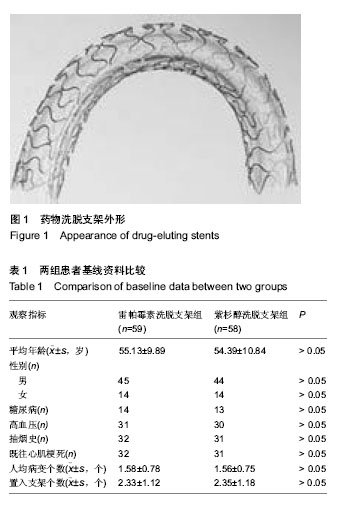
| [1] 尹栋,窦克非,杨跃进,等.冠状动脉慢性完全闭塞病变置入FIREBIRD雷帕霉素洗脱支架和TAXUS紫杉醇洗脱支架长期有效性及安全性观察[J].中国循环杂志,2013,28(3):172-175.
[2] 彭育红,汝磊生,王冬梅,等.国产无聚合物紫杉醇微孔载药支架与雷帕霉素涂层支架对比治疗急性心肌梗死[J].介入放射学杂志, 2013,22(6):458-460.
[3] 郑心田,陈康寅,RHA Seung-Woon,等.不同药物洗脱支架在冠状动脉弥漫性长病变中的2年随访结果比较[J].中国介入心脏病学杂志,2013,21(6):354-357.
[4] 尹栋,窦克非,杨跃进,等.冠状动脉长病变患者置入雷帕霉素洗脱支架和紫杉醇洗脱支架2年临床观察[J].中国介入心脏病学杂志, 2013,21(1):12-16.
[5] 宁尚秋,刘文娴,杨鲲,等.雷帕霉素洗脱支架与紫杉醇洗脱支架在急性心肌梗死直接经皮冠状动脉介入治疗中的疗效比较[J].临床荟萃,2012,27(8):660-663.8:55 2015-4-3
[6] 胡琦,江洪,徐昌武,等.雷帕霉素药物洗脱支架与紫杉醇药物洗脱支架治疗冠心病疗效的Meta分析[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2012,04(3):199-203.
[7] Sethi A, Bahekar A, Bhuriya R, et al.Drug-eluting stents versus bare metal stents in ST elevation myocardial infarction at a follow-up of three years or longer: A meta-analysis of randomized trials.Exp Clin Cardiol.2012;17(4):169-174.
[8] 张兰,刘干,钟金鹏,等.国产无聚合物紫杉醇涂层支架和可降解聚合物雷帕霉素涂层支架治疗冠心病疗效评价[J].临床心血管病杂志,2011,27(7):494-498.
[9] 孙奡燕,张景轩,葛华,等.国产生物可降解聚合物支架与进口永久聚合物支架在冠状动脉血运重建中的对比[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(42):7965-7968.
[10] 丁雪燕,刘夙璇,秦永文,等.冠状动脉西罗莫司洗脱支架植入术后晚期及超晚期支架内血栓形成的临床研究[J].介入放射学杂志, 2012,21(12):1023-1027.
[11] 陈佳慧,沈雳,王齐兵,等.冠状动脉生物可降解支架设计与应用:材料学的进一步革新将带来什么?[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(30):4878-4888.
[12] 耿学斌,李莉,田美蓉,等.冠状动脉长病变时应用进口及国产雷帕霉素涂层支架的比较:冠状动脉造影随访评估心血管管腔内的变化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(4):611-614.
[13] 张良,周胜华,刘启明,等.急性心肌梗死患者冠状动脉药物支架置入后血清胱抑素C水平:对心血管事件及靶血管病变的预测价值[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(13):2403-2406.
[14] 王哲颖,刘同库.雷帕霉素洗脱支架治疗无保护冠状动脉左主干严重狭窄性病变的安全性和远期效果研究[J].中国全科医学, 2013,16(27):3192-3195.
[15] 李雪峰,徐晶,游陆,等.雷帕霉素洗脱支架和紫杉醇洗脱支架置入在冠状动脉病变治疗中的生物安全性:2年随访[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(30):5807-5810.
[16] 张艳,李乐雯,钟书辉,等.冠状动脉支架涂层材料对置入后发生血管再狭窄的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(34): 6405-6408.
[17] 罗康华,许向东.冠状动脉支架表面涂层材料对置入效果的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(42):7927-7930.
[18] 曾伟杰,支峭原.药物缓释涂层支架的材料学特点及其生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(42):7903-7906.
[19] 佟子川,张建军,魏妤,等.不同类型药物洗脱支架介入治疗对血清C反应蛋白和白细胞介素-6水平的影响[J].临床心血管病杂志, 2010,26(10):766-769.
