Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (14): 2152-2158.doi: 10.12307/2024.271
Previous Articles Next Articles
Correlation analysis of circular RNAs involved in liver injury in mice with autoimmune hepatitis
Hou Yiwen, Liu Ying, Li Zhurong, Chen Chen, Li Zhencheng, Liu Yang
- School of Basic Medical Sciences, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2023-01-31Accepted:2023-03-12Online:2024-05-18Published:2023-07-28 -
Contact:Liu Yang, Professor, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Hou Yiwen, Master, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:Basic Research Program of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine in Rheumatic immune Diseases, No. 2023XKJS-03 (to LY [project participant]); Key Team Program of Shanxi Scientific and Technological Innovation Talents for Prevention of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine, No. 202204051002033 (to LY [project participant]); Science and Technology Innovation Project of Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2022TD2003 (to LY); Key Science and Technology Cooperation Project of Shanxi Province, No. 202104041101013 (to LY); Science and Technology Innovation Project of Higher Education Institutions in Shanxi Province, No. 2020L0423 (to LY); Science and Technology Innovation Capacity Cultivation Program of Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2020PY-JC-07 (to LY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hou Yiwen, Liu Ying, Li Zhurong, Chen Chen, Li Zhencheng, Liu Yang. Correlation analysis of circular RNAs involved in liver injury in mice with autoimmune hepatitis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2152-2158.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

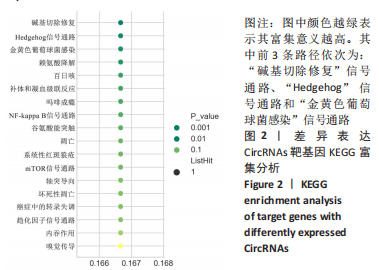
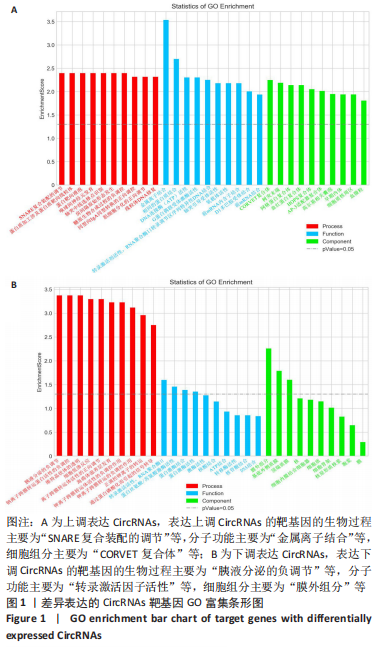
2.1 CircRNAs靶基因预测和GO富集 根据P值从小到大排列,选择前30个GO条目绘制条形图,见图1。GO的富集结果显示,在P < 0.05时,差异表达的CircRNAs可以被阐释为140个GO条目,其中19项细胞组分、28项分子功能和93项生物过程;在错误发现率≤0.05的条件下,差异表达的CircRNAs可以被阐释为59个GO项。图中按P值的升序排列列出了每个类别的前10个GO项,表达上调CircRNAs的靶基因的生物过程主要为“SNARE复合装配的调节”等,分子功能主要为“金属离子结合”等,细胞组分主要为“CORVET 复合体”等;表达下调CircRNAs的靶基因的生物过程主要为“胰液分泌的负调节”等,分子功能主要为“转录激活因子活性”等,细胞组分主要为“膜外组分”等。"

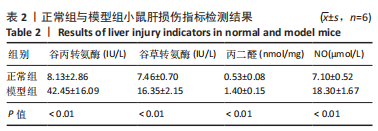
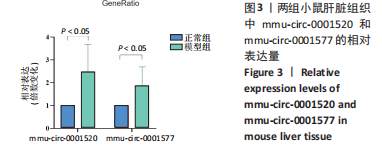
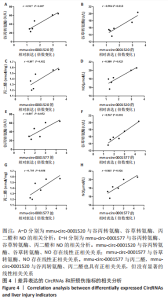
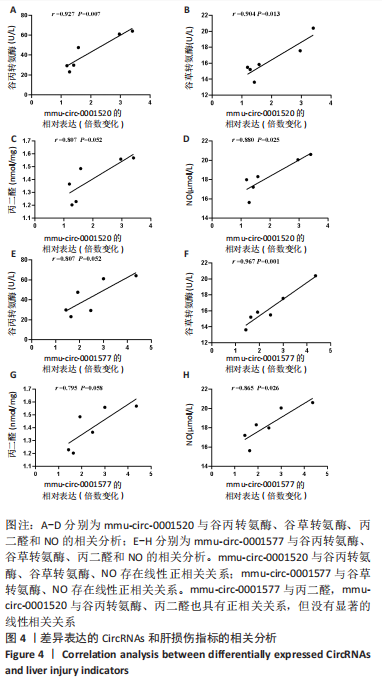
进一步的分析显示,mmu-circ-0001520与谷丙转氨酶(r=0.927,P=0.007)、谷草转氨酶(r=0.904,P=0.013)、NO(r=0.880,P=0.025)存在线性正相关关系;mmu-circ-0001577与谷草转氨酶(r=0.967,P=0.001)、NO(r=0.865,P=0.026)存在线性正相关关系。mmu-circ-0001577与丙二醛(r=0.807,P=0.052),mmu-circ-0001520与谷丙转氨酶(r=0.807,P=0.052)、丙二醛(相关系数r=0.795,P=0.058)与其他指标的变化趋势也具有一致性,但没有显著的线性相关关系。"

