Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (49): 8608-8614.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.49.023
Previous Articles Next Articles
Induced pluripotent stem cells and cell reprogramming technologies
Zhao Xing1, 2, Huang Yuan-hua1, Ma Yan-lin1
- 1Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, Haikou 570102, Hainan Province, China
2First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
-
Revised:2013-09-28Online:2013-12-03Published:2013-12-03 -
Contact:Ma Yan-lin, M.D., Associate professor, Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, Haikou 570102, Hainan Province, China mayanlinma@hotmail.com -
About author:Zhao Xing★, Studying for master’s degree, Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, Haikou 570102, Hainan Province, China; First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China 1602830576@qq.com -
Supported by:the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program), No. 2012CB966502*; Key International Cooperation Program of Science and Technology Department of Hainan Province, No. GJXM20100004*, GJXM201106*; Merit-funded Scientific Research Projects for the Overseas Students in 2011, Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security of China, No. 201150804*; Natural Science Foundation of Hainan Province, No. 812185*; Key Science and Technology Plan Program of Haikou City, No. 2012078*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhao Xing, Huang Yuan-hua, Ma Yan-lin. Induced pluripotent stem cells and cell reprogramming technologies[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(49): 8608-8614.
share this article
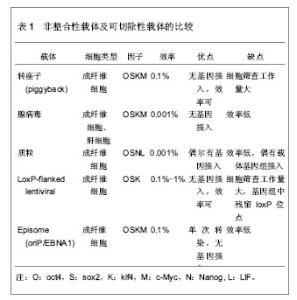
2.1 诱导多能干细胞与细胞重编程 2.1.1 诱导多能干细胞 细胞的胞质环境和核质环境决定了不同基因的表达,而不同基因的表达又决定了胞质环境和核质环境,这是细胞按照自身命运分化形成终末细胞的基础。因此,通过调控细胞的基因表达,改变胞质环境和核质环境,有可能使细胞命运发生改变,将其重编程为全能干细胞。 Wilmut等[3]将体细胞的细胞核移入去核的MII卵母细胞中,使其恢复全能性,发育成囊胚,移植入代孕母羊后,诞生了克隆羊。Wakayama等[2]通过体细胞核移植技术,建立了体细胞来源的胚胎干细胞株。Cowan等[4]通过细胞融合技术,得到体细胞与胚胎干细胞的杂交细胞,这种四倍体细胞具备胚胎干细胞的特性。这提示,卵母细胞和胚胎干细胞中存在某些因子,能赋予体细胞全能性。研究发现,Oct3/4、Sox2、Nanog等对早期胚胎和胚胎干细胞全能性的维持极为重要[5-7]。此外,某些原癌基因在维持胚胎干细胞不分化和快速增殖中起着重要作用,如Stat3、c-Myc、Klf4等基因[8-10]。Takahashi等[11]通过筛选24个候选基因,选择了4因子Oct3/4、Sox2、c-Myc和Klf4,以反转录病毒为载体将其导入小鼠胚胎成纤维细胞,使体细胞重新获得全能特性,重编程为诱导多能干细胞。诱导多能干细胞与胚胎干细胞相似:克隆边界清楚、细胞核质比高、能无限增殖并维持不分化状态、具备向3个胚层分化的潜能。重编程技术无需经过胚胎阶段,即可使体细胞重编程进入全能干细胞状态,为细胞再生技术走向临床治疗奠定了基础。 2.1.2 重编程的基本原理 几乎生物体的每一个细胞都具有该物种的全套遗传物质,具备发育成完整个体的全部基因,而不同的基因表达模式是形成各种功能细胞的基础。将Oct3/4、Sox2、c-Myc和Klf4导入体细胞,其中Oct43/4双重调控下游基因的表达:抑制一些促使细胞发生分化的基因表达,同时激活有助于维持细胞多能性的基因的表达。它就像一种开关,控制着多能干细胞在自我复制和分化两种命运之间的转变[12]。在其他因子的协同作用下,基因表达模式进入多能干细胞的模式。此外,细胞核的重编程与表观遗传修饰的改变密切相关。组蛋白修饰、DNA甲基化、染色质重塑等表观遗传因素调控着基因的表达。Doege等[13]发现,在重编程早期,两种表观遗传调控因子Parp1和Tet2被募集到多能性基因位点上,使多能性基因处于激活的染色质状态,便于重编程因子接近多能性基因,诱导多能性基因的转录。