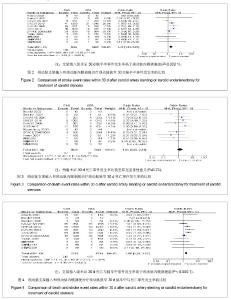
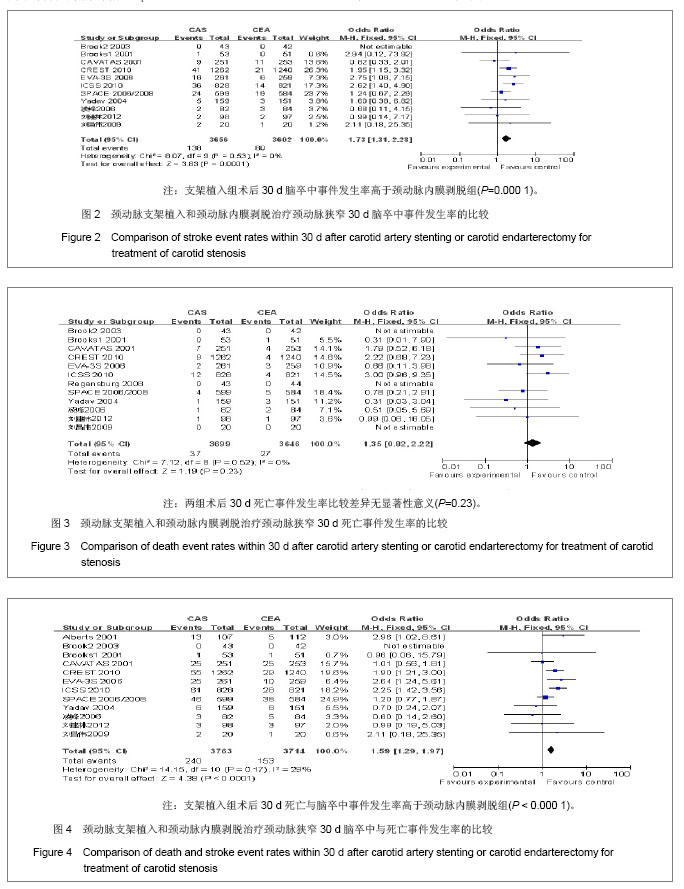
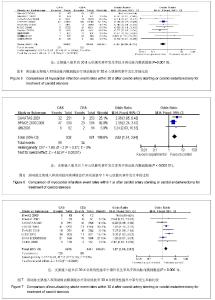
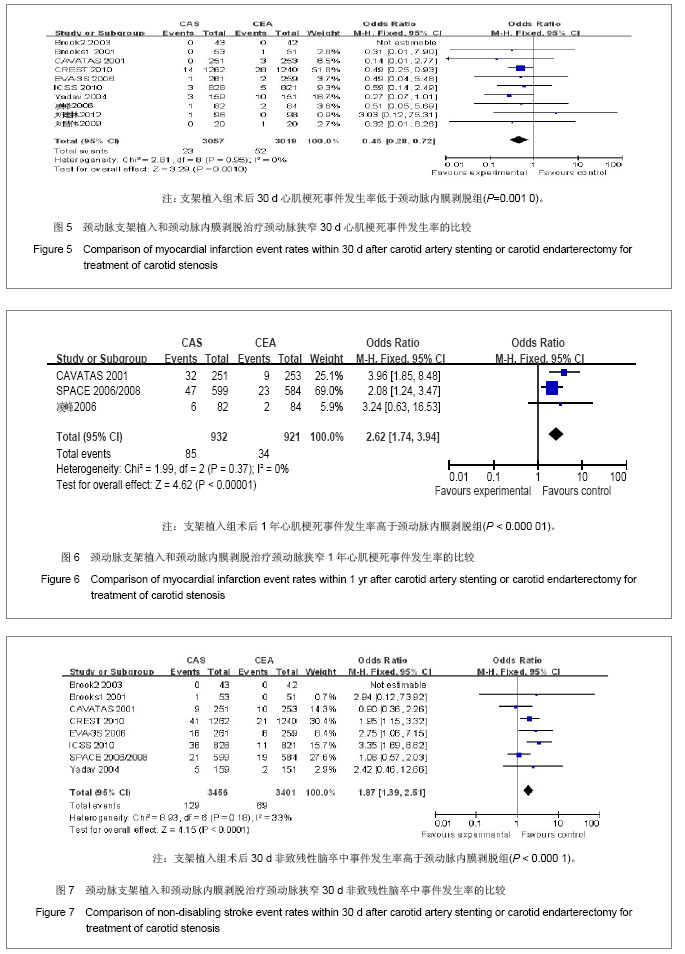
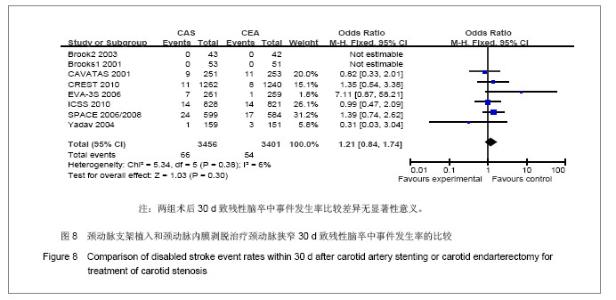
| [1]Brooks WH,McClure RR,Jones MR,et al.Carotid angioplasty and stenting versus carotid endarterectomy: randomized trial in a community hospital.J Am Coll Cardiol.2001;38(6): 1589- 1595.[2]CAVATAS investigators.Endovascular versus surgical treatment in patients with carotid stenosis in the Carotid and Vertebral Artery Transluminal Angioplasty Study (CAVATAS):a randomised trial.Lancet.2001;357(2):1729-1737.[3]Alberts MJ.Results of a Multicenter Prospective Randomized Trial of Carotid Artery Stenting vs.Carotid Endarterectomy. Stroke.2001;32(1):325-d.[4]Brooks WH,McClure RR,Jones MR,et al.Carotid angioplasty and stenting versus carotid endarterectomy for treatment of asymptomatic carotid stenosis: a randomized trial in a community hospital.Neurosurgery.2003;54(2):318-325.[5]Yadav JS,Wholey MH,Kuntz RE,et al.Protected carotid-artery stenting versus endarterectomy in high-risk patients.N EnglJ Med.2004;315(15):1493-1501.[6]Mas JL,Chatellier G,Beyssen B,et al.Endarterectomy versus stenting in patients with symptomatic severe carotid stenosis. N EnglJ Med.2006;355(16):1660-1671.[7]SPACE Collaborative Group,Ringleb PA,Allenberg J,et al.30 day results from the SPACE trial of stent-protected angioplasty versus carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic patients:a randomised non-inferiority trial.Lancet.2006; 368 (7):1239-1247.[8]凌峰,焦力群.颈动脉内膜剥脱术与支架成形术对颈动脉粥样硬化性狭窄治疗的初步研究[J].中国脑血管病杂志,2006,3(1):4-8.[9]Steinbauer MG,Pfister K,Greindl M,et al.Alert for increased long-term follow-up after carotid artery stenting: Results of a prospective,randomized, single-center trial of carotid artery stenting vs carotid endarterectomy.J Vasc Surg.2008;48(1): 93-98.