| [1] TRIVEDI PJ, HIRSCHFIELD GM. Recent advances in clinical practice: epidemiology of autoimmune liver diseases. Gut. 2021;70(10):1989-2003. [2] SUCHER E, SUCHER R, GRADISTANAC T, et al. Autoimmune Hepatitis-Immunologically Triggered Liver Pathogenesis-Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies. J Immunol Res. 2019;2019:9437043. [3] 林秋香,李圣聪,林爱芳,等.自身免疫抗体谱及抗核抗体核型检测在自身免疫性肝病中的诊断价值[J].热带医学杂志,2022,22(11): 1507-1510. [4] 高璇,张翠丽,曾涛.自身免疫性肝炎的发病机制与治疗现状研究进展[J].肝脏,2022,27(8):928-931. [5] 胡明礼,王绮夏,马雄.自身免疫性肝炎发病机制进展与临床干预新靶点[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2022,38(4):743-747. [6] 吴亚彬,刘建华,秦晓松.环状RNA在自身免疫性疾病中的研究进展[J].中国免疫学杂志,2021,37(19):2416-2422. [7] 周家名,李彬彬,余宏宇.环状RNA在肝纤维化中的调控机制及研究进展[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2022,38(11):1340-1343. [8] 赵国云,朱梦迪,孙宇辉.环状RNA在肿瘤免疫中的研究进展[J].临床与病理杂志,2022,42(3):726-730. [9] LIU Y, LI Z, HAO J, et al. Circular RNAs associated with a mouse model of concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis: preliminary screening and comprehensive functional analysis. FEBS Open Bio. 2020;10(11): 2350-2362. [10] FLOREANI A, RESTREPO-JIMÉNEZ P, SECCHI MF, et al. Etiopathogenesis of autoimmune hepatitis. J Autoimmun. 2018;95:133-143. [11] 马雄,王绮夏,肖潇,等.自身免疫性肝炎诊断和治疗指南(2021)[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2022,38(1):42-49. [12] WEBB GJ, HIRSCHFIELD GM, KRAWITT EL, et al. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Autoimmune Hepatitis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2018;13:247-292. [13] TANAKA A. Autoimmune Hepatitis: 2019 Update. Gut Liver. 2020;14(4): 430-438. [14] 余真君,何泽宝.自身免疫性肝炎研究进展[J].中国免疫学杂志, 2019,35(22):2813-2818. [15] 李应,庞源源,陈虹余.自身免疫性肝炎临床特点分析及血清相关抗体检测水平分析[J].分子诊断与治疗杂志,2022,14(2):346-349+353. [16] ZHOU Z, SUN B, HUANG S, et al. Roles of circular RNAs in immune regulation and autoimmune diseases. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(7):503. [17] ZENG X, YUAN X, CAI Q, et al. Circular RNA as An Epigenetic Regulator in Chronic Liver Diseases. Cells. 2021;10(8):1945. [18] 胡锦辉.CircRNA在自身免疫疾病中的研究进展[J].免疫学杂志, 2021,37(7):639-644. [19] 王雪华,彭辉勇,丁祥梅,等.环状RNA(circRNA)与自身免疫性疾病[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2019,35(10):949-953. [20] 雷波,玄秀云,樊卫平.CircRNA在自身免疫疾病中的研究进展[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2019,32(3):347-350. [21] TIEGS G, HENTSCHEL J, WENDEL A. A T cell-dependent experimental liver injury in mice inducible by concanavalin A. J Clin Invest. 1992; 90(1):196-203. [22] ARCIELLO M, GORI M, BALSANO C. Mitochondrial dysfunctions and altered metals homeostasis: new weapons to counteract HCV-related oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013;2013:971024. [23] BELOT A, GOURBEYRE O, PALIN A, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress controls iron metabolism through TMPRSS6 repression and hepcidin mRNA stabilization by RNA-binding protein HuR. Haematologica. 2021;106(4):1202-1206. [24] BHARADWAJ U, KASEMBELI MM, ROBINSON P, et al. Targeting Janus Kinases and Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 to Treat Inflammation, Fibrosis, and Cancer: Rationale, Progress, and Caution Pharmacol Rev. 2020;72(2):486-526. [25] ALCOVER A, ALARCÓN B, DI BARTOLO V. Cell Biology of T Cell Receptor Expression and Regulation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2018;26(4):103-125. [26] TRIPATHI KP, PICCIRILLO M, GUARRACINO MR. An integrated approach to infer cross-talks between intracellular protein transport and signaling pathways. BMC Bioinformatics. 