Wang等[14]发现vitamin C能促进小鼠和人诱导多能干细胞的形成,进一步研究表明vitamin C是通过促进组蛋白去甲基化酶Jhdm1a/1b的作用实现的。可见,表观遗传修饰在重编程中起着重要作用。 尽管诱导多能干细胞与胚胎干细胞相似,但两者在多个方面存在差异。研究表明,诱导多能干细胞和胚胎干细胞在染色体畸变、拷贝数变异等方面存在差异[15-16]。突变可能源自体外培养环境的改变,或是重编程技术本身,也可能来自体细胞遗留下来的突变。在表观遗传水平,诱导多能干细胞和胚胎干细胞也存在差异[11]。来自体细胞的表观遗传记忆可能影响着诱导多能干细胞的分化潜能,例如,胚胎干细胞和来源于骨髓的造血前体细胞能分化成B细胞,然而B细胞来源的诱导多能干细胞却抵抗向B细胞分化[17-19]。 尽管诱导多能干细胞具有广泛的应用前景,但目前,诱导多能干细胞的临床应用仍存在技术瓶颈,如合适的细胞来源、效率低、安全问题等等。近些年,随着对干细胞多能性和重编程机制的研究深入,重编程技术有了快速发展,在此,文章将从以下5个方面论述重编程的研究进展。 2.2 细胞重编程技术的进展 2.2.1 选择合适的体细胞来源 不同类型的细胞,其基因表达模式不同,细胞环境不同,分化潜能不同,对重编程的反应不同,重编程的效率也就不同。有必要寻求一种合适的、效率比较高的体细胞,并比较不同体细胞来源诱导多能干细胞之间的差异。 继Wakayama等[2]通过转基因技术将小鼠胚胎成纤维细胞重编程为诱导多能干细胞之后,研究者尝试以角质细胞、脐带基质细胞、羊膜间充质细胞、外周血(成熟B细胞、单个核细胞)、脐带血(CD34+细胞)、羊水细胞、胰腺β细胞、神经干细胞、尿细胞等为细胞来源[20-29],将其重编程为诱导多能干细胞。其中Zhou等[30]从尿液中提取脱落的肾小管上皮细胞(即尿细胞),并将其重编程为诱导多能干细胞,尿细胞来源丰富,取材简单无创,遗传背景稳定。Niibe等[31]认为应用成体干细胞建立诱导多能干细胞的效率和质量更高,如间充质干细胞,鼠肌肉组织的干细胞(星形细胞和间充质前体细胞)等。然而,成体干细胞来源有限,使其不能广泛地用于诱导多能干细胞的重编程。 理想的体细胞来源,一方面要求重编程效率高,遗传背景稳定,另一方面要求取材容易,不受年龄、性别、身体条件限制,不存在伦理争议。 不同细胞来源的诱导多能干细胞在分化潜能上存在差异。研究表明,与成纤维细胞或神经前体细胞来源的诱导多能干细胞相比,小鼠骨髓来源和B细胞来源的诱导多能干细胞能更能有效地向造血干细胞系分化[19]。诱导多能干细胞可能保留了体细胞的表观遗传记忆并累积了一些体细胞的突变[16,32-33]。这种残留的表观遗传记忆,可能使不同组织来源的诱导多能干细胞在分化潜能上存在偏倚。这种分化潜能的倾向性可能有助于诱导多能干细胞定向分化成特定的功能细胞。 2.2.2 载体的改进 研究早期常以反转录病毒、慢病毒等作为载体[11,34],但是,这些载体导入的转基因将永久存在于靶细胞的基因组中,可能引起插入型突变。这限制了诱导多能干细胞和重编程技术在临床治疗中的应用。为克服这一局限性,研究者主要从3个分子水平探索载体的优化:①DNA水平:以非整合性载体或者可切除载体取代整合性载体,例如,转座子(piggyBac)、腺病毒载体、episome、质粒、LoxP-flanked慢病毒等[35-39]。其中可切除的载体在切除后还需要进行大量筛查,检测其切除效果。这些载体的重编程效率各不相同,各有优劣,见表1。②RNA水平:Warren等[40]通过非病毒方法,将体外转录的mRNA(编码Oct4、Sox2、Klf4和c-Myc)导入成纤维细胞,以1%-4.4%的效率获得人诱导多能干细胞,但是,技术相对复杂,需要多次转染,1次/d,周期长达17 d,这导致大量细胞死亡。Geertrui等[41]利用阳离子脂质体,将OSKM 4种因子导入小鼠胚胎成纤维细胞,获得诱导多能干细胞,只需转染两三次,简化了实验技术,然而脂质体存在一定的毒性。③蛋白质水平:Kim等[42]利用细胞穿透肽将4种重编程蛋白Oct4、Sox2、Klf4和c-Myc直接导入人肾成纤维细胞,获得诱导多能干细胞,这种蛋白质转导系统克服了由DNA转染引起的插入型突变。但是,这种方法重编程速度非常慢,效率很低,约0.001%,而且还需要大量高纯度的蛋白质。寻找一种的合适的载体是解决诱导多能干细胞安全问题的关键。"
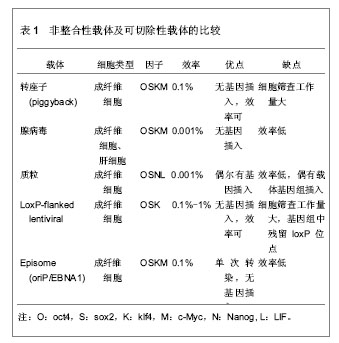
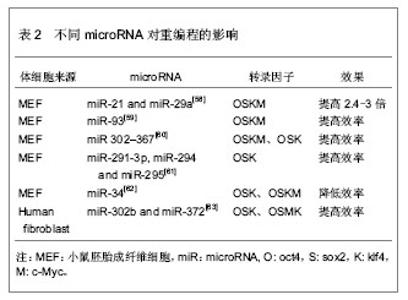
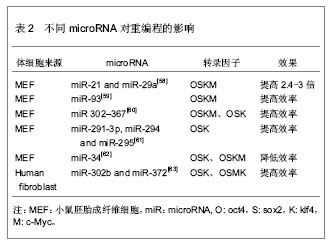
2.2.3 转录因子的不同组合 经典的重编程技术是以病毒为载体将OSKM导入小鼠成纤维细胞,获得诱导多能干细胞[11]。该重编程体系中c-Myc是原癌基因,该基因的导入及过度表达,可能使细胞发生肿瘤化,用于临床存在安全问题。此外,诱导多能干细胞和胚胎干细胞在全基因表达模式和DNA甲基化状态上并不完全相同,这表明其重编程可能不够彻底,可能存在某些重要的因子未被发现,有必要探索新的转录因子和尝试不同的组合,以提高重编程的安全性和效率。 某些新的转录因子可以代替经典的重编程因子,使体细胞重编程为诱导多能干细胞,甚至能提高重编程效率。Yu等[34]选择Oct4、Sox2、Nanog和Lin284种因子(简称OSNL),将人成纤维细胞重编程为人诱导多能干细胞,Lin28和Nanog可以提高早期重编程细胞的存活率及克隆形成率。Maekawa等[43]发现转录因子Glis1与OSK共表达于小鼠和人成纤维细胞时,可获得诱导多能干细胞,并能明显促进诱导多能干细胞的形成。Moon等[44]采用两步法重编程诱导多能干细胞,首先转导分化抑制蛋白家族Id3,使小鼠胚胎成纤维细胞转分化,获得似神经干细胞,再转导Oct4,使其重编程为诱导多能干细胞。 对某些成体干细胞进行重编程,可以减少转录因子,简化重编程技术。Lyssiotis等[45]以神经干细胞为靶细胞,导入OctT3/4和Klf4基因,成功获得了诱导多能干细胞,而Kim等[46]仅将Oct4导入神经干细胞即可获得诱导多能干细胞。 随着对多能性机制的深入研究,发现更多的多能性和分化相关因子,这些因子可能用于重编程,优化重编程技术。 