[10]Eckstein HH,Ringleb P,Allenberg JR,et al.Results of the Stent-Protected Angioplasty versus Carotid Endarterectomy (SPACE) study to treat symptomatic stenoses at 2 years: a multinational, prospective,randomised trial.Lancet.2008; 7(10): 893-902.[11]刘昌伟,刘暴,叶炜,等.颈动脉内膜剥脱术和颈动脉支架的前瞻性随机对照研究[J].中华外科杂志,2009,47(4):267-270.[12]International Carotid Stenting Study investigators,Ederle J,Dobson J,et al.Carotid artery stenting compared with endarterectomy in patients with symptomatic carotid stenosis (International Carotid Stenting Study): an interim analysis of a randomised controlled trial.Lancet.2010;375(9719):985-997.[13]Brott TG,Hobson RW 2nd,Howard G,et al.Stenting versus endarterectomy for treatment of carotid-artery stenosis.N Engl J Med.2010;363(1):11-23.[14]刘建林,杨林,马强,等.颈动脉内膜切除与支架置入治疗症状性颈动脉狭窄的疗效比较[J].中华神经外科杂志,2012,28(4): 382-385. [15]Gahremanpour A,Perin EC,Silva G.Carotid artery stenting versus endarterectomy: a systematic review.Tex Heart Inst J.2012;39(4):474-487.[16]Naylor AR,Bolia A,Abbott RJ,et al.Randomized study of carotid angioplasty and stenting versus carotid endarterectomy: A stopped trial,J Vasc Surg.1998;28: 326-334.[17]刘昌伟.颈动脉内膜剥脱术和颈动脉支架的客观评述[J].临床外科杂志,2009,17(5):291-292.[18]张勤奕.颈动脉内膜剥脱术与颈动脉支架成形术的优劣比较[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2009,11(9):651-652.[19]缪中荣.颈动脉狭窄的血管成形和支架置入术[J].中华脑血管病杂志:电子版,2007,1(1):41-44.[20]苏克江.颈动脉狭窄患者的卒中预防内膜切除术,支架置入血管成形术,还是最佳的药物治疗? [J].国际脑血管病杂志,2009, 17(5):393-399.[21]Hoffmann A,Engelter S,Taschner C,et al.Carotid artery stenting versus carotid endarterectomy-a prospective randomized controlled single-centre trial with long-term follow-up (BACASS).Schweiz Arch Neurol Psychiatr.2008; 159:84-89.[22]关敏,王晓白,刘小亚.颈动脉狭窄患者内膜剥脱术与支架植入术1年疗效Meta分析[J].中国介入影像与治疗学,2011,8(1):37-41.[23]刘庆国,周宁,宋志斌,等.颈动脉支架与内膜切除术治疗颈动脉狭窄的疗效和安全性的META分析[J].中华老年医学杂志,2011, 30(5):369-373. |