2018;19(2):58. [27] LI X, YANG L, CHEN LL. The Biogenesis, Functions, and Challenges of Circular RNAs. Mol Cell. 2018;271(3):428-442. [28] CHEN X, LEGRAND AJ, CUNNIFFE S, et al. Interplay between base excision repair protein XRCC1 and ALDH2 predicts overall survival in lung and liver cancer patients. Cell Oncol. 2018;41(5):527-539. [29] ZIÓŁKOWSKA S, CZARNY P, SZEMRAJ J. Impaired base excision repair is related to the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver diseas. Acta Universitatis Lodziensis Folia Biologica et Oecologica. 2020;16:5-11. [30] MATTAR MAM, ZEKRI ARN, HUSSEIN N, et al. Polymorphisms of base-excision repair genes and the hepatocarcinogenesis. Gene. 2018;675: 62-68. [31] SYN WK, CHOI SS, LIASKOU E, et al. Osteopontin is induced by hedgehog pathway activation and promotes fibrosis progression in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2011;53(1):106-115. [32] TAO S, DUAN R, XU T, et al. Salvianolic acid B inhibits the progression of liver fibrosis in rats via modulation of the Hedgehog signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2022;23(2):116. [33] HU J, CAO G, WU X, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine Inhibits Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells through Hedgehog Signaling Pathways In Vitro. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:603067. [34] TANG X, ZHANG L, WEI W. Roles of TRAFs in NF-κB signaling pathways mediated by BAFF. Immunol Lett. 2018;196:113-118. [35] MOSTAFIZAR M, CORTES-PÉREZ C, SNOW W, et al. Challenges with Methods for Detecting and Studying the Transcription Factor Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-κB) in the Central Nervous System. Cells. 2021;10(6):1335. [36] BARNABEI L, LAPLANTINE E, MBONGO W, et al. NF-κB: At the Borders of Autoimmunity and Inflammation. Front Immunol. 2021;12:716469. [37] TAN S, LIU X, CHEN L, et al. Fas/FasL mediates NF-κBp65/PUMA-modulated hepatocytes apoptosis via autophagy to drive liver fibrosis. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(5):474. [38] WANG Z, SUN X, WANG W, et al. NF-κB-coupled IL17 mediates inflammatory signaling and intestinal inflammation in Artemia sinica. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022;128:38-49. [39] 徐博,田晶,马宁,等.肝损伤动物模型的研究进展[J].中国当代医药,2019,26(14):38-40+44. [40] 周燕锋,陈龙,刘信禹.自身抗体联合生化指标检测对自身免疫性肝炎的诊断价值[J].深圳中西医结合杂志,2022,32(4):72-74. [41] 蒋妮,李俊峰,李敏,等.急性重症自身免疫性肝炎治疗研究进展[J].肝脏,2022,27(3):370-373. [42] ZHANG P, DAI M. CircRNA: a rising star in plant biology. J Genet Genomics. 2022;49(12):1081-1092. |
| [1] | Sheng Siqi, Xie Lin, Zhao Xiangyu, Jiang Yideng, Wu Kai, Xiong Jiantuan, Yang Anning, Hao Yinju, Jiao Yun. Involvement of miR-144-3p in Cbs+/- mouse hepatocyte autophagy induced by high-methionine diet [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1289-1294. |
| [2] | Wu Maodong, Su Qinglun, Huang Yiming, Shen Longying, Lu Yu, Zhao Qin. Correlation between coronal pressure variation and coronal imbalance in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 852-856. |