2.2.4 信号转导通路与重编程 胚胎干细胞之所以能维持其多能性,主要依赖于某些外源性信号分子的作用和某些内源性转录因子的表达。信号转导通路是联系外源性信号和内源性转录因子的重要途径。例如,LIF与其受体结合后,活化JAK-STAT通路,进一步激活一系列目标基因的表达,以维持干细胞的自我更新与多能性[47]。骨形态发生蛋白4抑制转化生长因子β受体,通过激活SMAD家族的转录因子,进一步激活下游基因,或者通过抑制P38-MAPK途径,实现其调控功能[48-49]。Wnt家族作用于受体,抑制GSK-3活性,使β-catenin在核内累积,调控靶基因的表达[50]。MAPK-ERK1/2通过依次磷酸化调控下游转录因子的作用,进而调控基因表达[51]。这些信号转导通路在早期胚胎发育中起着重要作用,涉及细胞命运决定、多能性、细胞分化等。 最近研究发现,在重编程体系中加入某些小分子化合物,通过抑制或激活某些信号转导通路,可以明显提高重编程效率。例如Zhang等[52]在重编程体系中加入丁酸钠、SB431542和PD0325901三种小分子化学物,分别抑制组蛋白去乙酰化酶(HDAC)、转化生长因子β受体、ERK,将成纤维细胞重编程为诱导多能干细胞,该方法不仅快速,而且明显减少不完全重编程的诱导多能干克隆,效率为0.93%左右。Shimada等[53]将5种抑制剂加入重编程体系,首次转导后第6天就出现胚胎干样细胞,第10天出现完全重编程的干细胞,加快了重编程的进程。其中,A83-01、CHIR99021、PD0325901分别作用于转化生长因子β受体、GSK-3、ERK1/2,分别抑制SMAD、WNT、MAPK-ERK 3条信号转导通路,丁酸钠通过抑制组蛋白去乙酰化酶,促进了DNA的去甲基化,Y-27632抑制 ROCK通路,通过阻止诱导多能干细胞发生凋亡,提高诱导多能干细胞的存活率。值得一提的是,这些抑制剂需要及时的去除,否则将导致诱导多能干细胞分化。当某些分化相关通路受到抑制时,另一些通路可能被过度激活,最终导致分化的发生。其具体机制有待进一步研究。 2.2.5 MicroRNA的调控作用 MicroRNA是一类分布广泛、进化上高度保守的小分子非编码RNA,长度约为22个核苷酸,具有转录后调控基因表达的功能。它在炎症、代谢、肿瘤、细胞衰老、细胞分化及胚胎发育中起着重要作用。它的表达具有时空特异性和组织特异性。胚胎干细胞表达一套独特的、细胞快速增殖和周期进展相关的microRNA[54-57]。近年来,科学家尝试联合microRNA和转录因子共同诱导体细胞重编程。 主要研究见表2。"
| [1] Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 1998; 282(5391): 1145-1147.[2] Wakayama T, Tabar V, Rodriguez I, et al. Differentiation of embryonic stem cell lines generated from adult somatic cells by nuclear transfer. Science. 2001; 292(5517): 740-743.[3] Wilmut I, Schnieke AE, McWhir J, et al. Viable offspring derived from fetal and adult mammalian cells. Nature. 1997; 385 (6619):810-813.[4] Cowan CA, Atienza J, Melton DA, et al. Nuclear reprogramming of somatic cells after fusion with human embryonic stem cells. Science. 2005; 309(5739): 1369-1373.[5] Nichols J, Zevnik B, Anastassiadis K, et al. Formation of pluripotent stem cells in the mammalian embryo depends on the POU transcription factor Oct4. Cell. 1998; 95(3): 379-391.[6] Avilion AA, Nicolis SK, Pevny LH, et al. Multipotent cell lineages in early mouse development depend on SOX2 function. Genes Dev. 2003; 17(1): 126-140.[7] Chambers I, Colby D, Robertson M, et al. Functional expression cloning of Nanog, a pluripotency sustaining factor in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2003;113(5):643-655.[8] Matsuda T, Nakamura T, Nakao K, et al. STAT3 activation is sufficient to maintain an undifferentiated state of mouse embryonic stem cells. EMBO J. 1999;18(15):4261-4269.[9] Cartwright P, McLean C, Sheppard A, et al. LIF/STAT3 controls ES cell self-renewal and pluripotency by a Myc-dependent mechanism. Development. 2005; 132(5): 885-896.[10] Li Y, McClintick J, Zhong L, et al. Murine embryonic stem cell differentiation is promoted by SOCS-3 and inhibited by the zinc finger transcription factor Klf4. Blood. 2005; 105(2): 635-637.