.04,95%CI:0.00,0.07,P=0.039);白细胞计数与(未区分年龄段)全身骨密度呈负向因果关系(β=-0.10,95%CI:-0.16,-0.03,P=0.002),并且Bonferroni法调整P值后差异有显著性意义(P < 3.3×10-3)。当跟骨骨密度作为结局时,白细胞计数与跟骨骨密度呈负向因果关系(β=-0.04,95%CI:-0.07,-0.01,P=0.016),血红蛋白浓度及红细胞压积与跟骨骨密度呈正向因果关系(β=0.05,95%CI:0.01,0.08,P=0.007;β=0.05,95%CI:0.01,0.08,P=0.004)。外周血细胞与不同年龄段全身骨密度、跟骨骨密度因果关系的孟德尔随机化分析结果环状图,见图1。外周血细胞与不同年龄段全身骨密度、跟骨骨密度因果关系的孟德尔随机化分析结果森林图,见图2。 2.2.2 敏感性分析结果 MR-Egger法检验提示结果无水平多效性(P > 0.05),Cochran’s Q检验显示外周血细胞与不同年龄段骨密度、跟骨骨密度因果关系的孟德尔随机化分析结果均存在异质性(P < 0.05),见表2,但逆方差加权法数据表明因果关系明确,满足独立性假设,故此次研究的异质性不影响阳性结果的解读[22];Leave-one-out法未见明显离群值;散点图显示遗传预测的回归线基本一致(图3),除MR-Egger法外,其他 2 种主要分析结果均存在显著性意义,3种主要分析方法的效应值方向一致;漏斗图两侧单核苷酸多态性位点基本对称(图4)。以上分析结果表明此次孟德尔随机化分析结果可靠。 2.2.3 Meta分析结果 为了进一步验证结果的可靠性,将孟德尔随机化分析中逆方差加权法结果进行Meta分析(图5)。"
| [1] LONG G, LIU C, LIANG T, et al. Predictors of osteoporotic fracture in postmenopausal women: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023; 18(1):574. [2] LI Y, HAO W, GUAN J, et al. Relationship between indices of circulating blood cells and bone homeostasis in osteoporosis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:965290. [3] FAN J, SU YW, HASSANSHAHI M, et al. β-Catenin signaling is important for osteogenesis and hematopoiesis recovery following methotrexate chemotherapy in rats. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(5):3740-3751. [4] BISWAS S, SHAH MS, SARKAR SK, et al. Measurement of Bone Mineral Density in the Transfusion Dependent Thalassemic Patients. Mymensingh Med J. 2022;31(2): 428-430. [5] GIORDANO P, URBANO F, LASSANDRO G, et al. Mechanisms of Bone Impairment in Sickle Bone Disease. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(4):1832. [6] VAN ATTEVELD JE, DE WINTER DT, PIETERS R, et al. Recent perspectives on the association between osteonecrosis and bone mineral density decline in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Fac Rev. 2021; 10:57. [7] WONG CC, LIAO JH, SHEU SY, et al. Novel transplant of combined platelet-rich fibrin Releasate and bone marrow stem cells prevent bone loss in Ovariectomized osteoporotic mice. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):527. [8] BROWN JP. Long-Term Treatment of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2021;36(3):544-552. [9] YANG J, WU J. Discovery of potential biomarkers for osteoporosis diagnosis by individual omics and multi-omics technologies. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2023; 23(6):505-520. [10] DUDBRIDGE F. Polygenic Mendelian Randomization. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2021;11(2):a039586. [11] BIRNEY E. Mendelian Randomization. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2022;12(4): a041302. [12] CHEN MH, RAFFIELD LM, MOUSAS A, et al. Trans-ethnic and Ancestry-Specific Blood-Cell Genetics in 746,667 Individuals from 5 Global Populations. Cell. 2020;182(5):1198-1213.e14. [13] GKASTARIS K, GOULIS DG, POTOUPNIS M, et al. Obesity, osteoporosis and bone metabolism. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2020;20(3):372-381 [14] WEI Y, ZHAN Y, CARLSSON S. Childhood adiposity and novel subtypes of diabetes in adults: a Mendelian randomisation and genome-wide genetic correlation study. Lancet Glob Health. 2023;11 Suppl 1:S1. [15] WU X, WANG C, LI H, et al. Circulating white blood cells and lung function impairment: the observational studies and Mendelian randomization analysis. Ann Med. 2021; 53(1):1118-1128. [16] XU J, ZHANG S, TIAN Y, et al. Genetic Causal Association between Iron Status and Osteoarthritis: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization. Nutrients. 2022;14(18):3683. [17] HO J, MAK CCH, SHARMA V, et al. Mendelian Randomization Studies of Lifestyle-Related Risk Factors for Osteoarthritis: A PRISMA Review and Meta-Analysis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(19):11906. [18] BAURECHT H, FREUER D, WELKER C, et al. Relationship between periodontitis and psoriasis: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. J Clin Periodontol. 2022;49(6):573-579. [19] MA XB, LIU YM, LV YL, et al. Interaction between systemic iron parameters and left ventricular structure and function in the preserved ejection fraction population: a two-sample bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2024;21(1):64-80. [20] CAO Z, WU Y, LI Q, et al. A causal relationship between childhood obesity and risk of osteoarthritis: results from a two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis. Ann Med. 2022;54(1):1636-1645. [21] LIN L, LUO P, YANG M, et al. Causal relationship between osteoporosis and osteoarthritis: A two-sample Mendelian randomized study. