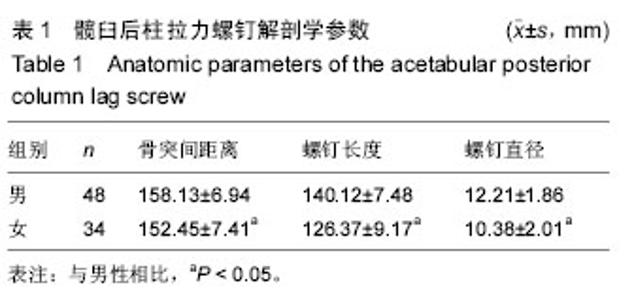
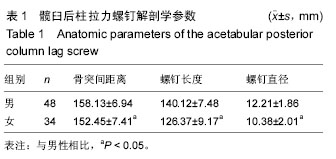
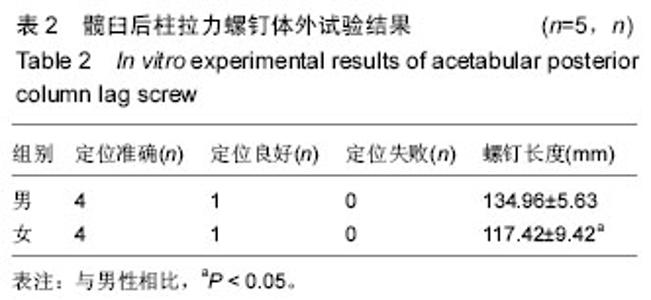
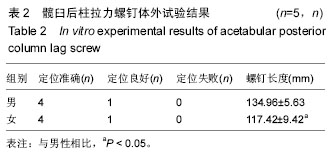
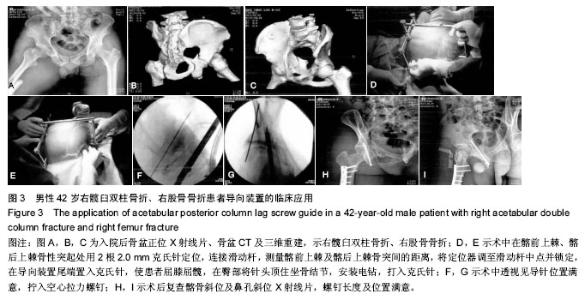
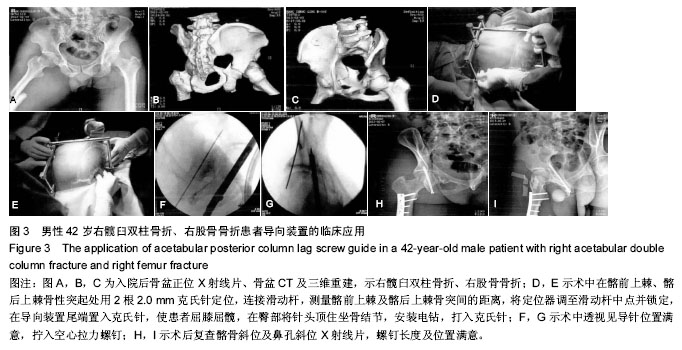
| [1] Ghalambor N, Matta JM, Bernstein L. Heterotopic ossification following operative treatment of acetabular fractureiAn analysis of risk factors. Clin Orthop.2012; (305):96-101.[2] Moed BR, Maxey JW. The effect of indomethacin on heterotopic ossification following acetabular fracture surgery. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;7(1):33-37.[3] Zhu SW, Wang MY,Wu XB,et al. Complications of operativetreatment of acetabular fractures. J Chin Exp Surg. 2013;41(5): 342-345.[4] Lin YC,Chen CH,Huang HT,et al.Pereutaneous antegrade screwing for anterior column fracture of acetabulum with fluoroscopic-based computerized navigation.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;128(2): 223-226.[5] Heeg M,Klasen HJ,Visser JD. Operative treatment for acetabular fractures. J Bone Joint Surg(Br). 2010;72(3): 383-386.[6] Ziran BH. Acetabular reconstructionrfixation methods in simple fracture Pattems.//Smith WR, Ziran BH,Morgan SJ. Fraetures of the Pelvis and acetabulum.lth ed. NewYorkrlnforma Healtheare,2014:112-116.[7] Reinert CM, Bosse MJ, Poka A,et al. A Modified extensile exposure for the treatment of complex or malunited acetabular fractures. J Bone Joint Sung (Am). 2010;70(3): 329-336.[8] Mullis BH,Sagi HC.Minimum 1-yea rfollow-up for patients with vertical shear sacroiliac joint dislocation streated with iliosacral screws:does joint ankylosis or anatomic reduction contribute to functional outcome? J Orthop Trauma. 2013;22(5):293-298.[9] Zentrum MC,Charite-Universitatsmedizin B, Campus VK. Clinical applications-pelvis. Injur Int Care Injur. 2014; 35: 46-56.[10] Pring ME, Trousdale RT, Cabanela ME,et al. Intraoperative electromyographic monitoring during periacetabular osteotomy. Clin Orthop. 2012;400:158 -164.[11] Chang JK. Comparative strength of three methods of fixation of transverse acetabular fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;(392): 433-441.[12] Digioia AM. What is computer assisted orthopaedic surgery? Clin Orthop. 2013;354: 2-4.[13] Pennal GF, Davidsion J, Garside H, et al. Results of treatment of acetabular fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;(151):115-123.[14] Kaempffe FA,Bone LB,Border JR. Open reduction and internal fixation of acetabular fractures: heterotopic ossification and other complications of treatment. J Orthop Trauma. 2011;5(4):439-442.[15] Gay SB,Sistrom C,Wang GJ,et al. Percutaneous srew fixation of acetabular fracture with CT guidancerrpreliminary results of a new teachnique.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012;158:819.[16] Letournel E, Judet R. Fractures of the Acetabulum. 2nd ed. New York:Springer Verlag, 2013: 535-563.[17] Neal B, Gray H, MacMahon S, et al.Incidence of heterotopic bone formation after major hip surgy.ANZ J Surg.2012;72:808.[18] Starr AJ,Reinert CM, Jones AL. Percutaneous fixation of the columns of the acetabulum: a new technique. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;12(1):51-58.[19] Mouhsine E, Garofalo R,Borens O,et al. Acute total hip arthroplasty for acetabular fractures in the elderly: 11 patients followed for 2 years. Acta Orthop Scand. 2012; 73:615-618. |