[11] Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006; 126(4): 663-676. [12] 潘光锦,裴端卿.维持胚胎干细胞多能性的分子机制[J].生命科学, 2007,19(4): 372-377.[13] Doege CA, Inoue K, Yamashita T, et al. Early-stage epigenetic modification during somatic cell reprogramming by Parp1 and Tet2. Nature. 2012;488(7413):652- 655.[14] Wang T, Chen K, Zeng X, et al. The Histone Demethylases Jhdm1a/1b Enhance Somatic Cell Reprogramming in an Vitamin-C-Dependent Manner. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;9(6): 575-587.[15] Ben-David U, Mayshar Y, Benvenisty N. Large-scale analysis reveals acquisition of lineage-specific chromosomal aberrations in human adult stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2011; 9(2): 97-102 .[16] Hussein SM, Batada NN, Vuoristo S, et al. Copy number variation and selection during reprogramming to pluripotency. Nature. 2011; 471(7336): 58-62. [17] Nakano T. Lymphohematopoietic development from embryonic stem cells in vitro. Semin Immunol. 1995; 7(3): 197-203.[18] Cho SK, Webber TD, Carlyle JR, et al. Functional characterization of B lymphocytes generated in vitro from embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.1999; 96(17): 9797-9802.[19] Wada H, Kojo S, Kusama C, et al. Successful differentiation to T cells, but unsuccessful B-cell generation, from B-cell-derived induced pluripotent stem cells. Int Immunol. 2011; 23(1): 65-74.[20] Aasen T, Raya A, Barrero MJ, et al. Efficient and rapid generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from human keratinocytes. Nat Biotechnol. 2008; 26(11):1276-1284.[21] Cai J, ESteban MA, Pei D, et al. Generation of human induced pluripotent stem cells from umbilical cord matrix and amniotic membrane mesenchymal cells. J Biol Chem. 2010; 285(15): 11227-11234.[22] Hanna J, Markoulaki S, Schorderet P, et al. Direct reprogramming of terminally differentiated mature B lymphocytes to pluripotency. Cell. 2008; 133(2): 250-264.[23] Hu K, Yu J, Suknuntha K, et al. Efficient generation of transgene-free induced pluripotent stem cells from normal and neoplastic bone marrow and cord blood mononuclear cells. Blood. 2011; 117(14):e109-119.[24] Giorgetti A, Montserrat N, Aasen T, et al. Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from human cord blood using OCT4 and SOX2. Cell Stem Cell. 2009;5(4): 353-357.[25] Haase A, Olmer R, Schwanke K,et al. Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from human cord blood. Cell Stem Cell. 2009; 5(4): 434-441.[26] Raymond M, Anchan, Philipp Quaas, et al. Amniocytes can serve a dual function as a source of iPS cells and feeder layers. Hum Mol Genet. 2011; 20(5): 962-974.[27] Stadtfeld M, Brennand K, Hochedlinger K. Reprogramming of pancreatic beta cells into induced pluripotentstem cells. Current Biology. 