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:1011246. [22] 杨敬言,马涉,黄仁俊,等.基于孟德尔随机化分析躯干及下肢脂肪量与椎间盘退变的因果关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(35):5688-5694. [23] JEONG HR, SHIM YS, LEE HS, et al. Hemoglobin and hematocrit levels are positively associated with blood pressure in children and adolescents 10 to 18 years old. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):19052. [24] CARSON JL, STANWORTH SJ, DENNIS JA, et al. Transfusion thresholds for guiding red blood cell transfusion. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021;12(12):CD002042. [25] LI L, GE JR, CHEN J, et al. Association of bone mineral density with peripheral blood cell counts and hemoglobin in Chinese postmenopausal women: A retrospective study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(28):e20906. [26] SIMIC MK, MOHANTY ST, XIAO Y, et al. Multi-Targeting DKK1 and LRP6 Prevents Bone Loss and Improves Fracture Resistance in Multiple Myeloma. J Bone Miner Res. 2023;38(6):814-828. [27] COWAN AJ, GREEN DJ, KWOK M, et al. Diagnosis and Management of Multiple Myeloma: A Review. JAMA. 2022;327(5): 464-477. [28] BELLELLI A, TAME JRH. Hemoglobin allostery and pharmacology. Mol Aspects Med. 2022; 84:101037. [29] MENG X, WIELOCKX B, RAUNER M, et al. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors Regulate Osteoclasts in Health and Disease. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:658893. [30] LI D, JIANG Y, HE P, et al. Hypoxia Drives Material-Induced Heterotopic Bone Formation by Enhancing Osteoclastogenesis via M2/Lipid-Loaded Macrophage Axis. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(15):e2207224. [31] LAPPIN KM, MILLS KI, LAPPIN TR. Erythropoietin in bone homeostasis-Implications for efficacious anemia therapy. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021;10(6):836-843. [32] SURESH S, LEE J, NOGUCHI CT. Erythropoietin signaling in osteoblasts is required for normal bone formation and for bone loss during erythropoietin‐stimulated erythropoiesis. FASEB J. 2020;34(9): 11685‐11697. [33] KRISTJANSDOTTIR HL, LEWERIN C, LERNER UH, et al. High Plasma Erythropoietin Predicts Incident Fractures in Elderly Men with Normal Renal Function: The MrOS Sweden Cohort. J Bone Miner Res. 2020; 35(2):298-305. [34] OU-YANG J, ZHANG J, TAN X, et al. Risk Interval of Complete Blood Counts May be Closely Associated with Bone Mineral Density in the Elderly Chinese Population. Clin Lab. 2020;66(10).doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2020.191238. [35] SALIMI M, KHANZADEH M, NABIPOORASHRAFI SA, et al. Association of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio with bone mineral density in post-menopausal women: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Womens Health. 2024;24(1):169. [36] NIE YZ, YAN ZQ, YIN H, et al. Osteosarcopenic obesity and its components-osteoporosis, sarcopenia, and obesity-are associated with blood cell count-derived inflammation indices in older Chinese people. BMC Geriatr. 2022;22(1):532. [37] KIM HL, CHO HY, PARK IY, et al. The positive association between peripheral blood cell counts and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women. Yonsei Med J. 2011;52(5):739-745. [38] LI Y, HAO W, GUAN J, et al. Relationship between indices of circulating blood cells and bone homeostasis in osteoporosis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:965290. [39] HEDAYATI MT, MONTAZERI M, RASHIDI N, et al. White blood cell count and clustered components of metabolic syndrome: A study in western Iran. Caspian J Intern Med. 2021;12(1):59-64. [40] LUO G, LI F, LI X, et al. TNF α and RANKL promote osteoclastogenesis by upregulating RANK via the NF κB pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2018; 17(5):6605-6611. [41] CHEN B, LI HZ. Association of IL-6 174G/C (rs1800795) and 572C/G (rs1800796) polymorphisms with risk of osteoporosis: a meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):330. [42] KIM JH, LEE YJ, PARK B. Higher monocyte count with normal white blood cell count is positively associated with 10-year cardiovascular disease risk determined by Framingham risk score among community-dwelling Korean individuals. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(17):e15340. [43] SONG BW, KIM AR, MOON DH, et al. Associations of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio with Osteoporosis and Incident Vertebral Fracture in Postmenopausal Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022;58(7):852. [44] QU L, ZUO X, YU J, et al. Association of inflammatory markers with all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis or osteopenia. BMC Womens Health. 2023; 23(1):487. [45] LIU YC, YANG TI, HUANG SW, et al. Associations of the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio with Osteoporosis: A Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022; 12(12):2968. [46] CHEN S, SUN X, JIN J, et al. Association between inflammatory markers and bone mineral density: a cross-sectional study from NHANES 2007-2010. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):305. [47] HO SC, LI GH, LEUNG AY, et al. Unravelling genetic causality of haematopoiesis on bone metabolism in human. Eur J Endocrinol. 2022;187(6):765-775. |
| [1] | Zhou Jinhai, Li Jiangwei, Wang Xuquan, Zhuang Ying, Zhao Ying, Yang Yuyong, Wang Jiajia, Yang Yang, Zhou Shilian. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of anterior femoral notching during total knee arthroplasty at different bone strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1775-1782. |
| [2] | Zhou Jiajun, Ma Fei, Leng Yebo, Xu Shicai, He Baoqiang, Li Yang, Liao Yehui, Tang Qiang, Tang Chao, Wang Qing, Zhong Dejun. Assessing distribution characteristics and clinical significance of vertebral fractures in patients with osteoporosis based on whole spine MRI [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1883-1889. |
| [3] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [4] | Zhao Jiacheng, Ren Shiqi, Zhu Qin, Liu Jiajia, Zhu Xiang, Yang Yang. Bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers for primary osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1741-1750. |
| [5] | Chen Shuai, Jin Jie, Han Huawei, Tian Ningsheng, Li Zhiwei . Causal relationship between circulating inflammatory cytokines and bone mineral density based on two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [6] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [7] | Li Yueyao, Zhang Min, Yang Jiaju. Cistanoside A mediates p38/MAPK pathway to inhibit osteoclast activity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1144-1151. |
| [8] | Zheng Lin, Jin Wenjun, Luo Shanshan, Huang Rui, Wang Jie, Cheng Yuting, An Zheqing, Xiong Yue, Gong Zipeng, Liao Jian. Eucommia ulmoides promotes alveolar bone formation in ovariectomized rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1159-1167. |
| [9] |
Huang Xiaobin, Ge Jirong, Li Shengqiang, Xie Lihua, Huang Jingwen, He Yanyan, Xue Lipeng.
Mechanisms of different yin nourishing and kidney tonifying methods on osteoclastysis pathway in ovariectomized rats #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1214-1219.
|
| [10] | Qian Kun, Li Ziqing, Sun Shui . Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the occurrence and development of common degenerative bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1285-1295. |
| [11] |
Zhao Wensheng, Li Xiaolin, Peng Changhua, Deng Jia, Sheng Hao, Chen Hongwei, Zhang Chaoju, He Chuan.
Gut microbiota and osteoporotic fractures #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1296-1304.
|
| [12] | Li Jiatong, Jin Yue, Liu Runjia, Song Bowen, Zhu Xiaoqian, Li Nianhu . Association between thyroid function levels and phenotypes associated with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1312-1320. |
| [13] | Wang Dongyang, Yang Qiaohui, Lin Xinchao. Relationship between vitamin D levels and reproductive characteristics and exercise dietary situation in postmenopausal women [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1021-1025. |
| [14] | Lan Shuangli, Xiang Feifan, Deng Guanghui, Xiao Yukun, Yang Yunkang, Liang Jie. Naringin inhibits iron deposition and cell apoptosis in bone tissue of osteoporotic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 888-898. |
| [15] | Zhang Lichuang, Yang Wen, Ding Guangjiang, Li Peikun, Xiao Zhongyu, Chen Ying, Fang Xue, Zhang Teng. Dispersion effect of bone cement after vertebroplasty using individualized unilateral external pedicle approach and bilateral pedicle approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 800-808. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||