| [3] | Zhang Jinpeng, Chen Chang, Pan Qiuyu, Mai Chenyao, Li Yinlong, Hao Yuxi, Hu Jun. Correlation between platelet count and lumbar bone mineral density in middle-aged and elderly people [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 5046-5051. |
| [4] | Wang Dongxu, Ren Jing, Li Jiping, Wang Yusu, Hu Pengfei, Zhang Guokun, Li Chunyi. Deer antler stem cell-derived exosomes prevent alcoholic liver injury via modulating nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(24): 3824-3830. |
| [5] | Li Shichao, Xie Guangyue, Sun Zhen, Han Peng, Hou Xiaohua, Sun Xiaowei, Zhang Qidong. Correlation of knee joint alignment correction between valgus stress and postoperative radiography after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(18): 2910-2914. |
| [6] | Li Yuanyuan, Sun Yue, Bao Rui, Chang Sirong, Wang Meng, Yu Mengxue, Yang Anning, Liu Zhihong. Ferroptosis is involved in the pathogenesis of liver injury induced by high methionine diet in ApoE-/- mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(17): 2681-2686. |
| [7] | Zhang Haolin, Wang Yalin, Liu Yafei, Zuo Yanping, Zhang Xiaohuan. Effect of maxillary protraction on temporomandibular joint changes in skeletal class III children: a correlation analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(11): 1641-1646. |
| [8] | Wu Liang, Wang Qiang, Wang Wenbo, Xin Tianwen, Xi Kun, Tang Jincheng, Xu Jingzhi, Chen Liang, Gu Yong. Risk factors for traumatic central cord syndrome underlying with cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1388-1394. |
| [9] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [10] | Chen Jiming, Wu Xiaojing, Liu Tianfeng, Chen Haicong, Huang Chengshuo. Effects of silymarin on liver injury and bone metabolism induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1224-1228. |
| [11] | Zhou Yuanbo, Huang Wenliang, Wang Jindong. Imaging analysis of the correlation between tibial tuberosity-trochlea groove distance and femoral trochlea morphology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(27): 4390-4394. |
| [12] | Jiang Lihong, Wu Xiaofeng, Ouyang Lin, Luo Aifang, Huang Li. Computer aided diagnosis of lumbar disc degeneration based on metabolomics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3796-3803. |
| [13] | Ma Minghe, Niu Yi . Thymosin alpha1 protects against liver injury in rats with zymosan-induced multiple organ failure [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1753-1758. |
| [14] | Wan Huazhe, Chai Guangxin, Xiao Xiaoling, Huang Wenying. Effects of phellinus igniarius crude polysaccharides on sporting ability and free radical metabolism of skeletal muscle in mice suffering passive smoking [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 689-693. |
| [15] | Lin Yuan, Xu Bin, Tu Jun, Xu Honggang, Guo Ruipeng. Effect of different femoral tunnel locations on patellofemoral joint during single-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(14): 2140-2146. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||