2008; 18(12): 890-894.[28] Kim JB, Zaehres H, Wu G, et al. Pluripotent stem cells induced from adult neural stem cells by reprogramming with two factors. Nature. 2008; 454(7204): 646-650.[29] Tan KY, Eminli S, Hettmer S, et al. Efficient generation of iPS cells from skeletal muscle stem cells. PLoS One. 2011; 6(10):e26406. [30] Zhou T, Pei D, Esteban MA, et al. Generation of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells from Urine. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011; 22(7):1221-1228.[31] Niibe K, Kawamura Y, Araki D, et al. Purified mesenchymal stem cells are an efficient source for iPS cell induction. PLoS One. 2011;6(3):e17610.[32] Kim K, Doi A, Wen B, et al. Epigenetic memory in induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature. 2010; 467(7313): 285-290.[33] Gore A, Li Z, Fung HL,et al. Somatic coding mutations in human induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature. 2011; 471 (7336): 63-67.[34] Yu J, Vodyanik MA, Thomson JA, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science. 2007; 318(5858):1917-1920. [35] Woltjen K, Michael IP, Mohseni P, et al. PiggyBac transposition reprograms fibroblasts to induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature. 2009; 458(7239): 766-770.[36] Zhou W, Freed CR. Adenoviral gene delivery can reprogram human fibroblasts to induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells. 2009; 27(11): 2667-2674.[37] Mack AA, Kroboth S, Rajesh D,et al. Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from CD34+ cells across blood drawn from multiple donors with non-integrating episomal vectors. PLoS One. 2011; 6(11):e27956. [38] Si-Tayeb K, Noto FK, Duncan SA, et al. Generation of human induced pluripotent stem cells by simple transient transfection of plasmid DNA encoding reprogramming factors. BMC Dev. Biol. 2010; 10:81.[39] Somers A, Jean JC, Sommer CA, et al. Generation of transgene-free lung disease-specific human induced pluripotent stem cells using a single excisable lentiviral stem cell cassette. Stem Cells. 2010; 28(10): 1728-1740.[40] Warren L, Manos PD, Ahfeldt T, et al. Highly efficient reprogramming to pluripotency and directed differentiation of human cells with synthetic modified mRNA. Cell Stem Cell. 2010; 7(5): 618-630. [41] Geertrui T, Katharina W, Joseph D, et al. Activation of pluripotency-associated genES in mouse embryonic fibroblasts bynon-viral transfection with in vitro-derived mRNAs encoding Oct4, Sox2, Klf4 and c-Myc. Biomaterials. 2012; 33 (2): 412-417.[42] Kim D, Kim CH, Kim KS, et al. Generation of human induced pluripotent stem cells by direct delivery of reprogramming proteins. Cell Stem Cell. 2009; 4(6): 472-476.