[20] Jang SI,Kim JH,Kim M,et al.Porcine feasibility and safety study of a new paclitaxel-eluting biliary stent with a Pluronic-containing membrane. Endoscopy. 2012;44(9): 825-831.
[21] 谢勉,党群.紫杉醇微孔载药支架在非ST段抬高急性冠脉综合征介入治疗中的应用研究[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2011,20(13): 1566-1568.
[22] 高展,杨跃进,陈纪林,等.国产雷帕霉素洗脱支架和进口紫杉醇洗脱支架的3年临床随访[J].中华医学杂志,2008,88(26): 1811-1814.
[23] Arroyave JC,Cepeda MC.Caracterización de la restenosis de stents coronarios convencionalesy liberadores de medicamentos en pacientes incluidos en el registro DRug Eluting STent (DREST)/ Characterization of conventional coronary stents restenosis and drug eluting stents in patients included in the Drug Eluting Stent. Rev Colomb Cardiol. 2012; 19(3):121-131.
[24] 候国梁,任长杰.紫杉醇微孔载药冠状动脉支架治疗老年急性冠脉综合征疗效及安全性的临床研究[J].济宁医学院学报,2012, 35(1):24-26,30.
[25] 谢洪智,方全,张抒扬,等.冠状动脉长病变串联置入雷帕霉素和紫杉醇洗脱支架重叠部分对分支血管影响的比较[J].中华心血管病杂志,2008,36(6):497-500.
[26] 庞新权,郭鑫,魏天辉,等.置入心血管支架后冠状动脉粥样硬化性心脏病患者的C-反应蛋白变化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(4):706-709.
[27] 毛幼林,袁义强,于力,等.国产雷帕霉素支架和进口紫杉醇支架治疗急性心肌梗死的对比研究[J].中国综合临床,2010,26(8): 828-830.
[28] 孙梦涵.无聚合物涂层紫杉醇药物支架与聚合物涂层雷帕霉素药物支架在急性心肌梗死患者中的远期疗效比较[D].大连医科大学,2012.
[29] 周旭晨,曾定尹,关启刚,等.雷帕霉素与紫杉醇药物洗脱支架对小型猪早期冠状动脉炎症性狭窄治疗的定量冠状动脉造影研究[J].中国循环杂志,2006,21(4):262-265.
[30] 陈纪林,高润霖,杨跃进,等.雷帕霉素和紫杉醇药物洗脱支架治疗冠心病复杂病变的临床近远期疗效比较[J].中华医学杂志,2005, 85(31):2183-2186.
[31] 王书林.紫杉醇微盲孔载药支架与雷帕霉素涂层支架在STEMI直接经皮冠状动脉介入治疗中应用的对比研究[D].天津医科大学,2011.
[32] 郭素峡,羊镇宇,王如兴,等.不同支架植入方式对小血管支架内再狭窄的影响[C].//全国第十二届心脏学会第十五届心功能学会和《心脏杂志》编委会联合学术会议论文集.2011:786-789.
[33] 宁尚秋,刘文娴,韩静,等.不同药物洗脱支架治疗老年急性心肌梗死疗效观察[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2012,26(6):531-533.
[34] 陈纪林,高润霖,杨跃进,等.雷帕霉素和紫杉醇药物洗脱支架在冠心病复杂病变中的临床近远期疗效的比较[J].医学研究通讯, 2005,34(9):14-16.
[35] 胡喜田,李子莉,薛铮,等.支架影像增强显影技术在冠状动脉置入支架可视性及球囊后扩张必要性评价中的应用[J].山东医药, 2013,53(43):52-53.
[36] 郭小超,邱建星,蒋学祥,等.64层CT高清模式扫描对冠状动脉支架的评估价值——与传统64层CT的对照研究[J].放射学实践, 2013,28(2):163-167.
[37] Chen JL,Gao LJ,Yang YJ,et al.Comparison of the incidence of late stent thrombosis after implantation of different drug-eluting stents in the real world coronary heart disease patients:three-year follow-up results.Chin Med J(Engl). 2010;123(7):778-781.
[38] Atary JZ,van der Hoeven BL,Liem SS,et al.Three-year outcome of sirolimus-eluting versus bare-metal stents for the treatment of ST-segment elevationmyocardialinfaretion(from the MISSION[Intervention Study).Am J Cardiol.2010; 106(1):4-12.
[39] Violini R,Musto C,de Fellce F,et al.Maintenance of long-term clinical benefit with sirolimus-eluting stents in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction 3-year results of the SESAMI (sirolimus-eluting stent versus bare-metal stent in acute myocardial infarction) trial.J Am CoIl Cardiol.2010; 55(8):810-814. |