[43] Maekawa M, Yamaguchi K, Yamanaka S, et al. Direct reprogramming of somatic cells is promoted by maternal transcription factor Glis1. Nature. 2011; 474(7350): 225-229.[44] Moon JH, Heo JS, You S, et al. Two-step generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from mouse fibroblasts using Id3 and Oct4. J Mol Cell Biol. 2012; 4(1): 59-62.[45] Lyssiotis CA, Foreman RK, Staerk J, et al. Reprogramming of murine fibroblasts to induced pluripotent stem cells with chemical complementation of klf4. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009; 106(22): 8912-8917.[46] Kim JB, Zaehres H, Scholer HR, et al. Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from neural stem cells. Nat Protoc. 2009; 4(10): 1464-1470.[47] Dani C, Chambers I, Smith A, et al. Paracrine induction of stem cell renewal by LIF-deficient cells: a new ES cell regulatory pathway. Dev Biol, 1998, 203(1): 149-162.[48] Ying QL, Nichols I, Chambers I, et al. BMP induction of Id proteins suppresses differentiation and sustains embryonic stem cell self-renew in collaboration with Stats. Cell. 2003; 115(3): 281-292[49] Qi X, Li TG, Zhao GQ, et al. BMP4 supports self-renewal of embryonic stem cells by inhibiting mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004; 101(16): 6027-6032.[50] Paling NR, Wheadon H, Welham MJ, et al. Regulation of embryonic stem cell self-renewal by phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent signaling. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279(46): 48063-48070.[51] Kunath T, Meloche S, Smith A, et al. FGF stimulation of the Erk1/2 signalling cascade triggers transition of pluripotent embryonic stem cells from self-renewal to lineage commitment. Development. 2007; 134(16): 2895-2902. [52] Zhang Z, Gao Y, Wu WS, et al. Efficient Generation of Fully Reprogrammed Human iPS Cells via Polycistronic Retroviral Vector and a New Cocktail of Chemical Compounds. PloS One. 2011; 6(10): e26592.[53] Shimada H, Hashimoto Y, Nakada A, et al. Accelerated generation of human induced pluripotent stem cells with retroviral transduction and chemical inhibitors under physiological hypoxia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012; 417(2): 659-664.[54] Zhang B, Pan X, Anderson TA, et al. microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 2007; 302(1): 1-12.[55] Ying SY, Lin SL. Current perspectives in intronic micro RNAs (MiRNAs). J Biomed Sci. 2006; 13(1): 5-15.[56] Calin GA, Sevignani C, Croce CM, et al. Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004; 101(9) 2999-3004.[57] Lin SL, Chang DC, Ying SY, et al. Mir-302 reprograms human skin cancer cells into a pluripotent ES-cell-like state. RNA. 2008;14 (10) 2115-2124.[58] Yang CS, Li Z, Rana TM, et al. microRNAs modulate iPS cell generation. RNA. 2011; 17(8): 1451-1460.[59] Li Z, Yang CS, Rana TM, et al. Small RNA-mediated regulation of iPS cell generation. EMBO J. 2011; 30(5): 823-834.[60] Liao B, Esteban MA, Pei D, et al. MicroRNA Cluster 302-367 Enhances Somatic Cell Reprogramming by Accelerating a Mesenchymal-to-Epithelial Transition. J Biol Chem. 2011; 286(19): 17359-17364.[61] Judson RL, Babiarz JE, Venere M, et al. Embryonic stem cell specific microRNAs promote induced pluripotency. Nat Biotechnol. 2009; 27(5): 459-461. [62] Choi YJ, Lin CP, He L, et al. miR-34 miRNAs provide a barrier for somatic cell reprogramming. Nat Cell Biol. 2011; 13(11): 1153-1160.[63] Subramanyam D, Lamouille S, Blelloch R, et al. Multiple targets of miR-302 and miR-372 promote reprogramming of human fibroblasts to induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2011; 29(5): 443-448. [64] Miyoshi N, Ishii H, Mori M, et al. Reprogramming of Mouse and Human Cells to Pluripotency Using Mature MicroRNAs. Cell Stem Cell. 2011; 8(6): 633-638.[65] Gardlik R. Inducing pluripotency using in vivo gene therapy. Med Hypotheses. 2012; 79(2): 197-201. [66] Zhou Q, Brown J, Melton DA, et al. In vivo reprogramming of adult pancreatic exocrine cells to β-cells. Nature. 2008; 455 (7213): 627-632.[67] Islas JF, Liu Y, Schwartz RJ, et al. Transcription factors ETS2 and MESP1 transdifferentiate human dermal fibroblasts into cardiac progenitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012; 109(32): 13016-13021. |
| [1] | Fei Jing, Zheng Hongdi, Yu Liya, Li Leiji. Involvement of GDNF/PI3K/AKT pathway in promoting facial nerve regeneration using electroacupuncture in a rabbit model of facial nerve crush injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1094-1100. |
| [2] | Ren Chunmei, Liu Yufang, Xu Nuo, Shao Miaomiao, He Jianya, Li Xiaojie. Non-coding RNAs in human dental pulp stem cells: regulations and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1130-1137. |
| [3] | Peng Ya, Qin Yu, Yi Hongcheng, Gu Chunsong, Li Lili. Cytotoxicity assessment of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-cuttlebone composite scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 3943-3946. |
| [4] | Yuan Guoqiang, Qin Yongsheng, Peng Peng. High-intensity interval training for treating pathological cardiac hypertrophy in spontaneously hypertensive rats: effects and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3708-3715. |
| [5] | Han Mingli, Lü Pengwei, Qian Xueke, Yang Xue, Yang Yunqing, Gu Yuanting. MicroRNA-10b regulates aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 mRNA and protein expression in breast cancer MCF-7 cell line [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(9): 1349-1353. |
| [6] | Zhou Yanxing1, Peng Xinsheng2, Hou Gan1, Li Jiangbin1, Zhang Hua1, Zhou Zhikun2, Zhou Yanfang3 . Inhibitory effect of capsaicin on fibroblast proliferation and its molecular mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(7): 1018-1022. |
| [7] | Chen Qingui, Zeng Mian, He Wanmei, Zhang Lishan, Zheng Haichong. Knockdown of foxM1 strengthens osteogenic differentiation ability of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(5): 673-679. |
| [8] | Mai Liping, Yang Xiangyu, Wu Yueheng, He Guodong, Li Xiaohong. Expression of recombinant Nkx2.5 and its effect during human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells reprogramming into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(5): 685-690. |
| [9] | Feng Haipeng, Zheng Yifei, Zhou Ying, Li Zhilu, Sun Yan, Liu Kun, Zhang Ruizhu, Wang Qiaoyun, Meng Bo, Lin Bo, Li Mengsen. Inhibition of GATA5 expression in HELA cells promotes expression of sox2, c-myc and CD44 in HELA cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(5): 710-715. |
| [10] | Liu Junyin, Feng Wei, Xie Yingchun, Li Yuwan, Zeng Jitao, Liu Ziming, Tu Xiaolin. Bone morphologic protein signaling pathway in bone regeneration and repair: accurate regulation and treatment targets [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 606-612. |
| [11] | Gao Hongqiang, Liu Jing, Li Zhiqiang, Wang Hailei, Zhao Xiongqi, Zhang Shengning, Ran Jianghua, Li Li . Ulinastatin improves rat liver metabolism after reduced-size liver transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 435-440. |
| [12] | Chen Deping1, Liu Shengze1, Chen Shi1, Cong Changchun2, Liu Shuyi3, Xiao Ying4 . Effect of nerve growth factor-beta on proliferation of intraspinal schwannomas [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2373-2379. |
| [13] | Deng Guiying1, 2, Zeng Gaofeng3, Cen Zhongxi1, Gao Yunbing1, Cao Baichuan1, Huang Jianhua1, Zong Shaohui1 . Effect of miRNA-136-5p on inflammatory factors in rat models of acute spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2397-2402. |
| [14] | Gong Hewei, Liu Chengwei, Liang Bingsheng, Li Gang. Lentiviral vector-mediated overexpression of miRNA-1 in L6 myoblasts: cell proliferation, differentiation and histone deacetylase expression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(13): 2075-2080. |
| [15] | Qi Minjun, Wu Xiaopeng, Zhou Zhongxing, Jiang Xiaodong. miR-142-3p effect on the stemness of bladder cancer stem cells via regulation of S1PR3 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(13): 2028-2034. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||